This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Tran Quoc Tuan - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalWhen you have diabetes, your blood sugar may always be higher than normal. Over time, this can lead to serious problems with overall health such as stroke, heart disease or kidney disease.
1. What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by higher than normal blood sugar levels. This happens because the body lacks the hormone insulin, causing the blood sugar metabolism to be disturbed.Normally, the hormone insulin is produced by the pancreas. They play an important role in transporting glucose into cells to provide an adequate source of energy needed for the body's activities. However, if the amount of glucose exceeds the allowable limit, insulin cannot do its job as well as it should. At this time, the amount of unmetabolized sugar will be in excess in the blood, leading to a high blood sugar level. This condition is called diabetes mellitus, or diabetes mellitus.
If blood sugar is high for a long time and is not controlled, it can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and lead to other health problems, such as damage to the kidneys and eyes. , or nerve.
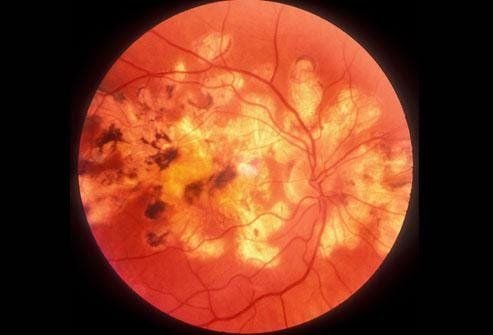
Bệnh tiểu đường gây ra nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm
2. Types of diabetes
Currently, diabetes is classified into three main types, including:Type 1 diabetes : This is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body's immune system mistakenly and attacks the pancreas itself. . This interferes with the production of insulin and leads to a significant deficiency in the amount of insulin needed for the body's activities to convert glucose into an energy source, thereby causing blood sugar to rise. Type 1 diabetes is quite rare, and occurs mostly in young children. Type 2 diabetes: This is the most common type of diabetes today, greatly affecting people who are obese. When you have type 2 diabetes, your body becomes resistant to insulin. Although the hormone insulin is still secreted by the pancreas, it cannot metabolize glucose, causing it to gradually build up in the blood. Most people with diabetes have this type of diabetes. Gestational diabetes: Usually occurs in women who are pregnant. In general, after a pregnant woman goes into labor, this condition will go away on its own. However, this disease can lead to some serious health problems for both mother and baby if not detected and treated promptly.

Mẹ bầu mắc tiểu đường thai kỳ cần có chế độ ăn khoa học
3. Causes of diabetes
Currently, the root cause of diabetes is still unknown. However, factors that can contribute to diabetes often include genetics, improper diet, unhealthy lifestyle, overweight, or obesity.The following people are at high risk for diabetes, including:
People with a history of abnormally high blood sugar or a family member with diabetes Older adults (age 45 and older) People with high blood pressure and cholesterol levels People who are physically sedentary People with a history of heart disease Women with a history of gestational diabetes.
Người mắc bệnh tim có nguy cơ mắc thêm bệnh tiểu đường
4. Signs and symptoms of diabetes
Some common signs and symptoms of diabetes include:Frequent urination: When blood sugar is high, it will be excreted through the urine. This causes the kidneys to work too hard to get rid of the excess sugar in the urine. At this time, the water in the body diffuses to dilute the urine, and causes the urine volume to increase, leading to frequent urination. Frequent thirst: This is one of the silent signs of diabetes. When the body loses a lot of water, it will need to be compensated to be able to perform well. Therefore, the patient will feel thirsty all the time and need to drink water constantly. Eat more: Due to a lack of insulin, glucose cannot be converted into energy, so patients will have cravings, hunger, and stimulation to eat more. Uncontrolled weight loss: Because the body cannot metabolize glucose for energy, they will have to break down fat and muscle tissue to compensate. Therefore, even if the patient eats and drinks more than usual, the body still loses weight, becomes thin and pale. This condition is common in people with type 1 diabetes. Some other symptoms: Such as nausea, dry mouth, slow wound healing, blurred vision, fatigue, depression, numbness in the extremities, infection fungus, or bad breath.

