This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International HospitalEosinophilic esophagitis is an inflammatory condition in which the wall of the esophagus is infiltrated with large numbers of eosinophils, first recognized in 1978. Accordingly. The purpose of X-ray is to investigate for pathological problems in the esophagus for timely examination and treatment.
1. Esophagitis and esophagitis
The esophagus is a muscular tube that helps the body push and swallow food from the mouth into the stomach. There are many causes of esophagitis, but the most common cause is acid reflux, which leads to a burning sensation in the throat, although acid reflux can cause ulcers on the inner lining of the esophagus.Other, rarer causes are viruses (herpes simplex), fungi (candidiasis), drugs (tetracycline), radiation (lung cancer treatment). Physicians believe that eosinophilic esophagitis (VTQDBCAT) is a type of esophagitis caused by asthma-like allergies, or fever, allergic rhinitis, and even atopic dermatitis. some other allergens.
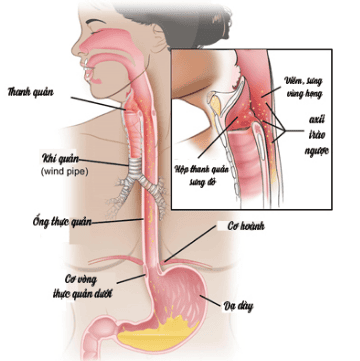
2. What is eosinophilic esophagitis (VTQDBCAT)?
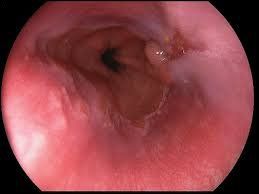
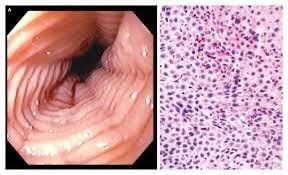
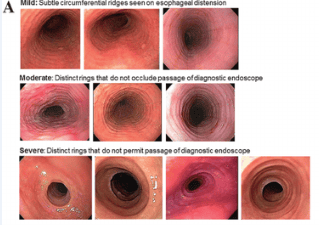
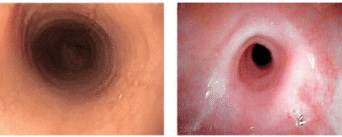
Eosinophilic esophagitis (VTQDBCAT) is an inflammatory condition in which the wall of the esophagus is infiltrated with large amounts of eosinophils, first recognized in 1978.Accordingly, the endoscopic image of Eosinophilic esophagitis is quite diverse, including white patches, concentric rings, narrowing, mucosal loss of capillary network, paper thin esophagus, Schatzki ring, pseudo-diverticulum, and on endoscopic ultrasonography. The esophageal wall can be seen thick. Endoscopy helps to evaluate disease activity by identifying inflammation (signs of edema, exudation, longitudinal groove of the esophagus) and narrowing (esophageal ring, stricture) from which to decide on treatment. Interventional dilation of the esophagus when indicated as well as monitoring in response to treatment. However, the endoscopic method also has some limitations such as sensitivity and specificity of endoscopic images that vary based on the severity and number of lesions recorded, besides that in 10-25% of patients. normal endoscopic image.
3. What is Barium or Baryt Contrast?
On conventional radiographs, the gastrointestinal tract is not shown well. However, if you drink a white liquid that contains a chemical called Barium sulphate (BaSO4), the image of the upper gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, and small intestine) will be clearly shown on the image. X-ray image. The reason is because X-rays do not pass through Barium.Depending on the location of the gastrointestinal tract to be examined, you may need one or more of the surveys listed below. Barium when ingested will form a layer that adheres to the lining of the digestive tract. Thus, abnormalities in the lining or structure of the gastrointestinal tract can be observed on radiographs.
In each of the following studies, radiographs were taken with a low dose of X-rays. The total radiation dose for each survey is quite small and is considered safe. The X-ray machine is connected to a TV monitor. A continuous snapshot or video X-ray may be considered if the doctor deems it necessary.
