This is an automatically translated article.
Arteriovenous malformations of the dura can cause cerebral hemorrhage, lead to death or leave severe sequelae for patients. Among the treatment methods, surgery for arteriovenous malformation is the most commonly applied option today.1. Overview of dural arteriovenous malformation
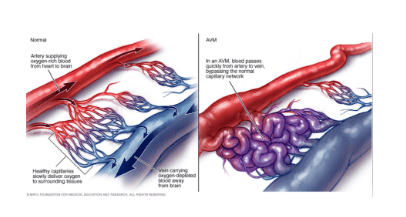
1.1 What is an arteriovenous malformation? Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM) is a group of blood vessels including arteries and veins that are abnormal, messy arrangement, easy to bleed. This condition can occur in any organ of the body. However, if the arteriovenous malformation occurs in the brain, especially the meninges (dural) and spine when bleeding, it can cause dangerous complications. This is because the brain and blood vessels are formed together during embryonic development. If blood vessels develop abnormally, brain tissue will be abnormal. Therefore, AVMs are often associated with surrounding abnormal brain tissue and this is quite advantageous for surgical treatment because it is possible to remove the arteriovenous malformation without damaging normal brain tissue.
The disease is common in young and middle-aged people (20-40 years old). Arteriovenous malformations of the meninges (dural) may be congenital or acquired following head or spinal trauma. In this case, the arteriovenous malformation is called an arteriovenous fistula or an arteriovenous fistula (English name is Arteriovenous Fistula – AVF).
1.2 Symptoms People with arteriovenous malformations are often asymptomatic and are discovered incidentally or during treatment for other conditions. However, approximately 12% of AVM patients have symptoms of varying severity such as: seizures; paralysis or muscle weakness; dizziness , headache ; loss of coordination, difficulty performing complex movements; visual disturbances; unpronounceable; dementia; numbness, tingling, or spontaneous pain; confusion, hallucinations, memory loss,...
Arteriovenous malformations are often diagnosed by a combination of cerebral angiography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Patients can have periodic scans to analyze AVM size change, new bleeding, or new hemorrhagic lesions. If left untreated, the patient can face the risk of an arteriovenous malformation that enlarges and ruptures, leading to cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, death, stroke, or neurological disease.
1.3 Treatment The goal of treatment is to eliminate the damage as best as possible and to minimize the risk of complications. There are 3 methods of treatment of dural dynamic-venous malformation, including: direct ablation by microsurgery, collective radiosurgery and endovascular intervention causing obstruction of the AVM. Usually, microsurgery offers the chance to remove the lesion immediately, but in some cases the best treatment option is a combination of methods.
2.Details of surgical methods of dynamic - dural venous malformation
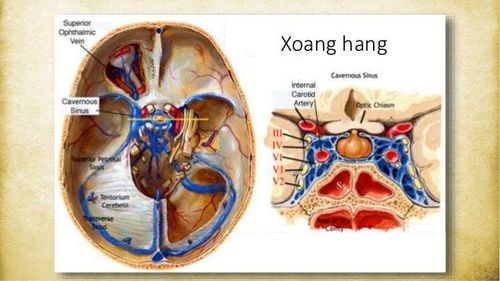
Trường hợp dị dạng động - tĩnh mạch màng cứng xuất hiện ở động mạch cảnh trong - xoang hang
The most common arteriovenous - dural venous malformations by location are: internal carotid artery - cavernous sinus, transverse sinus - sigmoid sinus and superior longitudinal venous sinus. However, the above sites often have indications for vascular intervention. The locations of AVM in surgical indications are the rectus venous sinus, the ethmoid sinus, the transverse sinus - the sigmoid sinus.
Because of the congenital nature of AVMs, in most cases, the brain tissue surrounding the site of the arteriovenous malformation is also abnormal. Therefore, it is possible to excise surrounding and deformed brain tissue with little damage to normal brain tissue. This is the basis of surgery to cut arteriovenous malformations.