Tụt cân không kiểm soát là dấu hiệu của bệnh tiểu đường
5. What blood sugar is normal?
Your blood sugar will be considered normal if they are lower than 100 mg/dL after not eating (fasting) for at least 8 hours, and less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating.During the day, blood sugar levels tend to be at their lowest just before meals. For most people without diabetes, pre-meal blood sugar levels will range between 70-80 mg/dL. In others, a blood glucose level of 60 – 90 mg/dL would be considered normal.
Low blood sugar also manifests differently from person to person. For some people, their glucose levels may never drop below 60, even if they fast for quite a while. In some other people, their blood sugar level may be slightly lower. In general, when you're fasting or dieting, your liver will keep your blood sugar in the normal range by converting fat and muscle into sugar.
6. Tests to diagnose diabetes
Here are some tests to help diagnose whether you have diabetes, including:Fasting plasma glucose test : Your doctor will perform a blood glucose test after You have fasted for 8 hours. If the results show your blood glucose level is higher than 126 mg/dL, this means you have diabetes. Oral glucose tolerance test: Your doctor will give you a sugary solution to drink, provided you haven't eaten for 8 hours. If, after two hours, the test shows your blood sugar is higher than 200 mg/dL, you may have diabetes. Random test: Your doctor will check your blood sugar at any time. If your blood glucose level exceeds 200 mg/dL, is accompanied by frequent thirst, increased urination, or you have experienced significant weight loss, the diagnosis indicates that you have diabetes. In general, any glycemic index higher than the specified level is bad for your health. In cases where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but have not yet reached what is considered full-blown diabetes, the condition is called prediabetes.
If prediabetes is not controlled with healthy lifestyle changes recommended by your doctor, they can lead to diabetes. In addition, it also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, but not as much as diabetes. You can completely prevent prediabetes from developing into diabetes through a reasonable diet, combined with exercise more often every day.

Xét nghiệm glucose cho phép chẩn đoán bệnh tiểu đường
7. How does high blood sugar affect the body?
Glucose will be considered a nutritious fuel source for all cells in the body if it is always in the normal range. However, it can also become a slow-acting “poison” if high blood sugar persists, which can even lead to dangerous complications to your health.When blood sugar levels are high, they can reduce the pancreas' ability to produce the hormone insulin. Over time, the pancreas can be permanently damaged. In addition, high blood sugar can also increase the risk of hardening of the blood vessels, also known as atherosclerosis.
In fact, high blood sugar can damage any part of the body. When blood vessels are damaged, it leads to the following problems:
Stroke Kidney disease, kidney failure Heart attack Weakened immune system, susceptible to infections Loss of vision or blindness Erectile dysfunction Blood flow poor communication to the legs and feet Damaged nerves (neuropathy), causing pain, tingling, or loss of sensation in the feet, legs, and hands Slow wound healing, in some cases rare cases of amputation To prevent these dangerous complications, try to keep your blood sugar close to normal. According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes should maintain blood sugar levels at 70-130 mg/dL before meals and below 180 mg/dL after meals.

Bệnh nhân có mạch máu bị hỏng tăng nguy cơ đột quỵ
8. How to control blood sugar level?
To keep your blood sugar in the normal range, you should follow some of the following measures:Build a healthy and scientific diet: Include lots of green vegetables, whole grains, Fruits, drink lots of water, limit the consumption of foods rich in saturated fat, trans fat, eat less sugar and salt. Keep calm: Stress is also a trigger for raising your blood sugar. Therefore, try to keep yourself in a comfortable mood, exercise regularly and give up smoking to improve your health. Use of medication: In case you have to use medication to treat diabetes, you need to take it exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Avoid quitting halfway, or taking the wrong dose, as this can be harmful to your health.
Thuốc uống theo chỉ định có thể kiểm soát mức đường huyết
Using the screening package for diabetes and dyslipidemia at Vinmec, patients will receive:
Endocrine CK examination (with appointment) Total urinalysis (by automatic machine) Quantitative Glucose Quantitative HbA1c Quantitative Uric Acid Quantification of Cholesterol Determination of HDL-C (High density lipoprotein Cholesterol) Determination of LDL-C (Low density lipoprotein Cholesterol) Determination of Triglycerides Determination of Urea Determination of Creatinine Measurement of AST Activity (GOT) Measurement of ALT Activity (GPT) Measurement of GGT activity (Gama glutamyl Transferase) Quantification of MAU (Micro Albumin Arine) Echocardiography, transthoracic pericardium, Normal ECG, Carotid Doppler ultrasound, Transcranial Doppler (carotid) Arterial Doppler ultrasound, Lower extremity veins (Bilateral lower extremity arteries) If you need consultation and examination at Hospitals of the National Health System, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com