When mentioning tuberculosis, many people often think of pulmonary tuberculosis. However, in addition to pulmonary tuberculosis, lymphatic tuberculosis is also a common disease and has many dangerous complications. Let's learn about the complications of lymphatic tuberculosis through the article below.
1. Learn about lymphadenopathy
Lymphatic tuberculosis is common in adolescents, especially children, with the rate of women getting the disease twice as high as that of men.
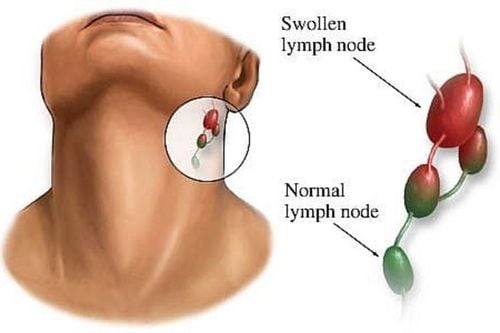
In most cases, lymphatic tuberculosis appears in areas such as the neck, armpits, and groin. In other cases, lymphatic tuberculosis can occur in internal organs, such as mesenteric lymph nodes, mediastinal lymph nodes, etc. The disease is often associated with pulmonary tuberculosis or tuberculosis of neighboring organs.
Lymphatic tuberculosis includes two forms, deep lymphatic tuberculosis and peripheral lymphatic tuberculosis. The main cause of this disease is tuberculosis bacilli entering the body through routes such as trauma, oral mucosa, infection, etc. Lymphatic tuberculosis often appears in the neck, rarely in the groin.
People with lymphatic tuberculosis often have swollen lymph nodes that develop over time. Over time, the lymph nodes swell and become painful, and are uneven in size. In addition, the patient may have a fever in the afternoon, fatigue and rapid weight loss.
Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes is diagnosed by ultrasound, fine needle aspiration, biopsy or sputum, blood and PCR testing of tuberculosis...
2. Is lymphadenopathy dangerous?
“Is lymphadenopathy dangerous?” is a question that many people want to be answered. In fact, this is not a life-threatening disease and can be cured. This is not an infectious disease, so it is necessary to follow the doctor's instructions for thorough treatment, avoiding tuberculosis bacteria from entering other organs of the body.
However, we should not be subjective, because this is a fairly common disease, with a long progression time and often leaves many sequelae, causing difficulties in daily life as well as greatly affecting health. Some patients with severe disease are left with unsightly deformed scars, making them uncomfortable, self-conscious and having many mental problems.
In addition, lymphadenopathy is often accompanied by pulmonary tuberculosis. Pulmonary tuberculosis is very dangerous and can cause death. Therefore, people with lymphadenopathy should not be subjective with this disease.
Another point to note is that whether the disease can be cured or not depends largely on the patient's resistance. Therefore, everyone should actively care for their health to support the treatment to achieve the best results.
3. Possible complications of lymphadenopathy
Although not too dangerous, patients should not be subjective because the complications of lymphadenopathy can cause many negative effects on health. Even complications of lymphadenopathy can cause death if not treated promptly.
Complications of lymphadenopathy that patients may encounter are:
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Prolonged pus leakage;
- Recurrence many times;
- Lymph nodes stick together;
- Lymph nodes compress nerves;
- Lymph nodes spread to other parts.
Not all patients experience complications of lymphadenopathy. However, each patient needs to be aware of coordinating treatment and limiting complications.
4. Effective treatment of lymph node tuberculosis
Treating lymph node tuberculosis is a process that requires coordination between the patient and the doctor. The treatment time can be fast or slow depending on whether the patient is persistent or not. Active treatment of lymph node tuberculosis will help the patient limit the complications of tuberculosis. Currently, lymph node tuberculosis is treated with the following methods:
Internal medicine: Patients need to follow the doctor's instructions. Take the medicine in the correct dose and time and especially do not stop halfway. The duration of internal medicine treatment of lymph node tuberculosis lasts about 8 months. Of which, about 3 months are for attack treatment and then maintenance treatment. Although in the early stages of treatment, the patient may notice that their health is better. However, the patient needs to complete the 8-month course of treatment to achieve the best results and prevent recurrence.
Surgical treatment: The doctor will perform surgery to remove the lymph nodes. However, not all patients can use this method. Usually, cases such as non-suppurative lymphadenopathy and lymphadenopathy with tuberculosis are indicated for surgical treatment. In short, for lymphadenopathy, if there are no complications, the disease can be treated with basic anti-tuberculosis drugs. The most important thing here is the patient's cooperation in treatment. In addition, patients need to improve their resistance by supplementing nutrition and exercising regularly to limit the risk of lymphadenopathy developing and recurring.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.