This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalColonic diverticula are small bulges in the colon wall. These pouches can become inflamed and infected, creating diverticulitis of the colon and endangering the patient if not detected and treated promptly.
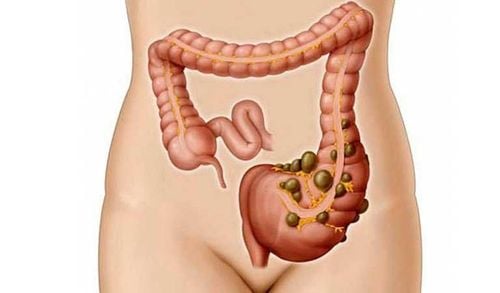
1. What is a colonic diverticulum?
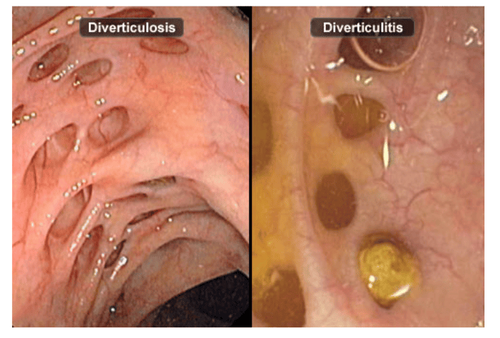
A diverticulum is a pouch-like protrusion of the colon wall. Diverticulosis is defined by the presence of a diverticulum. Diverticulosis may be asymptomatic or symptomatic.
Epidemiology:
The incidence of diverticular disease is age-dependent, less than 20% at age 40 and increasing to 60% at age 60. The distribution of colonic diverticulosis varies geographically:
Western countries and industrialized countries have a prevalence rate of 5-45%. Approximately 65% of patients have a sigmoid diverticulum. 24% of patients with diverticula mainly involve the sigmoid colon, but also other parts of the colon; 7% of patients were evenly distributed throughout the colon and 4% of the diverticulum was confined to a segment proximal to the sigmoid colon. The distribution of diverticula may also vary by race. In Asia, the prevalence of diverticular disease is between 13 and 25%, and diverticulosis is predominantly right-sided. The incidence of diverticular disease has increased both in the Western Hemisphere and in countries that adopt a more Western lifestyle, such as Japan.
2. Symptoms of colon diverticulum disease
Chụp CT scan có thể thấy những ổ mủ viêm tại đại tràng
3. Pathological complications of colonic diverticulum
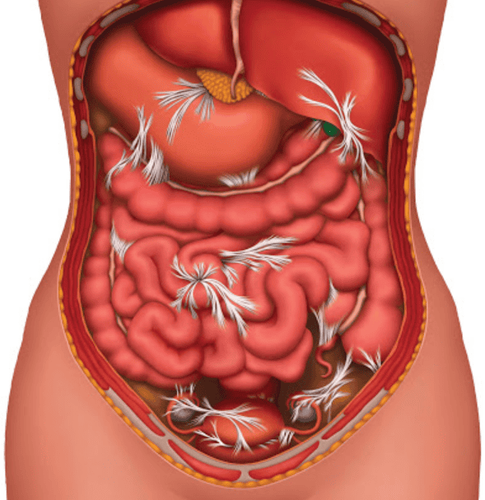
Vi trùng từ đại tràng thoát vào ổ bụng sẽ gây viêm phúc mạc
3.1 Colonic diverticulitis 4% of colonic diverticula have complications of diverticulitis, of which 15% have complications: abscess, obstruction, perforation, fistula. Abdominal pain is the most common symptom, usually pain in the left iliac fossa due to involvement of the sigmoid colon. However, right fossa or suprapubic sigmoid pain may be inflamed or, less commonly, right diverticulum (cecum). The pain is usually constant and usually occurs for several days before diverticulitis develops. Approximately 50% of patients have had one or more previous episodes of similar pain. Nausea and vomiting: encountered in 20-62% of patients due to intestinal obstruction or paralytic ileus due to peritoneal irritation. The patient may also have a low-grade fever. Hemodynamic instability with hypotension and shock is rare, associated with perforation and peritonitis. Acute diverticulitis can cause changes in bowel habits, constipation (50%) and diarrhea (25-35%). Very rare red blood in the stool. Approximately 10-15% of patients with acute diverticulitis present with urinary urgency, frequency, or dysuria due to bladder irritation from the inflamed sigmoid colon. A painful mass may be palpable in about 20% of patients due to pericolitis or diverticulitis. The patient may have focal peritoneal signs. Diverticulitis complications: 15% Abscess - Diverticulitis occurs in approximately 17% of patients hospitalized for acute diverticulitis. Symptoms of diverticulitis are similar to those of acute diverticulitis. Diverticular abscess may be noted on abdominal CT at initial presentation or may develop later. Therefore, a diverticulum abscess should be suspected in patients with uncomplicated diverticulitis who do not improve with persistent abdominal pain or fever despite three days of antibiotic therapy. In rare cases, the patient may develop a pyogenic liver abscess due to the spread of the infection through the portal circulation. Obstruction: Partial obstruction of the colon can occur due to relative