This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Vo Ha Bang Suong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalComputed tomography (CT scan) is a special diagnostic imaging technique that uses X-rays. This technique gives fairly clear images of the internal organs through reconstructive rendering. . In particular, it gives a better image of soft tissue in the body while conventional radiographs do not show soft tissue well.
1. What are the benefits of computed tomography?
CT scan can be used to examine any part of the body. It gives clear images of bones, soft tissues, organs, blood vessels that techniques such as X-ray, ultrasound cannot fully investigate. Therefore, computed tomography is a common technique used to:
Detect abnormal problems in cranial neurology such as tumors, brain hematomas, anemia, bleeding, cerebral edema. .. Detect tumors, abscesses, deformities, other pathological images in the head - face - neck, heart, chest, abdomen, pelvis, bones, soft tissues to vascular pathologies. Used to guide surgery, radiation therapy and follow-up after surgery. The 3D-CT scan technique allows accurate assessment of the lesion location in 3D space for good orientation for surgery as well as radiation therapy. Helps to reconstruct 3D images in congenital abnormalities, helping plastic surgeons better treat birth defects. It is a valuable means of monitoring disease progression and effectiveness of treatment at different time points. To clarify the image of an abnormal mass, the doctor may prescribe a combination of gastrointestinal and intravenous contrast for the most accurate diagnosis.
At Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital, the doctor is conducting a CT scan with a 128-slice MSCT scanner. This is a modern medical device that combines X-ray technology and computer technology to record the entire internal structure of the body in just 10 seconds, the data is encoded in Voxel form and then processed. Using 3D technology to reconstruct the image accurately. After each phase of scanning, the machine gives 128 cross-sectional images instead of one image like most other CT scanners. Therefore, the efficiency is almost absolute with 100% clear images, 97% accuracy and 99% disease exclusion prediction value.
Máy MSCT scan 128 lát cắt tại Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Phú quốc
2. What is contrast-enhanced computed tomography?
Contrast are solutions containing iodine, which are injected into the body during a CT scan, causing the structure or lesion to appear bright white on the CT scan, helping to distinguish it from other structures. other around.
Therefore, a contrast-enhanced CT scan will help to better clarify a tissue or lesion. Improve the accuracy of CT scan diagnosis.
3. When do I need a CT scan with contrast?
When you have health problems that need investigation and follow-up. Specifically:
Most cases of abdominal CT scan require contrast, unless you want to investigate urinary stones. Suspected cases of tumors. Most cases of inflammation and abscess require contrast media, except pneumonia, which has been diagnosed with certainty and does not need to be differentiated from other diseases. Vascular diseases such as aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, vascular malformations, arterial dissection. Some special cases: Find the source of the isolated pulmonary vasculature, assess the reperfusion area of the lesion, diagnose the degree of septalization of the subacute subdural hematoma...
4. What types of contrast agents are used in CT scans?
First generations are ionic contrast agents and have high plasma osmolality (1400 to 1800 mosmol/kg) These are now no longer used because of their more nephrotoxicity than later generations. this.
Currently used contrast agents have higher osmolality than plasma (500 to 850 mosmol/kg) and are nonionic (except Hexabrix). Only Iso-osmolal (Iodixanol) is nonionic and has the lowest osmolality (290 mosmol/kg).
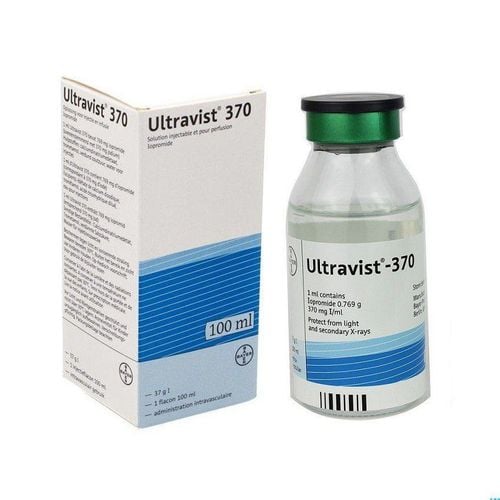
At Vinmec International General Hospital using Ultravist. Being non-ionic, the osmolality is higher than that of plasma (607-774 mosmol/kg). With Ultravist can ensure the purpose of survey when taking CT scan.
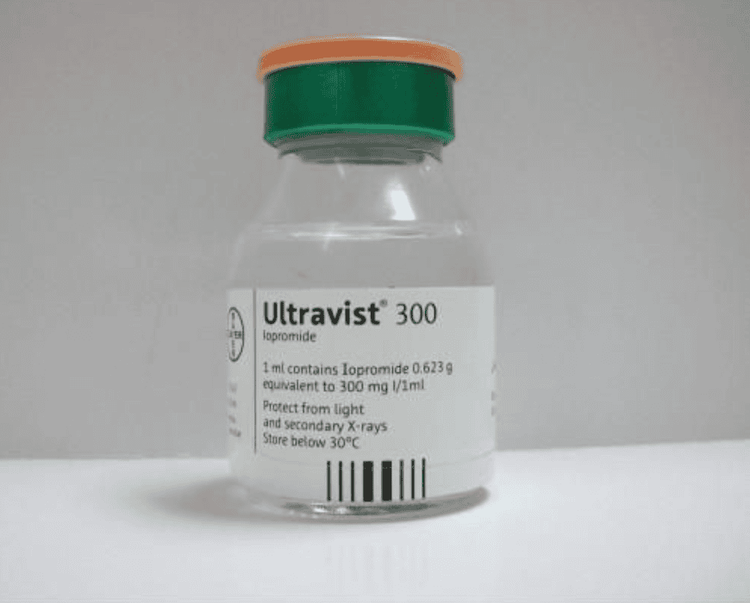
Thuốc cản quang Ultravist
5. What are the risks of a CT scan with contrast injection?
When injecting contrast, CT scan can have some risks, requiring prompt treatment if it occurs in the patient.
