This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Tran Quoc Tuan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. Doctor Tran Quoc Tuan has more than 12 years of experience in emergency resuscitation.An electrocardiogram is a graph that records the activity of the heart's electrocardiogram, which plays an important role in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases, monitoring treatment effectiveness, patient's response to drug treatment and monitoring side effects. of drugs,...
1. What is an electrocardiogram?
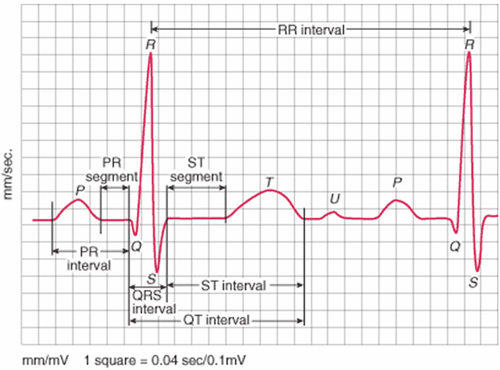
The heart contracts to a rhythm controlled by a conduction system in the heart muscle. These currents are very small (about a thousandth of a volt) but can be detected by electrodes placed on the patient's arms, legs and chest. These currents are routed to a recorder, amplified by the machine, and recorded on an electrocardiogram. Thus, an electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph that records the electrical activity of the heart. The electrocardiogram consists of 12 separate leads, including:6 limb leads: I, DII, DIII, aVR, aVF 6 thoracic leads: V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6 These leads help create a Multidimensional view of cardiac electrical activity.
Electrocardiogram has many clinical significance, is used to diagnose heart disease, monitor treatment effectiveness, patient's response to drug treatment and monitor drug side effects,...
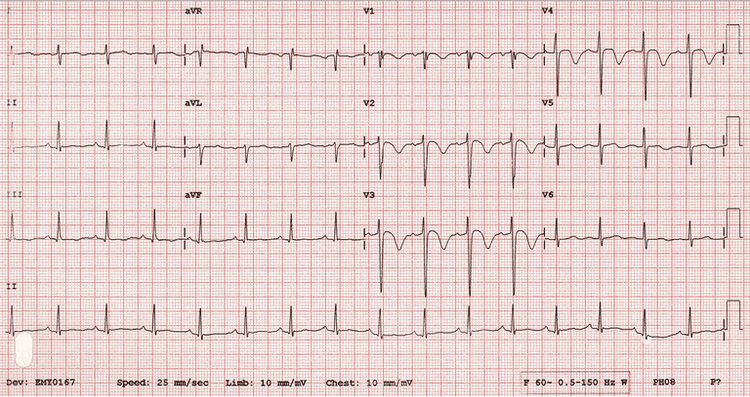
Các chuyển đạo biểu thị trên kết quả ECG
2. Mechanism of wave formation on electrocardiogram
The right atrium of the heart has sinus nodes, which are cells that are capable of generating electrical impulses on their own. This electrical impulse is transmitted to the surrounding muscles, causing the two atria to contract, creating a P wave on the electrocardiogram. The current then continues along a specific cell chain to the atrioventricular (AV) node located near the interventricular septum, and then along the Purkinje fibrous cell chain that runs along the septum and spreads to the surrounding muscles (forming the QRS complex). ) causes these two ventricles to contract. The electrical impulse then decreases, the ventricles relax, creating a T wave. Thus, a cardiac cycle manifests on the electrocardiogram as: P wave, QRS complex, T wave and U wave (may appear in the heart) certain diseases).3. Meaning of the waves on the electrocardiogram
3.1. P wave Normal P wave in:D1, D2, V3, V4, V5, V6, aVF: always positive D3, aVL, V1, V2: mostly positive, maybe mildly negative, 2 phases aVR: never also negative Whether positive, negative or biphasic, the P wave can be slightly hooked or split. The amplitude of the P wave is usually highest in D2. P waves are formed by atrial depolarization. Normal P waves have an amplitude of less than 2mm (0.2mmV), duration from 0.08-0.11 seconds. When the P wave increases in amplitude or lengthens, it is possible that the patient has a large atrial condition. If the amplitude increases, the patient's right atrium may be enlarged, if the depolarization time is prolonged, the patient's left atrium may be enlarged.
Sóng P
Q wave: is the first sound wave of the QRS complex, formed by depolarization of the interventricular septum. In normal people, Q waves are usually small and short. If the Q wave is large and prolonged negative amplitude may indicate myocardial necrosis. The R wave is the first positive wave of the complex, followed by the negative S wave. These are two waves formed by ventricular depolarization, which are similar in nature. 3.3. T wave The normal T wave is wide, the apex, the flanks asymmetric, the ascending and descending slopes steeper. Always positive in D1, aVF, V3, V4, V5, V6, greatest amplitude in V3, V4 and always negative in aVR. In D2 the majority is positive, a small number is biphasic. In D3, aVL is mostly positive, some biphasic or negative. In V1, most are negative, a few are positive or biphasic.
The T wave is the wave following the QRS complex, representing late repolarization of the two ventricles. The T wave plays an important role in the diagnosis of myocardial ischemia.
3.4. U wave Normally on the electrocardiogram there is no U wave, if there is, it is only a small wave after the T wave. In some diseases such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, .. When taking an electrocardiogram, there may be an inverted U wave or a sharp elevation.
Vị trí các cực EGC
3.6. ST segment ST segment is a straight line going from the J point to the T wave origin. The ST segment means early ventricular repolarization phase, normally the ST segment is very little deviated up or down the isoelectric line. In some pathological cases, the ST segment can be elevated or depressed, so the ST segment is of great value in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
3.7. QT segment The QT segment is the electrical systolic time of the ventricles. The normal value of QT depends on heart rate. If the QT interval is abnormally prolonged, the patient may be at risk for ventricular arrhythmias, especially torsades de pointes.
To protect cardiovascular health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.

Khám sức khỏe tim mạch giúp người bệnh phát hiện sớm bệnh lý bất thường
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
What is Holter electrocardiogram and what does it mean in the diagnosis of arrhythmias? How is arrhythmia diagnosed? Stress electrocardiogram helps detect many dangerous cardiovascular diseases