narrowing due to diverticulitis or due to compression of the diverticulum by an abscess. Acute diverticulitis can also cause small bowel obstruction if a loop of the small intestine is associated with an inflammatory mass around the colon. Depending on the extent and location of the obstruction, the patient may experience abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distension. Fistula - Inflammation from acute diverticulitis can lead to the formation of a fistula between the colon and adjacent organs. Patients with colonic fistula may experience hematuria, fecal incontinence, or dysuria. Patients with vaginal fistulas may report passing stools or bloating through the vagina. Perforation - perforation causing generalized peritonitis may result from rupture of a diverticulum abscess into the peritoneal cavity or free rupture of an inflamed diverticulum with fecal contamination of the peritoneum. Although only 1-2% of patients with acute diverticulitis experience perforation due to purulent peritonitis or stool, mortality is as high as 20%. Abdominal distention, abdominal wall reaction, peritoneal tenderness, loss of bowel sounds. Diverticular bleeding: accounted for 5 -15% 3.2 Hemorrhage is a complication of colonic diverticulosis that occurs due to rupture of blood vessels in the diverticulum. The stool may be bright red or dark or brown depending on the location of the diverticulum and the flow rate. Hemorrhagic complications often occur in right colonic diverticulum.
3.3 Perforation of the diverticulum is an uncommon situation but the most dangerous complication. When a colonic diverticulum is perforated, bacteria from the colon escape into the abdomen, causing peritonitis or an abscess. The patient needs surgery to resolve.
4. Treatment of colonic diverticulosis
Người bệnh cần kiểm soát stress nhằm giảm co thắt đại tràng
If diverticulitis is mild, the patient only needs to take antibiotics for 7-10 days, to let the intestines rest. The patient has to eat for a few days, using liquid food until the pain is completely gone. In addition, patients can take pain relievers and antispasmodics.
If the patient faces more pain, the condition is more severe, needs to be treated in the hospital, first of all, intravenous fluids, intravenous antibiotics, intravenous analgesia can be given intravenously and followed. Monitor appropriate treatment for diverticulitis.
In cases where the disease often recurs, the patient may have to have the diseased bowel removed.
Bleeding diverticulum: compensate circulating volume. Depending on each case, choose the appropriate treatment method: endoscopic treatment, vascular intervention, surgery.
5. Prevention of diverticular disease
We can completely prevent colon diverticulum disease by increasing fiber in each meal. The fiber found in the brown skins of rice, wheat, cereals and many foods will make stools softer, reducing pressure in the intestinal lumen during digestion. Besides, it is necessary to control stress to reduce colon spasms, limit the risk of colonic diverticulum.Advice from doctors, to prevent and treat diverticulosis effectively, each person needs:
Have a reasonable diet, eat a lot of fiber, vegetables, grains, reduce fat, limit red meat. Avoid foods with a lot of seeds such as regions, strawberries, popcorn, corn, guava... Drink enough 2 liters of water/day. Exercise regularly. Lose weight if overweight. Maintain bowel habits on time, avoid constipation. Quit smoking. Colonic diverticulum can be prevented and treated early to limit the risk of dangerous complications. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and treatment of diverticular disease at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.