This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Vascular malformation embolization is the most common method used to treat AVM venous malformation today. This method can help to restore the circulation of the limbs and improve the nutritional status.
1. What is an AVM?
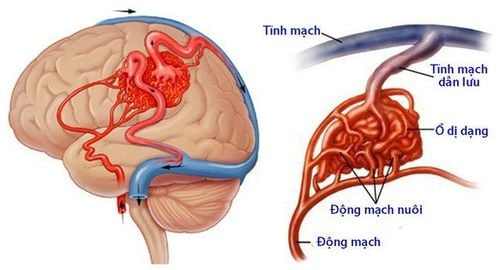
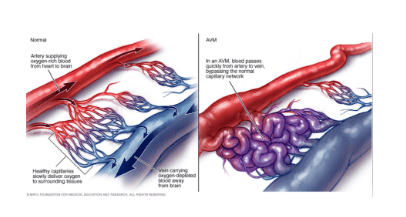
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a congenital abnormality of blood vessels, formed during embryonic development. When many direct flows between the arterial system and the venous system, but not through the capillary system, will lead to loss of metabolic capacity in the tissues surrounding the malformation, this is also called the phenomenon of blood robbery.Arteriovenous malformation lesions will progress with the growth of the body, leading to hypotrophy or tissue dystrophy.
Manifestations of this disease will be symptoms of pain, deformity, ulceration - necrosis and bleeding. Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) can occur anywhere in the body and can be treated by embolization.
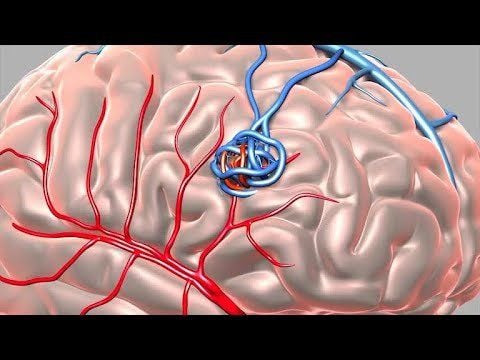
2. Indications and contraindications for vascular node malformation
2.1 Designation
Complicated soft arteriovenous malformation: Pain, ulceration, skin dystrophy, soft tissue necrosis around the malformation or downstream of the malformation. Software arteriovenous malformations have a downstream blood-stealing effect.2.2 Contraindications
Vascular malformation of the limb is contraindicated in the following casesAllergy to iodine contrast agents. Severe renal failure (grade IV). Severe and uncontrolled coagulopathy (prothrombin 1.5, platelet count < 50 G/l). Pregnant.
3. Participants who performed circuit malformation of the limb
Specialist. Auxiliary physician. Optical technician. Nursing. Doctor, anesthesiologist (if the patient cannot cooperate).4. Means used in circuit breaker circuit malformation
Digital background removal angiography (DSA). Film, film printer, image storage system. Dedicated electric pump. Lead suit, apron, X-ray shielding.
5. Medicines to prepare before the method
Local anesthetics Anticoagulants General anesthetics (if anesthesia is indicated) Water-soluble iodinated contrast agents Neutralizing anticoagulants Antiseptic solutions for skin and mucous membranes6. Basic medical supplies for vascular malformations
Syringe 1; 3; 5, 10; and 20ml Syringe for electric pumps Gloves, gown, cap, surgical mask Distilled water or physiological saline Cotton, gauze, surgical tape. Aseptic intervention kit: knife, scissors, tongs, 4 metal bowls, bean tray, tool tray. Medicine box and first aid kit for contrast drug accidents.7. Materials used for embolization
Synthetic plastic beads (PVA) Bio-foam (gelfoam) Metal spirals of all sizes (coils) Bio-glue (Histoacryl, Onyx) Absolute alcohol8. What should the patient do to prepare before performing angioplasty?
Patients must have a clear understanding of the procedures performed in the method of embolization of the limb vascular malformation so that they can coordinate with the doctor in the process. At the same time, 6 hours before the procedure, the patient needs to fast, but still can drink less than 50ml of water.In the intervention room, the patient lies in the supine position, fitted with a machine to monitor breathing, pulse, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, SpO2. Disinfect the skin, then cover with a sterile, perforated cloth. In case the patient is too excited and cannot lie still, it is necessary to give sedation or take appropriate measures.

9. Steps to proceed with circuit malformation of limb
Step 1: Anesthesia methodLet the patient lie on his back on the table, proceed to place an intravenous line.
Usually local anesthesia, general anesthesia is used only in exceptional cases such as young children (under 5 years old) who have not yet had a sense of cooperation or are too afraid to be afraid.
Step 2: Put the tube into the vascular cage
Use the tube to open the way into the lumen regardless of the type of malformation so that the pulse can be taken.
If the access is to an artery or a vein, use a 21G micro-needle set.
Insert the tube into the lumen (luminal tube) 4-5Fr.
Step 3: Angiography to assess the lesion
Using catheters, microcatheters to approach the arteriovenous malformation.
Conduct non-selective and selective angiography to assess the type and hemodynamic status of the malformation.
Step 4: Approach the lesion
Depending on the type of malformation, it can be approached through an artery, a vein or directly into the malformation.
When the center of the malformation is accessible, perform angiography to confirm the malformation and assess the hemodynamic status.
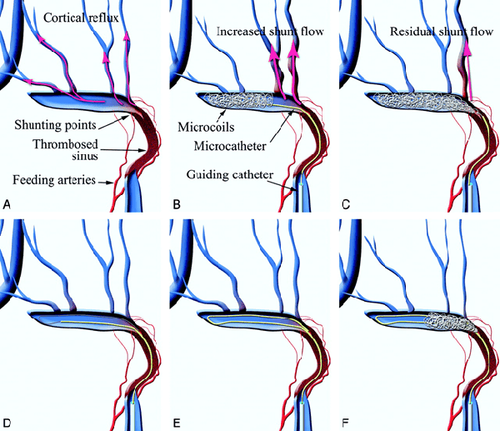
Step 5: Embolization treatment
Embolize the malformed fovea with embolization material.
The plug material will be selected according to the type and the most suitable drive access path.
Step 6: End of treatment
Angiography check after the node, evaluate adjacent and downstream branches. Close the vascular access. Before accepting a job at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, the position of Doctor of Radiology since February 2018, Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh used to work as a resident in the Department of Radiology at other hospitals. Hospitals: Cho Ray, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Oncology, People's Gia Dinh, Trung Vuong... from 2012-2015. Officially worked at Cho Ray Hospital from 2015-2016, City International Hospital from 2016-2018.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
LEARN MORE
Overview of dynamic - venous malformations Dynamic and dural vein malformation surgery Digital imaging of background erasure and cavernosal carotid artery anastomosis