This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by MSc Hoang Quoc Chinh - Vinmec Institute of Stem Cell Research and Gene Technology.Families with children with birth defects often wonder why their child has it? And will their next children develop these deformities? Abnormalities in genetic material can be passed from parents to children. This article is intended to provide more information to answer questions about genetic disorders and birth defects, as well as an introduction to genetic mutation screening and malformation tests. natural.
1. What are genes?
Gene is the smallest functional unit of genetic material. Genes contain information necessary for the formation, development and functioning of an individual. Gene is understood as a recipe that contains all the information needed to create a certain dish. Each gene will have two copies, one from the father and one from the mother.2. What is Chromatography?
A chromosome is a genetic structure that contains a set of many genes. Chromosomes are like a book chapter and each article in that book chapter is a gene. Chromosomes also exist in homologous pairs in somatic cells. Each somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes and is divided into 23 homologous chromosome pairs including 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome pair. Sperm and egg cells are reproductive cells, so there are only 23 single chromosomes (one from each homologous pair). When the sperm fuses with the egg during fertilization, the 23 chromosomes from the father will pair with the 23 homologous chromosomes from the mother to create a complete set of chromosomes.
Nhiễm sắc thể.
3. What determines the baby's gender?
The sex of the baby is determined by the presence of sex chromosomes. There are two sex chromosomes, X and Y. Egg cells have only X chromosomes while sperm cells can contain either X chromosomes or Y chromosomes. When the egg and sperm join together to form a sperm cell. produces a zygote containing either an XX or an XY chromosome. A zygote containing an XX chromosome will develop into a girl while a zygote containing an XY chromosome will develop into a boy.Trắc nghiệm: Xét nghiệm Triple test là gì? Cần thực hiện khi nào?
Triple test và một trong những xét nghiệm sàng lọc trước sinh quan trọng nhất trong thai kỳ, giúp chẩn đoán nguy cơ dị tật thai nhi, là cơ sở để các bác sĩ chỉ định thực hiện các xét nghiệm sàng lọc xâm lấn như chọc ối, sinh thiết gai nhau. Theo dõi bài viết sau để biết Triple test là gì và nên thực hiện khi nào?4. What is a gene mutation? What is a chromosomal disorder?
Gene mutations are the result of structural and/or quantitative abnormalities in a gene.Chromosomal disorders are the result of abnormal changes in the structure and/or number of chromosomes. Most babies born with a chromosomal disorder have a morphological defect and in a few cases an intellectual disability. The risk of having a baby with a chromosomal disorder increases with increasing maternal age.
Trisomy is a chromosome number disorder in which a somatic cell has 3 homologous chromosomes rather than two homologous chromosomes like normal cells. The most common trisomy is the addition of an extra chromosome 21 (Down's disease). Other common trisomies are extra chromosome 13 (Patau syndrome) and extra chromosome 18 (Edwards symptom).
Monosomy is another chromosome number disorder in which somatic cells have only one chromosome left instead of the two homologous chromosomes found in normal somatic cells. X-chromosome loss or damage is a common monosomy and a cause of Turner syndrome.

Nhiễm sắc thể khi bị bệnh Down.
5. What is a genetic disorder?
Genetic disorders are the result of genetic mutations passed from parents to children. Gene mutations can occur on any chromosome. Genetic disorders are divided into autosomal dominant and recessive disorders, and sex-linked disorders.What is an autosomal dominant disorder? Autosomal dominant disorders are usually disorders caused by just one abnormal gene that a child inherits from either the father or the mother, meaning the child will get the disease if one of the homologous genes is mutated. and the remaining genes are normal. If one parent has the abnormal gene, their children have a 50% chance of carrying the same abnormality because 50% of the child's genome is inherited from the father and the remaining 50% is inherited from the mother. An example of an autosomal dominant disorder is the disorder that causes Huntington's disease.
What is an autosomal recessive disorder? A recessive genetic disorder is a disorder that occurs only when both parents carry the abnormal gene, meaning that the child only gets the disease when inheriting both abnormal genes, one from the father and the other from the mother. The child will not have any abnormality if the child carries only one abnormal gene of a homologous gene pair, that is, out of two homologous genes, only one gene is mutated. An example of an autosomal recessive disorder is the disorder that causes cystic fibrosis.