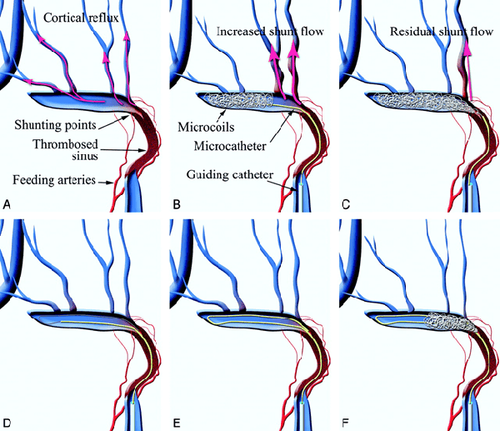
2.1 Indications/Contraindications Apply Borden's classification to guide and predict in the treatment process. Specifically: there are 3 types as follows:
Borden type 1: Dynamic-venous malformation with drainage into the dural venous sinus or into the dural vein; Borden type 2: Has features of type 1 but has retrograde drainage into the cortical vein; Borden type 3: There is drainage into the cortical vein but not into the dural vein or dural venous sinus. Indication
Type 1 dynamic-venous malformation with important venous drainage; Dynamic malformation - transverse sinus - sigmoid sinus type 3; Dynamic - venous malformation of the ethmoid sinus, rectus venous sinus. Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications. Cases that do not prioritize surgery often turn to vascular intervention.
Dynamic-venous malformation type 1 without significant drainage; Arteriovenous malformation type 2 without significant drainage; Arteriovenous - venous malformations at the transverse sinus - sigmoid sinus type 1 and 2. 2.2 Preoperative preparation Personnel: Neurosurgeon and assistant; Facilities: Microsurgical glasses system, intraoperative video and image recording equipment system, craniotomy kits, microsurgery vascular instruments, microsurgery instruments, hemostatic instruments, .. Patient: Wash hair, place urinary catheter, stomach; were clinically examined, cranial magnetic resonance imaging, 64-sequence CT brain angioplasty and cerebral angiography erased the background. Patients must be consulted before performing surgery. The patient's family and patient are also thoroughly explained about the purpose of the procedure, the technical procedures before, during and after surgery, possible complications, etc.
2.3 Surgical procedure
Sử dụng thuốc gây mê theo chỉ định của bác sĩ trước khi phẫu thuật
Patient position: Determine the access route depending on the location of the dynamic-venous malformation: The ethmoid, transverse or rectilinear sinuses will be intervened in different positions. Then put cushions on both sides of the chest and hips, and the patient's legs; Anesthetize 10 minutes before skin incision with a solution of adrenaline 1/1000 and Lidocaine; Anesthesia: Endotracheal anesthesia, using anesthetics, fluids, blood,... as directed by the doctor; Open the skull cap: Incision of the skin, dissection of the fascia, using high-speed drilling to avoid damage to the venous sinus system. With the subfrontal incision, it is necessary to open the skull cap close to the base of the skull anteriorly, exposing the part to be avoided to avoid damage to the involved structures. When sinus damage needs to be treated as indicated. Then open the dura with a small knife size 11; Treatment of dural arteriovenous fistula: Expose to the lesion, use temporary clip to clamp the arterial inlet site with the vein to evaluate the effect after clamping. If the shunt thread is gone, there is no red color at the position after the clip clip, then the clip is changed forever. Next, use bipolair to burn the segment between the 2 clips, severing the arteriovenous bridge; Epidural closure: Use weight or thigh fat if necessary and Bioglue, Tisseel to form adhesion; Reposition of bones: Secure the bones with skull pins; Close the skin and the nasal fascia is loose. 2.4 Post-operative monitoring Closely monitor the patient's vitals such as respiration, pulse, blood pressure, temperature; Use 3rd generation antibiotics 1 week after surgery; Use Inimod antispasmodic for the first 21 days after surgery; Angiography check 1 month after surgery.
2.5 Some complications and how to handle them
Sau phẫu thuật có thể chảy máu não cần xử trí theo tổn thương chảy máu và mổ lấy máu tụ nếu cần thiết
Brain bleeding after surgery: Treat according to bleeding lesions and surgically remove hematoma if necessary; Infection: The treatment is to use antibiotics according to the antibiogram if blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid have bacteria. In case there is no bacteria but there is evidence of bacteria causing infection, use the drug as prescribed by the doctor; Other complications: Cerebral ischemia (due to clamping of the corresponding cerebral branch, hypoplasia of the contralateral artery) or cerebrospinal fluid leak. Treatment measures according to the doctor's prescription. In order to recover quickly after surgery for arteriovenous malformation, and reduce the risk of complications, patients need to strictly follow the instructions of the treating doctor during the procedure.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind to examine and treat raised intracranial pressure at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.