The appearance of an abnormal lump or node under the armpit is very common. While most are benign, they can sometimes indicate a more serious underlying condition.
1. What is the armpit lump?
A fatty lump in the armpit is a condition of one or more enlarged lymph nodes under the arm. Lymph nodes, which are essential components of our immune system, are small, oval-shaped glands located throughout the body. While these lumps are typically small, they can be felt upon examination. Both men and women of all ages can experience this condition.
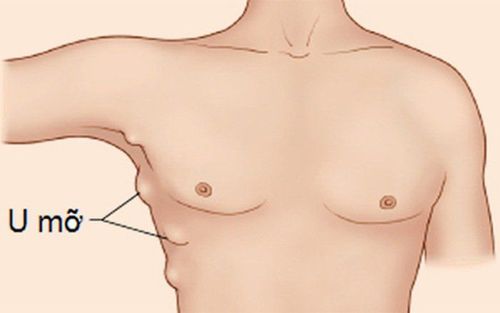
2. Causes of armpit lump
Causes of armpit lipomas can be:
- Hidradenitis: Because of blockage of sweat glands or hair follicles, bacteria can cause infection and accumulation of pus, creating a lump. If the pus ruptures, it can spread infection to the surrounding skin. Doctors may prescribe medication or laser hair removal, according to Reader's Digest.
- Cysts or Abscesses: Frequent underarm shaving irritates hair follicles and soft skin, which can cause cysts or abscesses, which are pus-filled bumps.
- Mastitis often occurs in lactating women. An infection can cause enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit. If left untreated, there is a risk of developing breast cancer.
In addition, armpit lipomas are caused by:
- Infection (viral or bacterial)
- Overgrowth of fat cells (benign)
- Allergic reactions
- Post-vaccination reactions
- Fungal infections
- Noncancerous fibrous tissue growth
In this case, these tumors are generally harmless, they’re just an overgrowth of local tissue.
In the following cases, a tumor can signal a serious disease, especially in women such as:
- Breast cancer reaction
- Lymphatic system cancer
- Blood or bone marrow cancer
- Autoimmune disease (such as lupus erythematosus)
As a result, anyone who finds an unusual lump in their armpit should seek medical attention immediately.
3. Diagnosis of armpit lipomas
Several diagnostic methods can detect potentially dangerous armpit lipomas:
- Physical examination is the initial step in diagnosing an armpit mass. A physical examination involves a doctor feeling the lump to determine its texture and checking the lymph nodes. If it's a benign lipoma, no treatment may be necessary. However, if it's a malignant tumor, surgery may be required to remove it.
- Blood cell count: To identify red and white blood cells.
- Mammogram: An imaging test that allows the doctor to see the tumor more easily.
- Biopsy
- Allergic reaction test
Một số phương pháp chẩn đoán để giúp phát hiện ra các khối u mỡ ở nách nguy hiểm là:
- Khám tổng thể là bước đầu tiên để chẩn đoán một khối u vùng nách. Khám bằng tay khối u vùng nách sẽ giúp các bác sỹ xác định kết cấu của khối u và kiểm tra các hạch bạch huyết. Nếu phát hiện đó là khối u lành tính như u mỡ ở nách thì không cần điều trị. Nếu đó là khối u ác tính thì cần được tiến hành phẫu thuật để cắt bỏ khối u.
- Đếm số lượng tế bào máu: Để xác định tế bào hồng cầu và bạch cầu.
- Chụp X quang tuyến vú: Là một chẩn đoán hình ảnh cho phép bác sỹ có thể nhìn thấy khối u một cách dễ dàng hơn.
- Sinh thiết
- Xét nghiệm phản ứng dị ứng

4. Armpit lump treatment
After diagnosing to determine axillary lipoma and its cause, the doctor will recommend a suitable treatment plan for each patient's condition.
- Bacterial infections will be treated with oral antibiotics.
- For lipomas related to allergies, patients will be prescribed medication and advised to avoid allergens. The lipoma will gradually disappear.
- If the armpit lipomas are malignant, patients will be referred to the oncology department for comprehensive care and treatment using a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
In cases where the armpit lipoma is benign and does not require treatment, patients can self-treat at home by applying warm compresses and taking over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate discomfort. Non-treatment lipomas include:
- Lipomas
- Virus-related cysts
- Fibroadenomas (non-cancerous breast lumps)
Also see:
- How to reduce underarm sweating can be done at home?
- Why do armpits smell?
- Can halitosis be cured?
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.