This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Do Thi Hoang Ha - Doctor of Biochemistry, Laboratory Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalBlood chemistry test is one of the common tests ordered by doctors when it is necessary to diagnose disease and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The following article will provide you with the meanings of some common blood chemistry tests.
1. What is a blood biochemical test?
Blood chemistry test is a type of test that measures the concentration or activity of certain substances in the blood, thereby helping to evaluate the function of organs in the body.2. Blood biochemical test indicators
2.1. Blood urea Urea is the main degradation product of proteins in the body and is filtered through the glomeruli for excretion in the urine. Urea blood test is used to evaluate kidney function, monitor kidney diseases as well as assess the protein supply of the diet. Normal value: 2.5 - 7.5 mmol/lBlood urea is increased in kidney diseases such as glomerulonephritis, nephritis, renal failure, kidney stones, ureteral stones, congestive heart failure, dehydration due to high fever, diarrhea, malnutrition, burns, gastrointestinal bleeding ...
Blood urea decreased due to low protein diet, high fluid infusion, pregnant women, nephrotic syndrome, impaired liver function lead to decreased urea synthesis.
2.2. Serum creatinine is a waste product of the breakdown of creatinine phosphate in the muscle and is completely filtered through the glomeruli, not reabsorbed by the renal tubules. Therefore, the creatinine value is mainly a reflection of kidney function and serum creatinine is used to assess kidney function
Normal value for men is between 62 - 120 mmol/l and for women is between 53 - 100 mmol/l.
Serum creatinine increased in renal failure, heart failure decompensated, gout, hyperthyroidism, hypertension, diabetes..
Serum creatinine decreased in pregnancy, muscle atrophy, paralysis, use antiepileptic drugs,...
2.3. AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), GGT The AST, ALT, GGT indexes are used to evaluate liver diseases such as acute and chronic hepatitis, liver parenchymal damage (viral hepatitis, hepatitis caused by hepatitis). drink alcohol...). Normal values for all three are about <35 U/L for women and <50 U/L for men.
2.4. ALP ALP, also known as alkaline phosphatase, is present mainly in the liver and bone. ALP is increased in hepatobiliary diseases and bone diseases such as bone metabolic disorders, rickets, osteomalacia, bile duct obstruction, prostate cancer,...
Normal ALP index <120 U/L.

2.5. Bilirubin Bilirubin is used to diagnose and monitor cases of jaundice caused by: hemolysis, hepatitis, biliary obstruction.
There are 3 bilirubin values including: Total Bilirubin; Direct bilirubin; Indirect bilirubin.
Normal total Bilirubin <21 umol/L.
2.6. Albumin This is a protein synthesized in the liver and accounts for about 60% of total serum protein. The function of Albumin is to create osmotic pressure, transport some metabolites, metal ions, bilirubin, free fatty acids, hormones, drugs... and provide amino acids for protein synthesis in tissues.
Albumin is an indicator used in the assessment of liver function. Normal Albumin values are around 35 - 50 g/L.
2.7. Blood Glucose Test Index Includes blood glucose test and HbA1C test. These two tests are aimed at diagnosing diabetes, monitoring and treating patients with diabetes; Monitor patients with hypoglycemia.
Normal blood glucose concentration is about 3.9-6.4 mmol/, HbA1C concentration is about 4 - 5.9%.
2.8. Blood fat test index
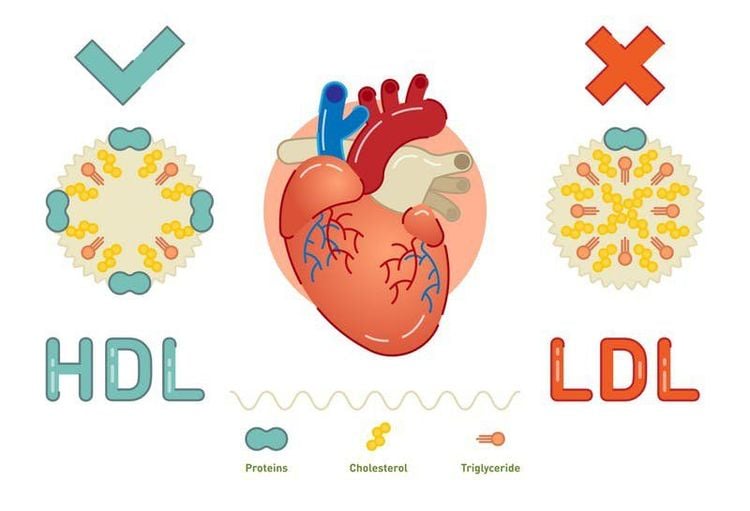
Normal total cholesterol levels are around 3.9 - 5.2 mmol/L. Blood cholesterol increased in the following cases: dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, obstructive jaundice, hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome, pre-eclampsia, pregnancy... Blood cholesterol decreased in all cases. cases: hyperthyroidism, liver failure, anemia, malnutrition,...
