This is an automatically translated article.
Chromosome test helps detect abnormalities of human chromosomes that cause some dangerous diseases. This is a modern subclinical, helping to diagnose diseases related to genetics, birth defects or find causes of infertility in couples.
1. What is a chromosomal test?
Chromosome testing (also known as karyotype test) is a modern laboratory that helps identify chromosome sets in human cell samples, helping to diagnose a number of genetic disorders that cause heterogeneity. birth defects or malignancies of the blood. Chromosome testing helps doctors describe 2 prominent features:
Number of chromosomes Abnormal changes in the structure of chromosomes Characteristics of a normal set of chromosomes
Female: The female set of chromosomes has 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes (XX), chromosomal symbols are: 46, XX Males have 22 pairs of autosomes. and 2 sex chromosomes (XY), the chromosome number is: 46, XY
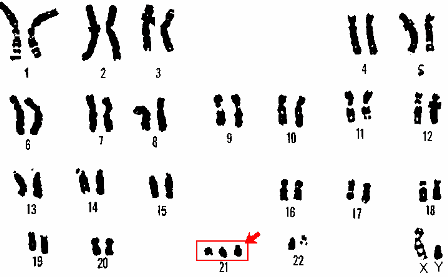
Làm nhiễm sắc thể đồ hay còn gọi là xét nghiệm karyotype
2. When to order chromosomal testing?
Some blood malignancies such as: acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, myeloproliferative disease, myelodysplastic disorder need to identify infectious abnormalities Chromosomes include quantitative abnormalities (haploid, polyploid) or structural abnormalities (deletions, translocations, duplications, inversions). Infertile couples are infertile or have multiple miscarriages of unknown cause. Check for some genetic abnormalities of birth defects. Check for chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus in the womb.
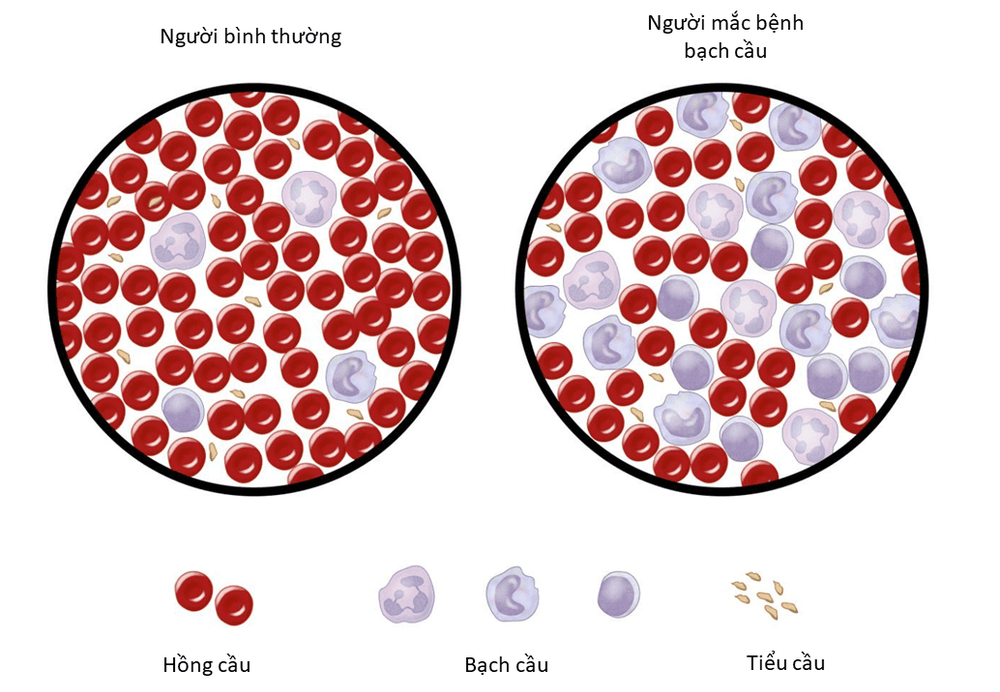
Bệnh nhân bệnh bạch cầu cấp dòng tủy cần xét nghiệm nhiễm sắc thể đồ
3. Chromosome test procedure
3.1 Type of sample for karyotype . testing
Proceed to withdraw 2ml of bone marrow or 4ml of peripheral blood (for samples with blast >10%).
For myelodysplastic disease, multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, 2ml of bone marrow is required, bone marrow sample will be taken through biopsy method Chronic myelogenous leukemia with elevated white blood cells > 50,000/mm3, it is necessary to take 4ml of peripheral blood. For genetic diseases, infertility, birth defects: 2mL of peripheral blood is required. In some cases, the test sample is amniotic fluid obtained through the method of biopsy of the amniotic cavity in the uterus.
All samples after collection are anticoagulated with Heparin 300UI.. and transferred to the laboratory within 1 hour after collection.
3.2 Procedure for performing chromosomal testing
After taking samples, they will be cultured in special dishes or tubes in the laboratory. After a suitable period of time, cells are harvested, smeared and stained with GTG (Giemsa trypsin G-banding) technique.
After staining, the cells will be observed under a microscope with magnification up to 1000 times to observe the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in the cell sample. The results will be photographed, arranged and made chromosomal using specialized machines, thereby detecting abnormalities in the number and structure of chromosomes.

Các tế bào sau khi nhuộm sẽ được quan sát dưới kính hiển vi độ
4. Some common chromosomal abnormalities
Down syndrome The chromosome number for Down syndrome is 47, XX (XY), +21 or trisomy 21. This birth defect occurs due to an extra chromosome 21 (trisomy 21 or 21). Trisomy 21), most common in newborns after birth with a frequency of 1/700 - 1/1000.
Manifestations of Down syndrome are children born often with mental retardation, mental retardation, low IQ and almost complete loss of memory and learning ability. Besides, more than half of sick children will follow birth defects in other organs such as cardiovascular, digestive...
Klinefelter syndrome The symbol for chromosome set is 47, XXY. The disease mechanism of this syndrome is an extra X sex chromosome, the disease occurs only in males. Klinefelter syndrome is the most common sex-linked chromosomal abnormality with a frequency of 1/1000. Symptoms are usually small testicles and affect fertility or infertility.
Edward's syndrome Chromosome notation is 47, XX(XY), +18 or trisomy 18. Abnormal number of chromosomes causes this syndrome with the manifestation of an extra chromosome 18, prevalence rate about 1/3000 live births. Usually, children with this disease live no more than 1 year old and often have birth defects in the heart, kidneys and other internal organs.
Turner syndrome The chromosomal symbol is 45, XO. This is a quantitative abnormality caused by a lack of an X sex chromosome with an incidence of about 1/2500 female babies. Turner syndrome often causes short girls, large necks, low hair growth, low ears, small uterus and ovaries, amenorrhea, infertility...
Hội chứng Down là một bất thường bộ nhiễm sắc thể hay gặp
Patau syndrome The symbol for the chromosome is 47, XX(XY), +13 or trisomy 13. This is a syndrome caused by an extra chromosome 13, the rate of 1 in 10,000 live births. Most cases of fetus with Patau syndrome often have miscarriage, stillbirth or labor but die soon after birth and are accompanied by birth defects of other organs such as nerves (small brain, ventricles, etc.). unique...), heart defects, cleft lip and palate, polydipsia...
Philadelphia chromosome This is an abnormality related to chromosomal structure, with the mechanism being the Philadelphia translocation, infectious abnormality. Specific chromosomes are associated with the CML (Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia) form of acute leukemia. This is the result of a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, t(9;22)(q34;q11).
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.