4. What is Baryt Swallow Contrast Esophageal X-ray?
In this survey, you drink a liquid containing Baryt. The liquid usually has a fruity flavor that makes it pleasant to drink. You stand in front of an X-ray machine and X-rays will be taken while you swallow this liquid. The purpose of the survey is to look for problems in the esophagus such as: esophageal stricture, diaphragmatic hernia, tumors, gastroesophageal reflux, swallowing disorders, etc. Usually you will be asked not to eat. drink a few hours before taking this survey. A contrast-enhanced esophagogram with Baryt takes about 10 minutes.4.1. X-ray image of normal oesophagus Normal esophagus has a clear border, mucosal folds running parallel to each other, divided into three segments:
Short neck segment. The longest thoracic segment, located close to the posterior border of the heart, has two imprints of the aorta and the left main bronchus. The abdomen is very short, after passing through the diaphragmatic foramen and ending with the cardia, it pours into the posterior surface - in the large gastric aneurysm and creates with this part an acute angle that is the angle of His, which has the function of preventing gastric reflux. - esophagus.
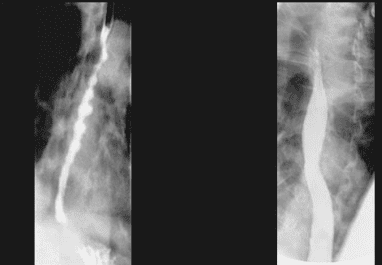
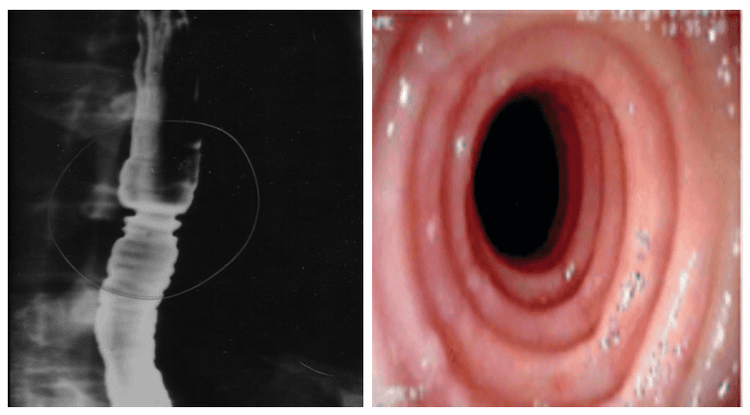
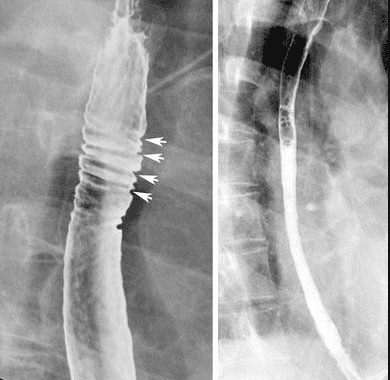
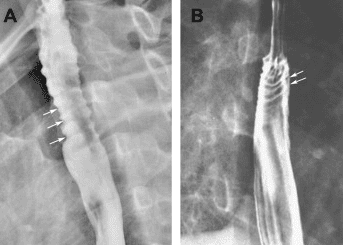
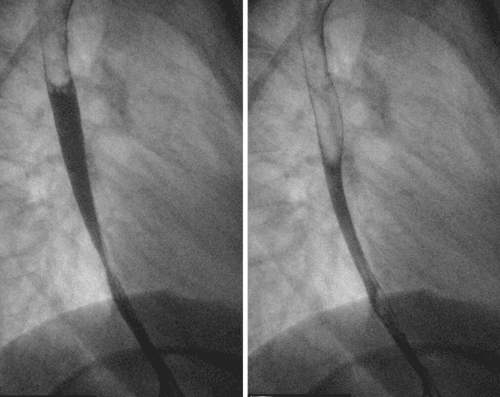
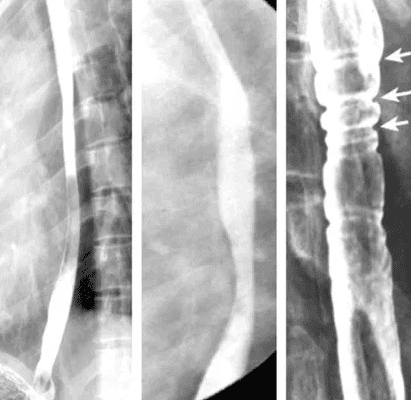
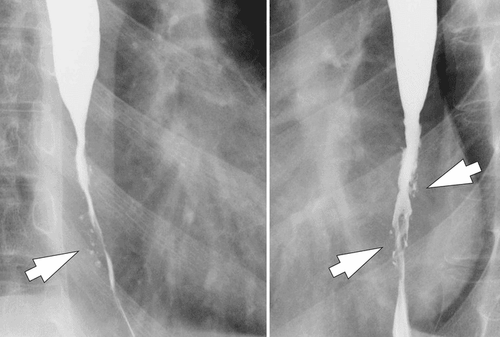
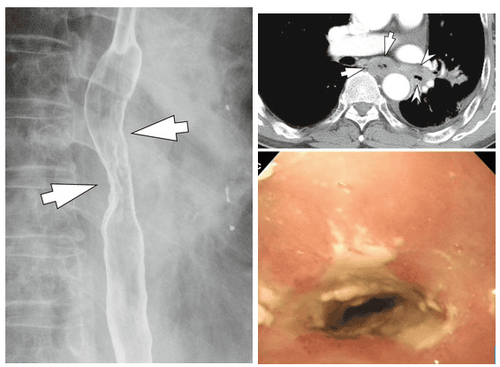
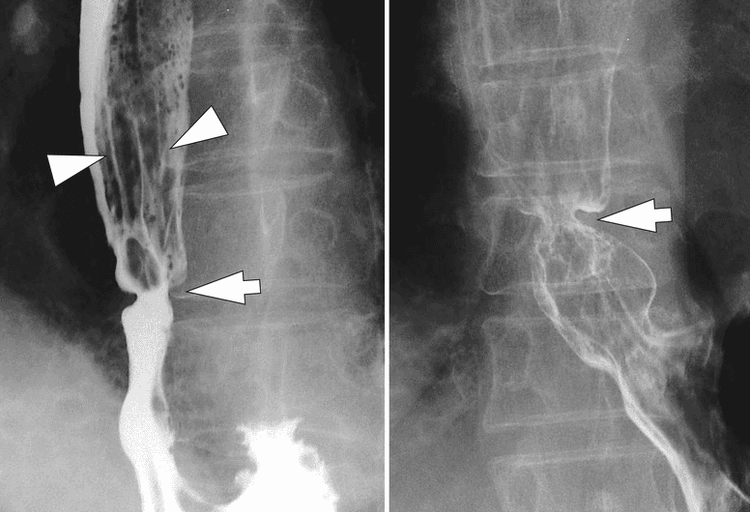
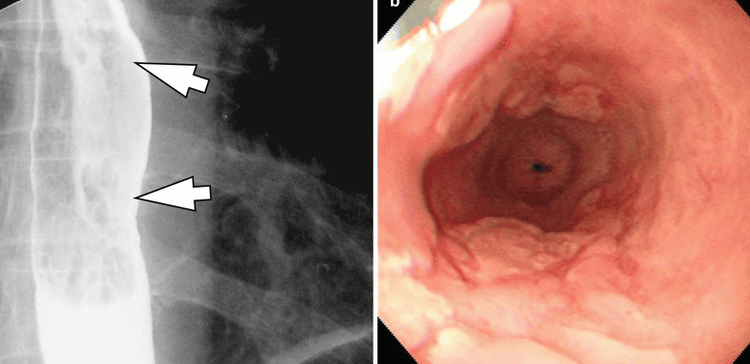
Although Eosinophilic esophagitis has some characteristic features, however, it should be differentiated from the narrow inflammatory images of Barrett's esophagus, mediastinal radiotherapy, and the use of certain drugs such as NSAIDs, quinidine , and requires endoscopy, biopsy for histopathology to confirm the diagnosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.