This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Nguyen Van Anh - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Bladder neck polyps are benign bladder tumors. With today's medical technology, the diagnosis of polyps is now made easy and convenient thanks to bladder ultrasound and cystoscopy. So how to diagnose early bladder neck polyp by ultrasound?
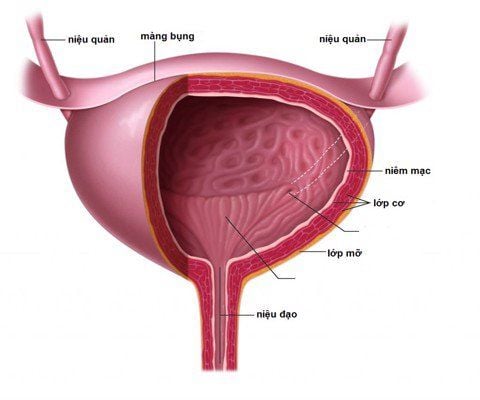
1. What is a bladder?
The bladder, also known as the bladder, is located just below the peritoneum, behind the pubic joint. The position of the bladder when empty and when filled with urine is shifted.If in the empty state, the bladder will lie completely in front of the pelvis, behind the rectum and genitals. The bladder functions to store urine. When it is filled with urine, it expands into a sphere, extends over the pubic joint, and then rests in the abdomen.
2. Symptoms of bladder neck polyps
Patients see the appearance of obvious symptoms:Blood in the urine: Sudden, painless, recurrent. Urinary disorders: Difficulty urinating, burning sensation, frequent urination - caused by compression of the bladder neck) Pain in the pelvic region, low back pain when urinating... Examination of the urinary system: Bladder bridge There is blood in the mouth of the penis, .. Bladder bridge: When there is acute urinary retention (caused by polyps covering the inner urethral hole).
3. Early diagnosis of bladder neck polyps by ultrasound
Bladder ultrasound is the most common imaging method used today when patients have bladder problems. Ultrasound can detect birth defects, detect tumors, assess bladder wall invasion, and urinary retention. Through that, the doctor will determine the problem you are having.In addition, ultrasound can also detect some other diseases such as urethritis, prostatitis. Bladder ultrasound is a highly effective measure, with mild patients often only needing to carry out this measure. This is also a common method for early diagnosis of bladder neck polyps.
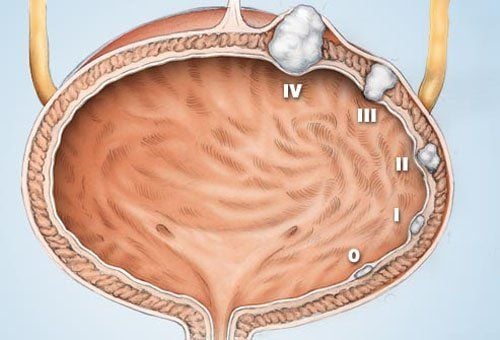
When performing abdominal ultrasound (when the bladder is full of urine), the image shows: solid tissue mass, protruding into the bladder lumen, moving in position, pedunculated. The bladder wall is thick, there is Blood clots if there is inflammation, accompanied by hematuria.

4. Method to remove bladder neck polyp
Depending on the size of the bladder neck polyp, large or small, the doctor will decide whether the patient is treated with oral medications or performed endoscopic bladder neck polypectomy.4.1 Designation
Patients are performed endoscopic bladder neck polypectomy when:Diagnosing the cause of hematuria, determining whether there is a bladder neck polyp or tumor in the bladder. Differential diagnosis of: Overactive bladder due to or not due to neurologic causes, urinary incontinence, interstitial cystitis, vesicovaginal or vesico-enteric fistula and suspected cases of urogenital tuberculosis sex. Evaluation of anatomical and structural abnormalities of the lower urinary tract: Bladder neck stenosis, urethral stricture, bladder diverticulum, urethral diverticulum, urethral stone, bladder stone, foreign body in the bladder optical.

4.2 Contraindications
With the following cases, the patient cannot perform:The patient has acute urethritis. Acute prostatitis. Orchitis, acute epididymitis. Fever due to urinary tract infection. Blood clotting disorder.

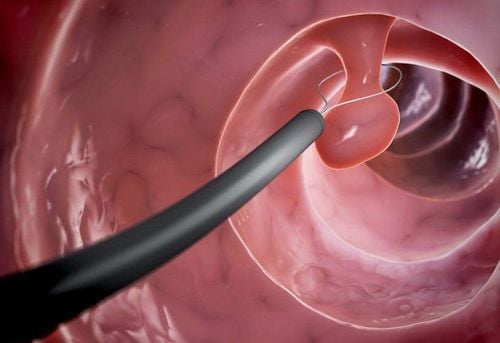
4.3 Steps to perform endoscopic bladder neck polypectomy
Follow the anesthesia method of spinal anesthesia or endotracheal anesthesia for the patient. The patient lies in the obstetric position. Use sterile Xylocaine Gel into a 10ml syringe to inject into the urethra for the purpose of lubricating the urethra. Insert the cystoscope into the urethra under the guidance of the camera slowly into the bladder Observe through the screen the bladder neck, the triangle of the bladder, 2 ureteral openings, 2 lateral walls, the fundus and anterior surface of the bladder optical. Bring the cutting blade to the polyp location, cut off the polyp leg and take it out for pathology Anatomy Burn hemostasis section Check hemostasis carefully, make sure that the polyp is gone. Unplug the scanner. Catheterization of 3 urethral branches to flush the bladder continuously After performing endoscopic polypectomy of the bladder neck, the patient goes to the recovery room for further monitoring. Follow-up ultrasound examination after 3 months. When seeing abnormal signs, patients should quickly go to medical facilities for timely examination, detection and treatment. With a system of facilities, modern medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit and receive treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital. Hospital urology department.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
Bladder neck sclerosis: Complications of many diseases Endotracheal anesthesia Laparoscopic surgery to remove bladder neck polyps Detecting bladder tumors, can it be cured?