This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Tran Thi Vuong - Doctor of Microbiology - Department of Laboratory - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
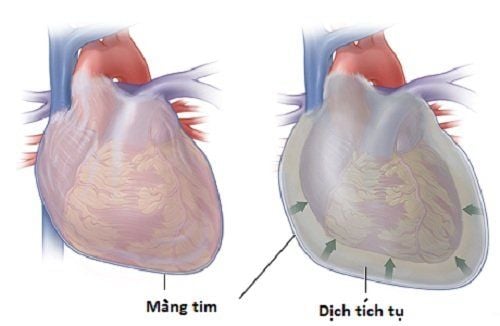
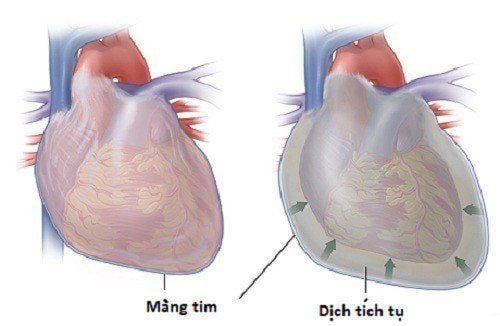
Pericardial fluid is a fluid located between the two layers of the pericardium, the parietal and visceral leaves. Fluid has a lubricating function and helps the heart work more smoothly and easily. When the amount of fluid is abnormally high or invaded by bacteria, it will cause diseases and syndromes such as pericardial effusion, acute pericarditis,...
1. What is pericardial effusion?
Pericardial effusion is the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the pericardial cavity leading to cardiac tamponade, blood vessel disorders, hypotension, shock, and even death.
There are many causes of pericardial effusion and are often identified through pericardial fluid tests such as biochemical tests (protein, glucose), cytological and microbiological tests (gram stain, AFB staining). ; culture of pericardial fluid for pathogenic bacteria, fungi, PCR molecular biology test;
The characteristic sign of pericardial effusion is Beck's triad when the doctor examines clinically:
Low blood pressure: Blood pressure drop suddenly and may not be measured, weak pulse, pale skin, sweating, loss of consciousness,... Portal vein elevation chest tightness, heart palpitations, cough, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, and often nervousness and anxiety
2. Test for pericardial fluid culture and specimen collection method
Pericardial fluid culture is a method of culturing pericardial fluid in nutrient media to detect the presence of pathogenic microorganisms. Bacteria and fungi, if any, will multiply and grow. By determining the bacterial morphology (staining), colony properties, biochemical properties (after culture 24-48 hours) and agglutination reactions will determine the type of bacteria. Then conduct an antibiotic chart and find antibiotic sensitive bacteria to treat the patient.
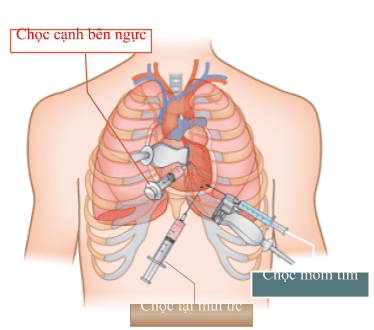
Method of taking samples: This is a technique by a doctor with high expertise and training in the field of cardiology. The doctor aspirates pericardial fluid by inserting a needle into the pericardial cavity and sucking the fluid out. The most important rule is to ensure sterility when taking samples.
Patient's position: The patient lies on his back, the head of the bed is raised about 60 degrees, the pillow is under the back, exposing the puncture area. Conduct disinfection around the surface of the needle puncture area twice with iodine alcohol and alcohol 70 degrees. Anesthetize the patient. The doctor locates the needle puncture site and conducts aspiration to remove the fluid. After aspiration is complete, the doctor disinfects the puncture site and then covers it with sterile gauze. Let the patient lie down and tell him what to pay attention to after the puncture. After collection, the tube should be brought quickly to the laboratory for analysis. Store at room temperature can be kept up to 6 hours, if not sent immediately, it should be stored in accordance with regulations.
3. The process of culturing pericardial fluid in the laboratory
When the sample is sent, the testing staff will check the quality of the fluid to see if it meets the requirements or not. The quantity is guaranteed to be over 2mL and the transport and storage have proper and sufficient administrative information.
After examining the sample, making a gross assessment: quantity, color..., laboratory staff will conduct a microscopic assessment by Gram staining method, to observe the bacterial morphology (if any) . From the identification of the bacterial shape, it will help to choose the appropriate culture medium.
Proceed to use a sterile pipette to aspirate the solution and put it on the surface of the media dishes. Use sterile implant and moustache to inoculate the partition according to the technical procedure. Note that the operation when inoculating is required to be sterile, to avoid contamination. Put the agar plates in the incubator 5 - 10% CO2 at a temperature of 35 - 37 degrees C and monitor after 24 - 48 hours.
If no colonies grow, the result is negative and no pathogenic bacteria/fungi are found. Conversely, if a colony is found to grow, it is necessary to stain and test the biochemical properties and rapid test to identify the type of bacteria. Conduct antibiotic mapping for bacteria found.
It should be noted that a number of factors can affect the results such as non-sterile operations, improper transportation and storage, poor technical skills leading to incorrect reading of results, too little sample volume. not enough to do,...
To protect cardiovascular health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.