What is a recessive carrier? An inherited mutation carrier is a person who has a non-homologous gene pair, meaning that two genes in the homologous pair are not the same, one is mutated and the other is normal. Carriers of the recessive mutation may not have any symptoms at all or be very mild. If both parents are carriers of the recessive mutation, their child will have a 25% chance of having the disease caused by a recessive disorder and a 50% chance of being a carrier of the recessive mutation - like child's parents. If only one parent is a carrier of the recessive mutation, the child has a 50% chance of being a carrier of the recessive mutation.
What is a sex-linked genetic disorder? A sex-linked genetic disorder is a disorder caused by mutations in genes located on the sex chromosomes (X and Y). An example of a sex-linked disorder is hemophilia. It is a disease caused by a mutation in a gene located on the X chromosome.
Who is at risk of having a baby with a birth defect? Most babies with birth defects are born to parents with no known risk factors. However, the risk of birth defects is higher in people with risk factors. Screening for birth defects should start with checking if you have any risk factors? Like do you have a genetic mutation? Do you have a child with a genetic mutation, or do you have a family history of the genetic disorder? Some genetic disorders occur more frequently in certain populations.
What is genetic counseling? In some cases, you may be advised to see a genetic counselor. Genetic counselors have extensive training in genetics. In addition to taking a look at your family history, a genetic counselor may recommend that you visit your doctor and get tested. Based on this information, a genetic counselor will assess your baby's risk of birth defects, discuss options with you, and answer your questions.

Chuyên gia tư vấn di truyền hỗ trợ bạn
What types of prenatal testing can answer your questions about genetic disorders? Prenatal screening assesses a baby's risk of having a birth defect or genetic disorder.
Diagnostic tests can detect specific birth defects or genetic disorders of the fetus.
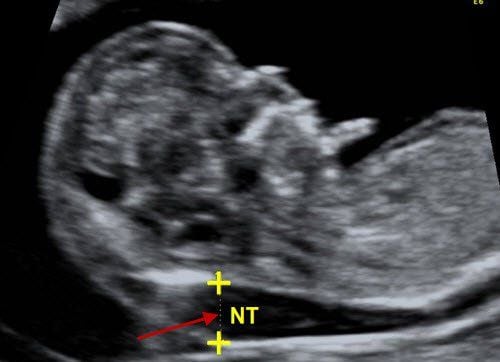
When should antenatal screening be performed in pregnancy and the type of genetic disorder evaluated? Prenatal screening is often part of reproductive health care and is often performed at different times throughout pregnancy. Prenatal screening includes checking for certain substances in a pregnant woman's blood and an ultrasound. These tests assess the baby's risk for Down syndrome and other trisomies, as well as neural tube defects.
What is genetic mutation testing? A genetic mutation test is a screening test to determine if a person has a genetic mutation.
Who should get tested for genetic mutations? Genetic mutation testing is generally recommended for individuals with a family history of genetic disorders or for populations at high risk for certain genetic disorders. Testing for cystic fibrosis is generally recommended for all women of reproductive age because it is one of the most common genetic disorders.
When is genetic mutation testing performed? Testing for genetic mutations can be done before and during pregnancy.
When is diagnostic testing performed in pregnancy and what abnormalities are detected? Diagnostic testing may be done when screening tests indicate a high risk for birth defects. Diagnostic testing may also be recommended for all pregnant women, even those who are not at risk. Diagnostic testing can detect certain birth defects or genetic disorders.
How are diagnostic tests performed? Diagnostic tests are performed on cells of fetal origin. These cells are present in the amniotic fluid and placenta, or, rarely, from fetal blood. The chromosomes and genes in these cells will be analyzed using testing techniques to diagnose certain genetic defects.
What are the risks of diagnostic testing? Diagnostic testing has certain risks including miscarriage.
How do I know which test is appropriate? Your doctor or genetic counselor can provide information about tests and help you choose the right test based on your individual risk factors.
Do I really need to take these tests? Whether you want to have the test done or not is up to you. Some couples don't want to know about their baby's risk of birth defects, but other couples want to know about these risks in advance. Knowing about the risks in advance will give you time to prepare your child for a particular disability and to prepare the medical support he or she may need. You can also choose not to continue the pregnancy.