This is an automatically translated article.
Bladder neck polyps form from an overgrowth in the lining of the urinary tract, calculated at the bladder neck. Bladder neck polyps are mostly benign and can be diagnosed through clinical signs and laboratory methods.1. Clinical manifestations of bladder neck polyps
Patients with bladder neck polyps will have symptoms such as:Hematuria: Sudden, painless, recurrent; Difficulty urinating, urinary obstruction when polyps compress the bladder neck; Painful urination, painful urination, pelvic pain, low back pain when urinating... Examination of the urinary system: There is a bladder bridge due to acute urinary retention, the mouth of the penis is bloody By paraclinical methods, the patient easily detect bladder neck polyps through:
Abdominal ultrasound: There is a picture of a dense mass, protruding into the bladder lumen, moving in position, with stalk, thicker than normal bladder wall, with Blood clots due to inflammation, blood in urine Computerized tomography accurately evaluates bladder polyps, bladder protrusions, stalks, no images of bladder wall invasion Endoscopy with biopsy for anatomy disease accurately diagnose bladder neck polyps Urinalysis with microscopic red blood cells helps in making an accurate diagnosis and screening.
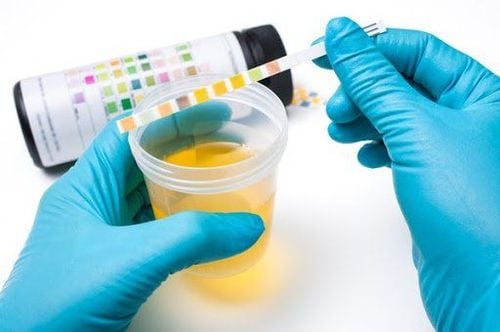
Xét nghiệm nước tiểu cũng là phương pháp chẩn đoán polyp bàng quang
2. Indications for laparoscopic surgery to remove polyps of the bladder neck
After concluding that there is a bladder neck polyp, the following patients are indicated for laparoscopic bladder neck polypectomy:Diagnosis of the cause of hematuria, identification of bladder neck polyps or bladder tumors. Differential diagnosis of diseases: Overactive bladder due to or not due to neurological causes, urinary incontinence, interstitial cystitis, vesicovaginal or vesico-enteric fistula and suspected cases of urinary tuberculosis - genital. Evaluation of anatomical and structural abnormalities of the lower urinary tract: Bladder neck stenosis, urethral stricture, bladder diverticulum, urethral diverticulum, urethral stone, bladder stone, foreign body in the bladder optical.
3. Contraindications to laparoscopic bladder neck polypectomy
Acute urethritis Acute prostatitis Acute testicular and epididymitis Fever Urinary tract infection Blood clotting disorder
Rối loạn đông máu là một trong số nhũng trường hợp được chống chỉ định mổ nội soi
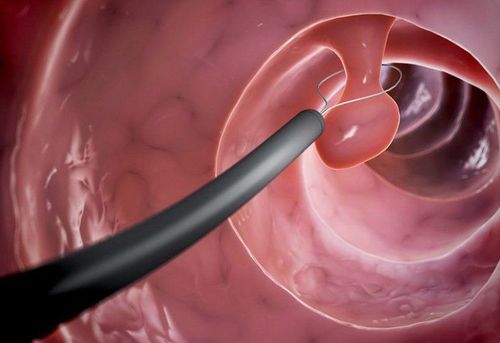
4. Perform laparoscopic bladder neck polyp removal
To prepare for laparoscopic bladder neck polypectomy, the patient needs to have a health check and perform tests as prescribed by a urologist. After performing anesthesia with spinal anesthesia, or endotracheal anesthesia, the patient is left in the obstetric position to perform endoscopy through the following steps:Use sterile Xylocaine gel into a 10ml syringe into the urethra for the purpose of lubricating the urethra Insert the scope through the mouth of the flute into the urethra under the guidance of the camera slowly into the bladder Observe through the monitor the bladder neck, bladder triangle area, 2 ureteral openings, 2 side walls, basal surface and anterior surface of the bladder Insert the blade to the polyp location, cut off the polyp's leg, remove it for pathology Anatomy Hemostasis of the cut area Check hemostasis carefully, make sure polyps are gone Remove the scope 3-pronged urethral catheter for continuous bladder irrigation. Patients after endoscopic bladder neck polypectomy should be monitored to minimize intra- and postoperative complications. At the same time, patients do not forget to monitor the progress of the disease by periodic ultrasound every 3 months.

Tai biến sau mổ nội soi cắt polyp cổ bàng quang
5. Complications after laparoscopic bladder neck polypectomy
Some patients will not be able to avoid some complications after surgery such as:Infection: The endoscopic process can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, causing infection, the patient can be given antibiotics before and after cystoscopy to prevent infection Bleeding: Endoscopy causes damage to the urethral mucosa, bladder bleeding, depending on the extent, the treating doctor will have appropriate treatment, usually urethral catheterization and continuous bladder lavage. Pain: The patient will have a feeling of abdominal pain, burning when urinating, this condition will decrease over time Bladder perforation in the lateral wall position due to stimulation of the obturator nerve causing leg jerks: Extraperitoneal perforation is common. , depending on the lesion, can be treated conservatively if the perforation is incomplete or open surgery if the perforation is complete. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MOREComplications of cystitis What is neurogenic bladder? Is acute cystitis dangerous?