This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalEosinophilic esophagitis (VTQDBCAT) is an inflammatory condition in which the wall of the esophagus is infiltrated with a large number of eosinophils, which was first recognized in 1978.
VTQDBCAT is a type of esophagitis caused by allergies like bronchial asthma, or fever, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis even some other allergens. The hallmark of eosinophilic esophagitis is the presence of large numbers of eosinophils in the tissue underlying the lining of the esophagus. VTQDBCAT affects both adults and children. The reason why is still not fully understood, men often suffer from the disease more than women.
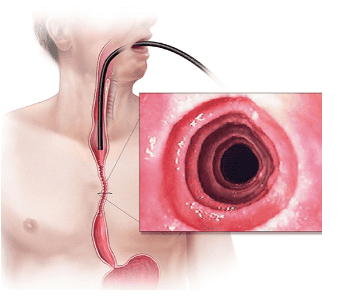
Endoscopy helps to assess disease activity by identifying inflammation (signs of edema, exudation, esophageal fissure) and narrowing (esophageal ring, stricture) and then decide on treatment. Interventional esophagectomy when indicated as well as monitoring of response to treatment.
However, the endoscopic method also has some limitations such as the sensitivity and specificity of the endoscopic images that vary based on the severity and number of lesions recorded, besides, there are 10 - 25% The patient had a normal endoscopic picture.
In addition, most of the studies evaluating the benefit of endoscopy for VTQDBCAT did not exclude patients with GERD and patients with esophageal elevations of BCAT who responded to PPIs. Therefore, relying only on endoscopic images will not be able to diagnose VTQDBCAT as well as assess the extent of the disease. Currently, in the recommendations of the American Gastroenterology Association in 2013 and the European Gastroenterology Society in 2017, both agree to use the scale to classify and evaluate the severity on endoscopy of VTQDBCAT in which the EREFS (Endoscopic Reference Score) has high reliability and can be used to monitor response to treatment.
1. Esophageal longitudinal grooves
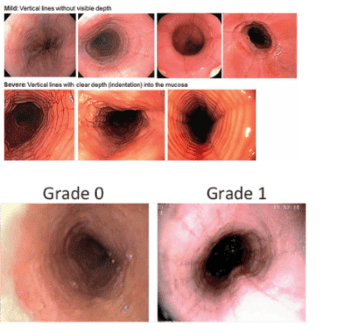
This is a typical image commonly seen in VTQDBCAT with grooves along the lining of the esophagus. Under white light and narrow tonnage light, these longitudinal grooves are clearly visible. The use of dyes will help the doctor see more clearly. Endoscopic ultrasonography showed thickening of the mucosa and submucosa.
The rate of this image in VTQDBCAT patients is 11 - 100%. This endoscopic image can occasionally be seen in patients with GERD or in the general population, but prominent and common longitudinal fissures in the distal esophagus are suggestive of VTQDBCAT.
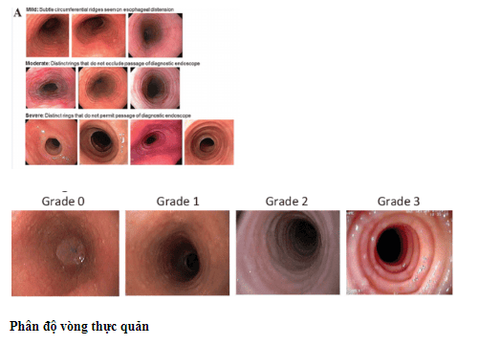
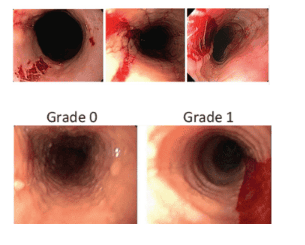
2. Concentric circle
This is a common endoscopic image with many concentric circles. This feature may appear alone or in combination with other endoscopic images, may be localized in certain segments of the esophagus or along the entire length of the esophagus.
This image differs from the Schatzki ring which is usually seen only in the gastroesophageal junction. Dellon et al. suggest that this is one of the endoscopic features that distinguish VTQDBCAT from GERD.
The mechanism that produces the images of these concentric circles is currently unknown but it is possible that penetration of BCAT into the muscle layer leads to contraction of the layers in the esophageal wall and interestingly After treatment, this endoscopic image will disappear. The incidence of this endoscopic feature in VTQDBCAT patients ranges from 19 to 88%.
