This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huy Hoang - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital. Doctor Vu Huy Hoang has 10 years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging.1. What is background scan and intervention of pancreatic vasculature?
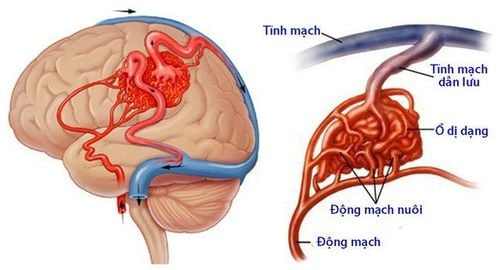
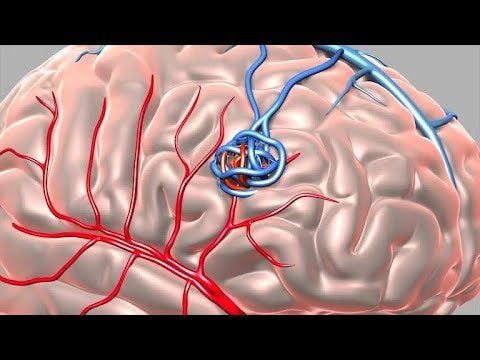
Interventional pancreaticoduodenal artery is mainly embolization techniques, which can be selective or non-selective, common in diseases of gastrointestinal bleeding, biliary tract bleeding, and intra-abdominal bleeding secondary to infection. , trauma, pancreatitis.... This technique is performed by using catheters, ultra-selective microcatheters and arterial branches that cause bleeding, and then embolize with permanent embolization material. .1.1 Indications Pseudoaneurysmolysis after liver and biliary tract infection Pseudoaneurysmal aneurysm after acute pancreatitis, peptic ulcer disease Pseudoaneurysm after interventional procedure: drainage – biliary support bracket placement , percutaneous abdominal drainage, laparoscopic sphincterotomy of Oddi... Closed abdominal trauma with vascular damage causing abdominal bleeding Aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms Arteriovenous malformations At the professional request of treating doctor 1.2 Contraindication Allergy to iodinated contrast agent Severe renal failure (grade IV) Coagulation disorder and loss of control (prothrombin <60%, INR >1.5, platelet count <50 G/l ). Pregnant women The above contraindications are relative
2. What do you need to prepare for a digitized pancreaticoduodenal angiogram and intervention?
2.1 Preparations Executor Specialist Assistant doctor Electro-optical technician Nursing Doctor, anesthesiologist 2.2 Means Digital erasure angiogram (DSA) Specialized electric pump Film, printer film, image storage system Lead vest, apron, X-ray shielding 2.3 Local anesthetics General anesthetics (if anesthesia is indicated) Anticoagulants Neutralizing agents Anticoagulants Photonic Iodine water-soluble antiseptic solution for skin and mucous membranes 2.4 General medical supplies Syringe 1; 3; 5; 10ml Syringe for electric pumps Distilled water or physiological saline Gloves, gowns, caps, surgical masks Aseptic intervention kits Cotton, gauze, surgical adhesive bandages Accidental first aid kit and kit contrast drug.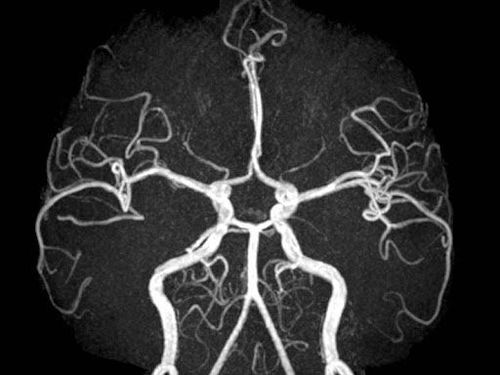
3. Steps to take and intervene in the digitized pancreatic vasculature to erase the background
4. Evaluation of results
Depending on the purpose of therapeutic intervention, there are different judgments:Pseudoaneurysm node: The pseudoaneurysm sac is completely removed from the splenic artery circulation. Circulation behind the pseudoaneurysm was normal. Post-traumatic hemostasis: The bleeding site is completely blocked, no longer draining the drug out of the vessel. The healthy vascular branches are intact and preserved.
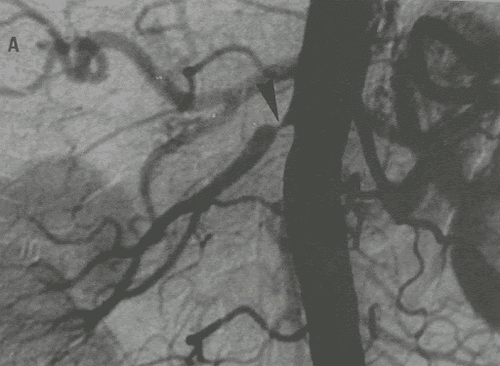
5. Complications and treatment
Hematoma at the site of opening the way into the vessel lumen: Bandage to stop bleeding. In the case of pseudoaneurysm formation at the site of opening of the lumen (common femoral artery), pseudoaneurysm embolizationNecrotizing enterocolitis: Due to occlusion of the arterial branch supplying blood to the intestine. Follow up medical treatment. If the bowel necrosis is extensive, there is a risk of intestinal perforation, surgical consultation.
Contrast allergy: Treat according to antiallergic/shock regimen.
In summary, digitized angiography and pancreaticoduodenal vascular intervention are optimal measures to control bleeding at sites on the pancreatic duodenal artery. The degree of intervention is minimal, the hemostatic effect is high, the occlusion through pancreaticoduodenectomy is good for hemostasis and the patient's hemodynamics will be restored.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
Things to keep in mind when digitizing background deletion angiography Digital background erasing angiography and super-selective adrenal venous blood collection Application of digital background erasure angiography (DSA) in cardiology