Anaphylaxis: After injection, within 1 hour appear the following symptoms: Facial flushing, itching, acute urticaria, rash, angioedema, bronchospasm causing difficulty breathing, stridor, laryngeal edema, withdrawal chest cavity, hypotension, shock, loss of consciousness. Anaphylaxis is not usually related to dose and rate of injection. It can occur even with exposure to a small amount of contrast medium. And manifests on many levels. Contrast-induced renal failure: A condition in which acute renal failure or an increase in renal failure occurs after contrast agent administration (excluding other causes affecting renal function): An increase of 25% or > 0. 5 mg/dl (44.2 mmol/l) of baseline creatine. Usually occurring within 24-48 hours of contrast media administration, creatinine elevation peaks after 5-7 days and in most cases returns to normal within 7-10 days. Thyroid storm : A severe condition in subjects with hyperthyroidism. Therefore, it is necessary for patients to inform their doctor about their medical history, especially thyroid disease. Other hazards : Harm to the unborn baby. On pregnant women, it is necessary to carefully consider and choose other methods such as ultrasound, X-ray usually with protective clothing. Some cases have allergic-like reactions such as mild itching, but these reactions quickly disappear.
6. In case I have to have a CT scan with contrast, what should I tell the doctor before the scan?
The doctor and the patient need to discuss in detail about the possible risks, take the history, do a physical examination. At the same time, ask the patient to provide detailed information about some of their conditions:
Medical history: Especially kidney disease, diabetes, hypertension, heart failure, thyroid disease, asthma .. ., current drugs, types of implantable machines in the body, cardiovascular interventions. Allergy history. Inform your doctor of all allergies. Have you ever had a contrast-enhanced CT scan? If so, did you have any unusual symptoms in the past? Are you currently experiencing dehydration? Make sure you're not pregnant.

Bệnh nhân cần thông báo về tình trạng sức khỏe của bản thân, khi có chỉ định chụp CT scan có cản quang
7. If I have a CT scan with contrast, what does the doctor prepare for me before the scan?
Depending on whether the patient is inpatient or the patient in the outpatient clinic, there will be little relative difference. However, basic preparation is required:Thorough physical examination
Indication for testing of renal function: creatinine (eGFR) should be assessed prior to contrast administration. Certain circumstances, such as on routine hemodialysis, acute kidney injury, or requiring urgent imaging for life-threatening situations (eg, suspected major trauma, threatened aortic dissection) may cause Consider performing a contrast-enhanced CT scan without waiting for creatinine results.
Stop using drugs with potential for nephrotoxicity, especially note: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics should be stopped before 24 hours, metformin should be stopped before 48 hours. ACE inhibitors and receptor blockers do not require strict discontinuation.
Other measures : Patients with no risk factors are not needed. Applies only to patients with risk factors. Includes:
Full rehydration: Can use NaCl 9%0, NaHCO3, Ringer Lactate. Most studies show that 9%0 NaCl is the most beneficial. Recommended dose: For intravenous contrast: 9% NaCl administered at a rate of 100 ml per hour beginning 6 to 12 hours before and continuing 4-12 hours after contrast for inpatients. Or NaCl 9%0 infused with 500 ml bolus over 30 minutes to 1 hour before and after the outpatient contrast agent administration. Outpatients may be able to supplement with oral fluids. Acetylcysteine: The contrast agent causes direct toxicity on the renal tubules and ischemia in the outer medulla of the kidney. Increased production of free radicals has a toxic effect on the kidneys. Acetylcysteine can act as an antioxidant, thereby preventing the death of kidney cells. In addition, it has mild renal vasodilating properties. Recommended dose: Acetylcysteine 1200 mg orally one hour before and one hour after contrast media. Then 2 times daily for the next 4 days. For cases of bronchial asthma, history or allergies, cortisone can be used, with or without anti-allergic drugs before taking pictures.
8. How long does it take for my body to clear the contrast and how soon can I have a CT scan with contrast again?
In subjects with normal renal function the half-life of most currently used contrast agents is about 2 hours, and is essentially eliminated after about 20 hours. . Therefore, for cases where contrast was used about 24 hours before, if necessary, it can still be used and these cases are not considered to be at risk for drug-induced nephropathy. Contrast.
9. How should I eat and drink after having a CT scan with contrast?
Depends on what risk factors the patient has.
If the patient is being treated as an inpatient, the doctor will have a regimen suitable for the patient's current condition. If the patient is an outpatient, without risk factors, he can go home. Drink plenty of water, monitor urine output for 24 hours. If you find that the amount of urine is less than normal, go to the hospital to check your kidney function. Return to the hospital when there are any unusual signs. If the patient has risk factors, then rehydrate, take Acetylcysteine according to the schedule. The diet is the same as any other normal day.
10. Where can I get more information or advice about contrast-enhanced CT scans?
With modern technology and equipment, Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital provides CT scan services to customers. With this service, customers will be assigned CT scans when necessary to improve the efficiency of diagnosis, treatment, and accurate disease monitoring. Customers will be consulted in detail, clearly, and are also best prepared to limit the possible risks of CT scans, especially when CT scans have contrast.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital, you can contact at the address: Bai Dai, Giac Dau, Phu Quoc, Ganh Dau, Phu Quoc.
Hotline: 0297 3985 588 or register online HERE.
Articles refer to the source: Heart.org; Update.com