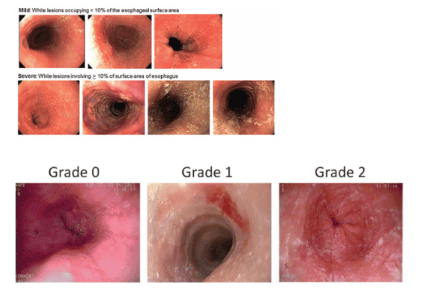
3. Pictures of exudates and patches
The exudative lesions have diverse morphology that can be dots, nodules, plaques or clusters with size from 1 to 3 mm or more along the lumen of the esophagus. The endoscopist may sometimes think of this lesion as mycosis of the esophagus, but in the case of VTQDBCAT, histopathology shows an accumulation of BCATs forming microabscesses on the mucosal surface. Stomach. This lesion is more common in children than in adults, with rates ranging from 15 to 26%.
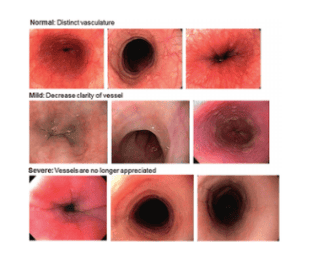
4. Loss of vascular network
Normal esophageal mucosa with subepithelial vascular network is clearly visible on endoscopy. In the presence of mucosal inflammation, the normal vascular morphology is no longer evident because the basal layer of the mucosa is edematous.
In one study by Strausmann et al., loss of capillary network morphology occurred in 93% of patients while some other studies also received reduced vascular distribution in 5-26% of VTQDBCAT cases. .
Although this image perception is subjective, now, with the development of endoscopic techniques such as high resolution endoscopy, magnification endoscopy, virtual staining endoscopy, image evaluation This image is easier and helps to provide additional evidence for the diagnosis of TQDBCAT.
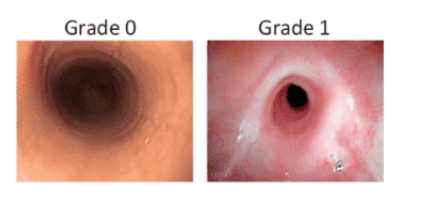
5. Esophageal stricture
According to studies, focal narrow lesions in the esophagus in the absence of concentric rings can range from 3 to 66% of patients with VTQDBCAT. Esophageal stricture is more common in adults than in children.
6. The esophagus is as thin as paper
The term "crepe - paper esophagus" - paper-thin esophagus was first proposed in 2003 by the author Straumann to describe the esophageal mucosa is vulnerable, no longer has normal contractility and is easy to create ulcers only by light impacts such as inflating the air, touching the lamp head.
7. Round Schatzki
Schatzki's ring is a narrowing of the gastro-oesophageal junction, a mucosal ring located at the gastroesophageal junction that causes dysphagia, which may be congenital, or may be due to gastroesophageal reflux - Stomach . Before dysphagia occurs, the lumen of the esophagus usually narrows to less than 13 mm.
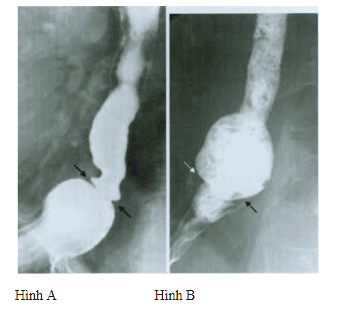
Figure A: Schatzki ring on contrast-enhanced radiographs of the esophagus.
Figure B: Bread soaked in Barium was swallowed and stuck at the Schatzki ring.
This picture can be seen in 0.2 - 15% of normal people and is often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease. However, there are also some studies in patients with VTQDBCAT that recorded endoscopic images with Schatzki ring such as Desai's study - 29%, Gonsaives' study -14%. However, to date there is no data demonstrating an association between the Schatzki ring and VTQDBCAT.
Eosinophilic esophagitis is a relatively rare disease of the esophagus, patients have symptoms of difficulty swallowing, choking, painful swallowing, burning, reflux, heaviness in the chest, chest pain... need Revisit a gastroenterologist and undergo an endoscopy to avoid missed diagnoses and delay treatment of this pathology.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.