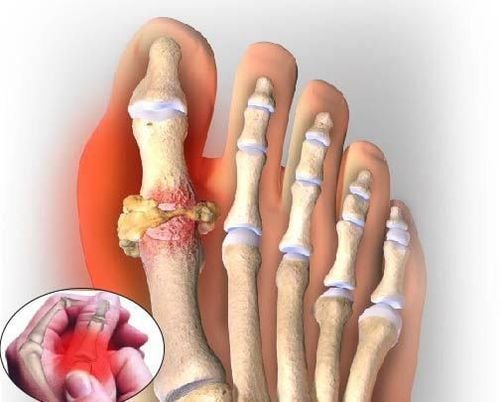
1. What is uric acid?
Uric acid is a natural metabolic product in the human body. It is derived from the breakdown of adenine and guanine in nucleic acids or from the metabolism of substances containing purine. The main sources of uric acid production include both endogenous and exogenous origins:
- Exogenous sources come from daily food intake that contains purine (approximately 100–200 mg/day). Foods and beverages rich in purines include organ meats, certain seafood, alcohol (especially beer), red meats…
- Endogenous sources come from the metabolism of nucleic acids within the body (approximately 600 mg/day), a process that mainly occurs in the liver, with a smaller contribution from the intestinal mucosa.
Most uric acid in the blood exists in a free form, with only about 4% bound to serum proteins. The average uric acid concentration in the blood is 210–420 μmol/L for men and 150–350 μmol/L for women. When a blood test reveals uric acid levels exceeding these thresholds, it is considered hyperuricemia (increased uric acid presence in blood).
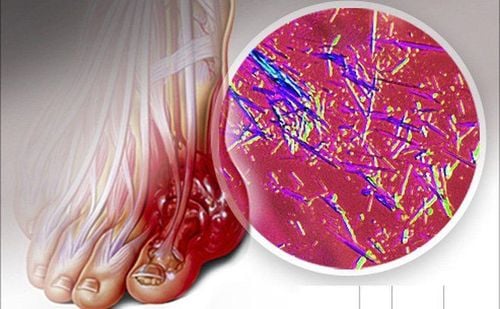
2. Causes of increased uric acid in the blood
There are many causes of elevated uric acid levels in the blood, including the following common factors:
- Increased production of uric acid
- Primary hyperuricemia (accounting for 30% of gout patients).
- Tissue destruction
- Accelerated cellular metabolism such as lymphoma or cancer
- Hemolytic anemia, malaria, or G6PD deficiency
- Consuming purine-rich foods such as organ meats, red meat, fish, and beer.
- Obesity
- Fasting, extreme dieting, or excessive exercise
Decreased excretion of uric acid
- Chronic kidney disease
- Alcohol abuse
- Use of diuretics
- Damage to the distal renal tubules.
- Medications reducing uric acid excretion through urine: aspirin and diuretics.
- Acidosis.
- Genetic factors
- Other causes: preeclampsia and eclampsia in pregnant women, hypothyroidism, lead poisoning, trauma also can increase uric acid levels.
Trắc nghiệm: Kiểm tra hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh gút
Bệnh gút là một dạng viêm khớp phổ biến, xảy ra chủ yếu do tình trạng tích tụ các axit uric trong cơ thể. Trả lời 15 câu hỏi trắc nghiệm sau sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về bệnh gút.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
3. Does elevated uric acid in the blood mean gout?
Many people mistakenly believe that elevated blood uric acid levels automatically indicate gout. This is a misconception. A diagnosis of gout requires not only high uric acid levels in the blood but also uric acid crystal deposits that cause damage to the joints. Therefore, to accurately diagnose gout, a thorough medical examination and advanced diagnostic tests are necessary to confirm the condition based on established clinical criteria.

4. Diagnostic criteria for gout
The diagnostic criteria for gout, according to the ACR/EULAR 2015 guidelines, include:
Entry criteria:
- One or more episodes of swelling and pain in a peripheral joint or synovial (or bursal) space.
- Detection of urate crystals in the affected joint, symptomatic synovial fluid, or tophi.
If urate crystals are not detected, additional clinical and laboratory diagnostic assessments are performed, including:
- Inflammation in one or a few joints, such as the ankle or midfoot (1 point), big toe joint (2 points).
- Characteristics of acute inflammation: Redness in the joint, pain aggravated by pressure or touch, or difficulty walking and moving the joint (1 point for each symptom).
- Pain peaks within 24 hours, resolves in ≤14 days, and completely subsides between episodes (1 point for one episode, 2 points for multiple recurrent episodes without anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Tophi detected (4 points).
- No tophi detected (0 points).
Laboratory tests:
Blood uric acid levels:
- < 240 mmol/L (-4 points)
- 240 – < 360 mmol/L (0 points)
- 360 – < 480 mmol/L (2 points)
- 480 – < 600 mmol/L (3 points)
- ≥ 600 mmol/L (4 points)
Joint fluid analysis:
- No urate crystals detected (-2 points).
Imaging diagnostics:
- Ultrasound: Presence of a double contour sign.
- DECT scan: Detection of urate deposits using dual-energy computed tomography. Evidence from either imaging modality scores 4 points.
If the total diagnostic score is ≥8 points, the patient is diagnosed with gout. This is the latest and most accurate "gold standard" for diagnosing gout.
5. Reducing blood uric acid levels and preventing gout
As mentioned earlier, elevated uric acid levels are a primary cause of gout. Therefore, it is crucial to control blood uric acid levels within the normal range to effectively prevent gout. Key measures include:
- Limit consumption of high-protein foods, such as seafood (squid, crab, shrimp), red meats (beef, buffalo, goat), and organ meats (lungs, liver).
- Increase intake of green vegetables, fruits, and root vegetables.
- Drink 1 to 1.5 liters of water daily to minimize urate salt crystallization and enhance uric acid excretion.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the joints.
- Avoid alcohol and carbonated beverages.
- Adopt healthy lifestyle habits, including:
- Avoid staying up late.
- Manage stress effectively.
- Maintain good hygiene to promote blood circulation.
- Engage in moderate exercise, such as walking gently for 30 minutes daily or practicing yoga.
- Regularly test uric acid levels and undergo periodic health check-ups.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.