HDL-C (HDL-Cholesterol) - HDL This is a blood lipid test to help evaluate blood lipid disorders. HDL-C plays a role in transporting cholesterol deposited in the walls of blood vessels back to the liver, helping to prevent the formation of plaque, so it is also known as good cholesterol.
Normal HDL-C levels are 0.9 mmol/L or more. HDL-C levels decrease in cases of atherosclerosis, obesity, smoking, inactivity,...
LDL-C (LDL-Cholesterol)
LDL-C test to assess disorder dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, coronary artery disease,...LDL-C transports cholesterol to blood vessels and is the main cause of atherosclerotic plaques when LDL-C levels increase in blood.
A normal LDL-C level is 3.4 mmol/l or less . LDL-C increased in the following cases: atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia, obesity..., decreased in the following cases: cirrhosis, exhaustion, malabsorption.
Triglycerid This index is indicated in cases of dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, obese people, inactivity...
Normal Triglycerid value is about 0.46 - 1, 88 mmol/l. Triglycerides increase due to dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, obesity, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, hypothyroidism, diabetes... and decrease when due to malabsorption, exhaustion, hyperthyroidism, after activity strong physical strength,...
Normal Na+ concentration in blood is 135 - 145 mmol/l. Blood Na+ concentration increases in case of hyperaldosteronism, corticosteroid use, dehydration.. Blood Na+ concentration decreases in case of fluid retention due to heart failure, renal failure, cirrhosis or sodium loss due to vomiting, bleeding, diarrhea, burns..
K+ K+ is the electrolyte of the intracellular fluid
Normally, the concentration of K+ in the blood is about 3.5 - 5.0 mmol/l. The concentration of K+ in the blood is elevated due to kidney failure or due to the use of drugs that increase potassium retention such as potassium-sparing diuretics, ACE inhibitors.. K+ levels in the blood decrease due to loss through the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, vomiting, etc.), lost through the urine, the amount of K+ put into the body is not enough, or K+ from the extracellular space enters the cell.
Cl- Cl- is a major anion of extracellular fluid. The Cl- ion along with the HCO3- ion plays a role in maintaining the alkaline-acid balance in the body. Cl- also has a number of functions such as participating in maintaining osmotic pressure and water balance in the body, acting as a component of the buffer system, maintaining charge neutrality (by counterbalancing with cations such as Na+ ) and contribute to the digestive process.
Normal Cl- value is around 98 - 106 mmol/l. The concentration of Cl- increases in the case of salt intake, metabolic acidosis, acute renal failure, anaphylaxis, coma, and increased osmotic pressure...; decreased due to binge eating, acute dehydration causing metabolic alkalosis, prolonged vomiting (pyloric stenosis), diuretics, diarrhea,...
Ca++ Is a metal ion that is most abundant in the body, but only 0.5% of these total ions are exchanged. Ca++ plays an important role in muscle contraction, heart function, nerve impulse conduction and hemostasis of the body. Ca++ is diffusible, blood levels increase with acidosis and decrease with alkalosis.
Normal Ca++ levels are around 4.2 - 5.2 mEq/l (2.1 - 2.6 mmol/l). Ca ++ increases in case of taking a lot of vitamin D, hyperparathyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, Paget's disease..; reduce in case of vitamin D deficiency, hypoparathyroidism, severe kidney disease ...
2.10 Uric Acid Test This is a test to help diagnose diseases that cause changes in blood uric acid levels (gout), kidney disease, ...
Normal uric acid concentration in the blood in men is 180 - 420 mmol/l, for women it is 150 - 360 mmol/l.
Uric acid increases in cases of gout, obesity, kidney failure, heart failure, hypothyroidism, psoriasis, preeclampsia...
Uric acid decreases in case of liver cell damage, Wilson's disease, Fanconi's disease , Hodgkin's disease...
Blood biochemical tests include many complicated stages, requiring highly specialized skills and the support of modern machinery systems. Therefore, we should choose to perform biochemical blood tests at reputable hospitals.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.