This is an automatically translated article.
Most cases of infectious mononucleosis are not serious and are easy to handle. But if the disease is not managed appropriately, complications can become serious.1. What is infectious mononucleosis?
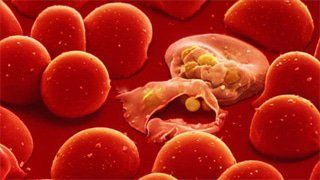
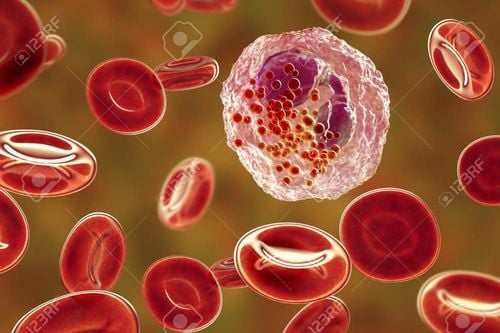
Infectious mononucleosis is a group of symptoms caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). This virus is mainly spread through saliva from the mouth of an infected person or when an infected person coughs, sneezes, kisses, eats together, the disease cannot be transmitted through blood.When infected with infectious mononucleosis, it usually takes about 4-8 weeks for symptoms to appear. such as:
Fever, sore throat Signs of toxicity such as fatigue, loss of appetite, muscle pain in the early stages Enlarged but non-adhesive lymph nodes, mild pain, no pus, The patient has an enlarged spleen. A maculopapular or petechiae rash. The virus causes exudative pharyngitis, tonsillitis, gingivitis and petechiae in the palate. Central nervous system damage such as peripheral cranial nerve palsy, lung damage causing cough, shortness of breath, airway obstruction Tachycardia, arrhythmia; Hepatitis; renal failure due to interstitial nephritis. Infectious mononucleosis is difficult to differentiate, so if your symptoms don't improve after a week or two, you should seek medical attention.
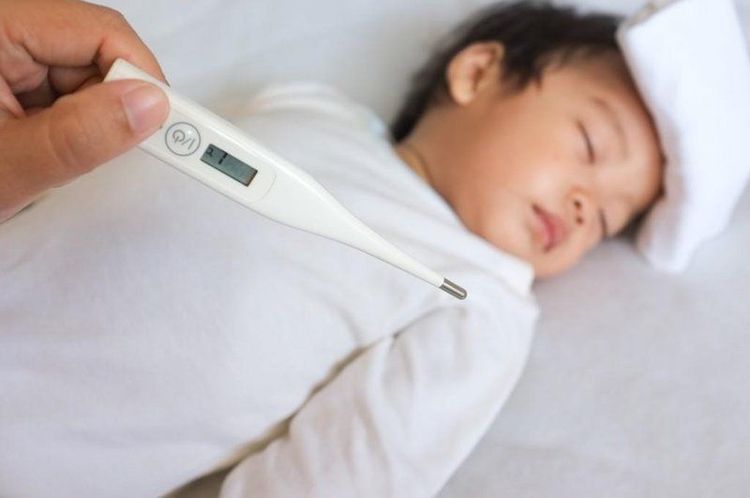

Sốt, đau họng, mệt mỏi là những dấu hiệu dễ nhận thấy khi nhiễm bệnh tăng bạch cầu đơn nhân nhiễm trùng
2. Is infectious mononucleosis dangerous?
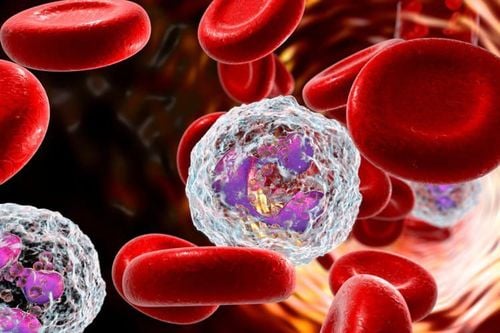
Most cases of infectious mononucleosis are not serious and are easy to handle. But if the disease is not properly managed, complications can become serious such as:Neurological complications such as: encephalitis, meningitis, myelitis, mental disorders... Hematological complications such as: Leukopenia ; thrombocytopenia; hemolysis, anemia; infection or bleeding. Spleen rupture can have serious consequences. Splenic rupture causes pain but occasionally hypotension. Respiratory complications: Airway obstruction, non-embolic pneumonia. Complications in the liver are usually increased amino acids In the absence of complications, the patient will have no fever within 10 days, lymph nodes and splenomegaly will shrink, but fatigue may last for 2-3 months.
3. Diagnosis and treatment of infectious mononucleosis
Hiện không có thuốc đặc trị tăng bạch cầu đơn nhân nhiễm khuẩn
Rest, drink plenty of water, take pain relievers when symptoms cause much discomfort. Sore throat: Use metronidazole to relieve sore throat. If there are signs of serious depression, antidepressants such as: imipramine (Imizin, Tofranil...), amitriptylin Vinmec International General Hospital with the current system of facilities and medical equipment With a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured that they will be examined and treated at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE ALSOIn what case is the white blood cell reduced? Elevated white blood cells indicate what disease? What is the number of white blood cells in the body?