This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Colonic diverticulitis is a fairly common disease, especially after the age of 40. When colonic diverticulitis becomes inflamed without being diagnosed and treated effectively, it can leave many serious complications, easily confused with colonic diverticulitis. colorectal cancer. Therefore, it is necessary to perform annual screening tests to detect diverticulitis in a timely manner.
1. What is diverticulitis?
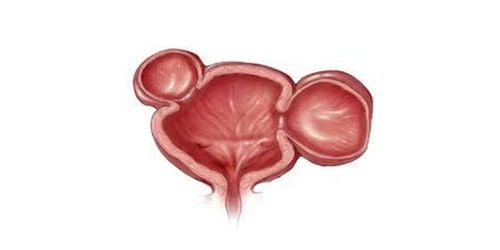
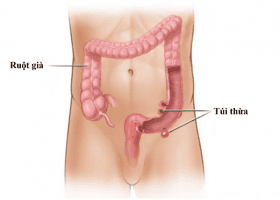
Diverticula are small, bulging pouches that can form anywhere in the digestive tract, from the esophagus to the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. However, diverticula are usually found in the large intestine. When you have a diverticulum in your digestive system, the condition is called diverticulosis.Diverticulosis is very common and occurs in 10% of people over the age of 40 and 50% of people over the age of 60 and if it is 80 years old, the rate goes up to 65%. Recent studies show that the prevalence of colonic diverticulum in obese young adults is increasing.
You may never know they exist in the body because they rarely cause any problems, unless you have diverticulitis or accidentally discovered during a colonoscopy.
Diverticulitis occurs when one or more diverticula of the digestive tract become inflamed or infected. The exact cause of diverticulitis is not fully understood. Some theories suggest that increased pressure in the colon may weaken the wall of the diverticulum, leading to infection. Other theories suggest that the narrow openings of the diverticulum are places for feces to accumulate, which can lead to infection, or that obstruction of the opening of the diverticulum can reduce blood flow, leading to inflammation.
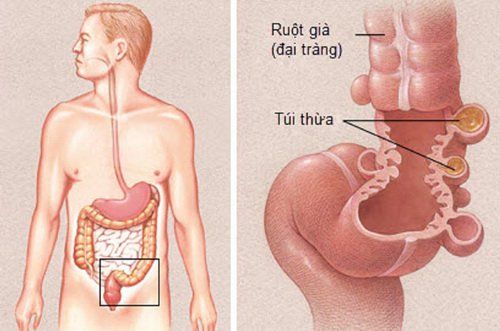
Viêm túi thừa xảy ra khi một hoặc nhiều túi thừa của ống tiêu hóa bị viêm, nhiễm khuẩn
2. Risk factors for diverticulitis
The following factors may increase your risk of diverticulitis :Older age : Your chance of developing diverticulitis increases when you are over 40 years old, this may be due to age-related changes , such as a decrease in intestinal wall firmness and elasticity may contribute to diverticulitis. Eat less fiber: Diverticulitis is common in industrialized countries, such as the United States, where diets are high in refined carbohydrates and low in fiber. Physical activity: Low or limited physical activity is thought to be associated with the risk of diverticulosis. The reasons for this condition are still not well understood. Obesity: increases the risk of diverticulitis and diverticulitis. Smoking: increases your chances of getting diverticulitis.
3. Symptoms of diverticulitis
Diverticulitis can cause mild to severe symptoms. These symptoms may come on suddenly or they may develop gradually over several days.Potential symptoms of colonic diverticulosis. Most people with diverticulosis will never experience any symptoms, only accidentally discovering them during a physical exam for other reasons. However, some patients may have symptoms such as:
Abdominal pain . Change bowel habits. Constipation and diarrhea may also occur, but are less common. There is a small amount of blood in the stool. Bloating. If this diverticulum becomes inflamed, the person will have the following symptoms:
Constant or severe abdominal pain. Urinate more often. Painful urination. Nausea and vomiting. Fever and chills. The patient may pass blood in the stool. Bleeding from the rectum. Abdominal pain is the most common symptom of diverticulitis, usually located in the lower left side of the patient's abdomen. But it can also grow to the right side of the abdomen. If you notice any of the symptoms above, such as vomiting or blood in your stools, it could be a sign of a serious complication from diverticulitis or another medical condition. medical facilities for timely examination and treatment.

Hút thuốc lá sẽ làm tăng nguy cơ viêm túi thừa đại tràng
4. How is diverticulitis diagnosed?
If you are experiencing symptoms of diverticulitis, it is important to see your doctor.Your doctor will ask questions about your medical history (such as bowel habits, symptoms, diet, and current medications) and perform a physical exam, which may include a rectal exam and endoscopy. colonoscopy.
One or more diagnostic tests may be performed. Tests often include blood tests to check for signs of infection, stool tests to check for the presence of blood in the stool or the presence of infection, and CT scans or MRI of the abdomen.
In people with rapid, heavy rectal bleeding, a doctor may perform a procedure called an angiogram to determine the source of the bleeding.
5. Differential diagnosis
Because abdominal pain can be a sign of many different conditions, your doctor will have to differentiate it from other causes of your pain such as:Appendicitis
Pelvic Inflammation
Syndrome irritable bowel
Stomach ulcer
Ectopic pregnancy
Colorectal cancer
Ovarian cancer
Ischemic colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Colonic diverticulum can be mistaken mixed with many other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with similar symptoms. Therefore, it is necessary to detect colonic diverticulitis early by screening tests or by diagnostic tests in the acute inflammatory phase so that the treatment can be more effective.
6. Complications of diverticulitis
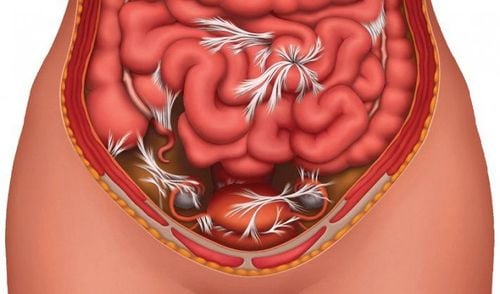
Viêm phúc mạc là một trong những biến chứng của viêm túi thừa đại tràng
Peritonitis: This can occur if the diverticulum becomes severely inflamed or the diverticulum perforated, allowing digestive juices or bowel stools to enter the abdominal cavity. . This can cause severe inflammation of the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). Peritonitis is a surgical emergency and requires immediate hospitalization. Gastrointestinal bleeding. Blockage in the large or small intestine due to scarring. Abscess, which occurs when pus accumulates in the sac. Leakage of nearby organs or an abnormal junction between different parts of the intestine, between the bowel and the bladder or vagina, or between the intestine and the abdominal wall. Although there doesn't appear to be a direct link between diverticular disease and colorectal cancer, diverticulosis can make cancer more difficult to diagnose and sometimes misdiagnosed with colorectal cancer. Therefore, your doctor recommends a colonoscopy check when you have recovered from an episode of diverticulitis.