This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Calprotectin assays and biomarkers provide valuable presentation information for gastrointestinal inflammation. These are considered to be fast, effective diagnostic tools and help monitor treatment for gastrointestinal diseases such as bleeding colitis.
1. Definitive diagnosis of bleeding ulcerative colitis
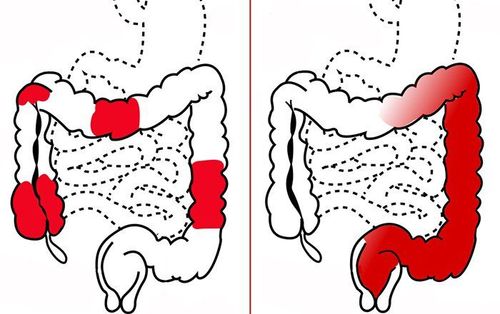
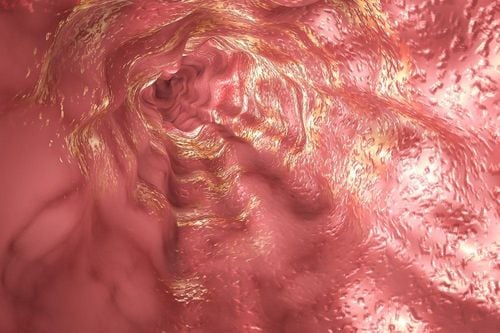
Definitive diagnosis of bleeding ulcerative colitis is based on many factors including clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, endoscopic imaging features and histopathology:Clinical symptoms (symptoms present at least 4 times) weeks): Diarrhea, small or large amount of blood in the stool, abdominal pain during or around the time of defecation. Gastrointestinal tract infections should be excluded. Laboratory tests: Iron-deficiency anemia, thrombocytopenia, hypoalbuminemia, autoantibodies (DANCA), increased fecal calprotectin. Colonoscopy imaging features: Characteristic diffuse inflammatory lesions in the rectum. Then, gradually spread to the upper segments of the colon with features such as loss of capillary network, loss of colonic folds, edematous mucosa, congestion, exudation, many erosions, upper ulcer surface, easy to bleed when inflated or touched with lights, real bleeding. In cases of long-term chronic inflammation, a pseudo-polyp may be seen. Histopathological features: Increased monocyte infiltration in the epithelial connective membrane, disappearance of mucin-secreting goblet cells, distorted glandular slits, branching, atrophy, microabscesses in glandular clefts .

2. Diagnosis of bleeding ulcerative colitis
Bleeding ulcerative colitis can be classified according to types based on location, severity, age of onset, and extra-gastrointestinal manifestations. Among them, the Montreal classification that assesses both location and severity is most commonly applied.Role of tests: Initial tests for patients with ulcerative colitis include blood count, electrolytes, liver and kidney function tests, iron levels, vitamin D, and protein levels. C-reactive (CRP) and fecal calprotectin. Immunological and microbiological tests to rule out C. difficile should also be performed.
2.1. The role of the fecal calprotectin test A feature of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases including hemorrhagic ulcerative colitis is the infiltration of neutrophils into the glandular cleft of the intestinal epithelium and the intestinal lining. epithelium, therefore, in the stool there will be components of white blood cells. If there is no presence of leukocytes in the stool, it is possible to rule out chronic inflammatory bowel disease and follow other diagnostic directions. Besides the direct test for leukocytes in stool with methylene blue, currently, there are a number of stool tests that help detect leukocytes in stool and are used to assess the severity of clinical IBD pathology. . Calprotectin, derived from granulocytes, is a calcium-binding protein used as a diagnostic marker for cases of diarrhea caused by inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, this index also partly reflects the "inflammation level" of the colon, so it can be used as a non-invasive monitoring method during treatment.
Similarly, lactoferrin, a protein from neutrophils, has been shown to help differentiate between IBD and irritable bowel syndrome.

High levels of pANCA are correlated with the risk of colostomy and ileostomy after total colectomy. Several other biomarkers are also being studied in IBD patients, such as antibodies to the outer membrane of the E.coli envelope (outer membrane 0 E.coli cell wall) or J2 peptide which is an RNA sequence derived from conjugates. related to Pseudomonas fluorescens. Both of these markers have been shown to be more associated with Crohn's than with ACS and are not really effective in differentiating types of IBD.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.