This is an automatically translated article.
Laparoscopic choledochal cystectomy has become a routine technique in the treatment of choledochal cysts. This surgical procedure shows its superiority and gradually replaces intra-abdominal surgical methods in general and surgical treatment of common bile duct cysts in particular. In addition, this method also combines the technique of suturing the common hepatic duct - jejunum.
1. Common bile duct cyst
The common bile duct cyst is a congenital defect in the bile ducts that transport the bile ducts from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine. The liver produces bile to help digest food. When you have a common bile duct cyst, there may be swelling in the duct, at which time bile can be trapped in the liver. This will cause liver problems or pancreatitis because it blocks the main tube from the pancreas to the intestines.
Nang ống mật chủ khiến ống bị sưng và mật có thể bị giữ lại trong gan
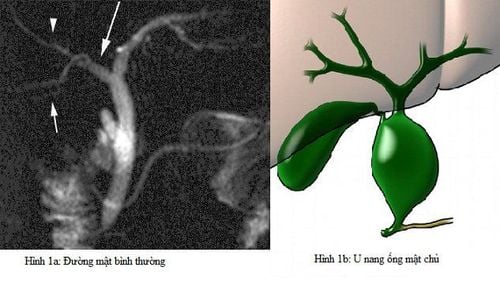
Common bile duct cysts can form in part of the bile duct inside the liver or outside the liver. There are many types of choledochal cysts and they are classified based on where they appear.
Type 1. Extrahepatic common bile duct cysts are sac or rhomboid. This type accounts for up to 90% of all common bile duct cysts. Type 2. Are isolated diverticula-like cystic ducts protruding from the wall of the common bile duct. This type, communicates with the common bile duct by a narrow anastomosis. Type 3 (choledochocell). This is a common bile duct cyst arising from the lower part of the common bile duct. Type 4. Cysts on both common and extrahepatic bile ducts. In neonates with common bile duct cysts, there may be obvious manifestations such as: jaundice and acholic stools. Newborns often have intermittent biliary obstruction or recurrent episodes of pancreatitis with features such as:
Biliary obstruction: palpable right upper quadrant mass and signs of jaundice initial presentation of pancreatitis. This condition can make diagnosis difficult because there are only intermittent episodes of abdominal pain. This is because elevated amylase and lipase levels lead to incorrect diagnosis. In adults, typical signs of a common bile duct cyst are abdominal pain, jaundice, and a palpable right upper abdominal muscle mass. However, these signs are found only in 10-20% of people with the disease. Therefore, abdominal pain in adults should be diagnosed as epigastric pain or right upper quadrant pain. May be accompanied by other symptoms such as dermatitis or cholangitis

Người lớn bị u nang ống mật chủ có biểu hiện vàng da
2. Laparoscopic surgery of common bile duct cyst, common hepatic-jejunostomy connection
Laparoscopic choledochal cystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a common bile duct cyst and restore biliary circulation by means of a common-jejunostomy.
Surgical procedure:
Before surgery: After being examined and diagnosed with a common bile duct cyst, the doctor needs to explain to the patient the benefits of laparoscopic surgery for cyst removal. bile ducts are extremely important. At the same time, this is a highly effective method in the treatment of diseases. In addition, the patient is also examined and tested necessary for the surgical process such as: basic tests, blood and urine amylase tests, blood bilirubin, ...
Surgery: The patient is anesthetized. endotracheal . First, the doctor will place the trocar. Next, the doctor will check the condition of the liver and common bile duct cysts and then release the gallbladder. However, due to the large size of the cyst, the doctor can open the gallbladder and drain the fluid. Then establish a Roux-en-Y bile duct with an anastomosis of the common-jejunostomy.
After surgery: Check the entire abdomen.
Some possible complications during and after surgery:
Bleeding. This can occur during dissection to release the common bile duct cyst. Or during surgery to injure the portal vein. Management of this situation requires finding the cause of bleeding and immediately stopping bleeding or suturing the portal vein tear. Mouth leak. After about 4-5 days of surgery but still see bile flowing through the drainage pipe under the liver or seeping through the bandage of the incision, it is necessary to ask medical staff to intervene. This case will be managed by observing the amount of fluid leaking through the drainage and adding water-electrolyte. Fistulas usually heal on their own after 10-15 days. However, if the anastomosis does not heal, surgery is needed to rebuild the anastomosis. Peritonitis due to anastomosis. Management of this disease according to the treatment of peritonitis. Acute pancreatitis after surgery. Treatment of the disease according to the treatment of acute pancreatitis. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
recommended video:
Health check recurring at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
SEE MORE
Prof. Nguyen Thanh Liem laparoscopic surgery for common bile duct cysts in Europe Choledochal cysts - Prof. Dr. Nguyen Thanh Liem Pain in the right lower quadrant is a symptom of what disease?