This is an automatically translated article.
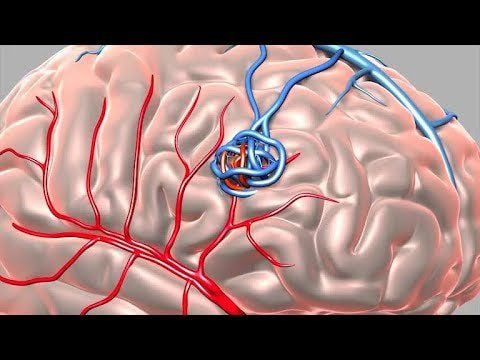
Arteriovenous fistula is a case of arteriovenous fistula. Most dural arteriovenous fistulas have no known cause. In patients with an underlying cause, most occur as a result of microangiogenesis caused by prior dural sinus thrombosis.
1. What is dural arteriovenous fistula?
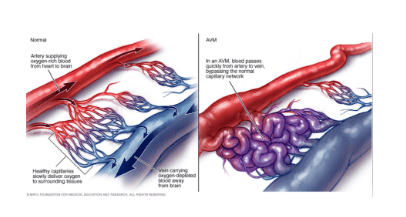
What is dural arteriovenous fistula? In the medical field, dural arteriovenous fistulas are heterogeneous conditions with arteriovenous shunts in the dural vasculature with diverse manifestations such as hemorrhage or venous hypertension. The current treatment is still very difficult.
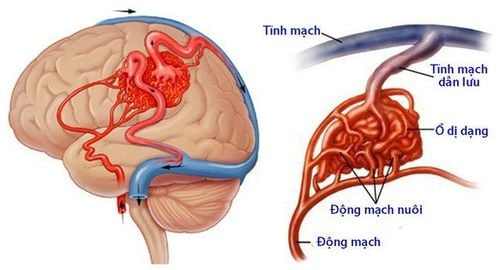
Arteriovenous fistula is a case of arteriovenous fistula. An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection between a vein and an artery. Normally, blood flows from arteries to capillaries and finally to veins. The nutrients and oxygen in the blood from the capillaries go to the tissues. However, with an arteriovenous fistula, blood flows directly from the artery into the vein, bypassing some capillaries, causing less blood to be supplied to the bypassed tissues. Arteriovenous fistulas can develop anywhere in the body.
Complications of dural arteriovenous fistula occur dependent on venous outflow and not on arterial supply. Some dangerous complications are as follows:
Bleeding: Some hemorrhagic complications of dural arteriovenous fistula are subdural hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage or intracranial hemorrhage... Congestive or increased venous pressure, edema Increased intracranial pressure and myelomalacia
Rò động tĩnh mạch màng cứng là một trường hợp của bệnh rò động tĩnh mạch
2. Symptoms of dural arteriovenous fistula
Similar to arteriovenous fistula, the symptoms of dural arteriovenous fistula are varied. In some cases, there will be no symptoms and go undetected until the disease has progressed to an advanced stage. Some of the symptoms of dural arteriovenous fistula may include:
Headache: This is the most common symptom of all types of dural arteriovenous fistulas. Tinnitus: A person with an arteriovenous fistula may hear an unusual buzzing or ringing in the ears. This symptom is more noticeable when an arteriovenous fistula occurs near the ear. Meanwhile, some patients hear a pulse as blood flows through the fistula. Eye symptoms: When the dura arteriovenous fistula is found near the eye, the patient may experience impaired vision, swollen and red eyes, and congested sinuses. Stroke: All types of arteriovenous fistulas, including dural arteriovenous fistulas, can cause symptoms such as stroke or seizures if a blood vessel ruptures. Bleeding in the brain can cause permanent disability or death. Some other symptoms: Cranial nerve paralysis; increased intracranial pressure; Venous hypertension and focal neurological deficit

Đau đầu là triệu chứng điển hình nhất với tất cả các loại bệnh rò động tĩnh mạch màng cứng
3. Causes of dural arteriovenous fistula
Most dural arteriovenous fistulas have no known cause. In patients with an underlying cause, most occur as a result of microangiogenesis caused by prior dural sinus thrombosis. Other causes include: Prior brain trauma and surgery or some patients with unexplained fistulas have asymptomatic thrombosis, especially hereditary prethrombotic conditions such as antithrombin, protein deficiency. C and protein S deficiency are associated with dural arteriovenous fistula.
Superior and paratentorial: Includes middle meningeal artery, superficial temporal artery Anterior skull floor: ethmoid branch of ophthalmic artery Cavernous sinus: pituitary meningeal artery and inferior trunk artery; accessory meningeal artery Posterior skull floor: includes the vertebral, occipital, and ascending pharyngeal arteries
4. Diagnosis and treatment of dural arteriovenous fistula
4.1. Diagnosis of DVT
The following methods are commonly used to diagnose DVT, helping to determine the size, location, and pattern of blood flow. Specifically:
Computed tomography: X-rays are used to create a 3-D image of the brain and identify the site of bleeding or bleeding. For more accurate vascular imaging, cerebral angiography and magnetic resonance imaging are often indicated. Magnetic resonance angiography: This method uses magnetic resonance imaging to create detailed images of blood vessels. The use of a strong magnetic field creates a 3-D image of the brain to detect, diagnose and assist in the treatment of dural arteriovenous fistulas and other vascular disorders. In some cases, dye may be injected into a vein. Cerebral angiogram: This is the most important method for diagnosing dural arteriovenous fistula, because the X-ray will show the structure of the blood vessel. During the procedure, a dye is injected into the artery that supplies blood to the brain to flow in the blood vessel to the brain and will show the site of a blockage or leak in the vein.
Chụp X quang mạch máu não là phương pháp quan trọng nhất để chẩn đoán rò động tĩnh mạch màng cứng
4.2. Treatment of dural arteriovenous fistula
The treatment of dural arteriovenous fistula also depends on the blood vessels involved, the type of fistula, the direct manifestation of symptoms due to the fistula, age and diseases present in the patient. The main treatment methods include:
Advanced treatment such as borden type II and III, Cognard class IIb-V: This method has a patient mortality rate of about 10% per year and a risk of intracranial hemorrhage should be considered during treatment. Conservative treatment such as Borden type I and Cognard types I and IIa Embolization approach: This method reduces blood flow to the fistula by blocking the blood vessels around the site. In this procedure, the fistula is filled with specially designed coils, glue, or spheres that block the blood vessel. Targeted radiosurgery: In some cases, there are some fistulas that will not be completely blocked by embolization, so surgery may be required to separate or close them. In this case, the doctor will close the fistula by Gamma knife method or target radiosurgery. Endovascular: Endovascular technique is a minimally invasive procedure performed through blood vessels. This approach was developed to safely treat dural arteriovenous fistulas. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and treatment of dural arteriovenous fistula at the Hospital.
SEE MORE
Find out about the cerebrospinal fluid test to find the cause of the headache Spinal puncture diagnose meningitis Is lumbar puncture painful and harmful?