Article Reviewed by MSc. Vu Quoc Anh, Pediatrician, Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital
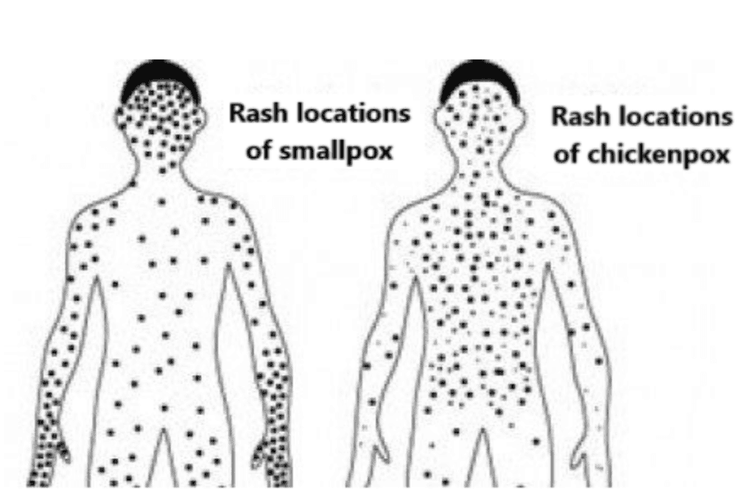
Smallpox and chickenpox are both diseases that present with vesicles and cause skin damage. However, chickenpox rashes tend to appear in clusters on the face, abdomen, and back, with some spreading to the arms, while smallpox lesions primarily concentrate on the hands and feet.
1. Distinguishing between smallpox and chickenpox
1.1 Similarities
Both smallpox and chickenpox cause skin lesions, fever, fatigue, and loss of appetite in affected individuals.
They are highly contagious and can lead to outbreaks.
Prevention for both diseases is only effective if vaccines are administered in advance.
Both carry risks of complications due to secondary infections from foreign viruses during treatment.
Transmission occurs through contact with fluid from skin lesions, clothing, shared linens, and personal items of the infected individual.
1.2 Differences
- Smallpox and chickenpox are caused by different viruses. Chickenpox is caused by the Varicella Zoster virus, while smallpox is caused by the Variola virus.
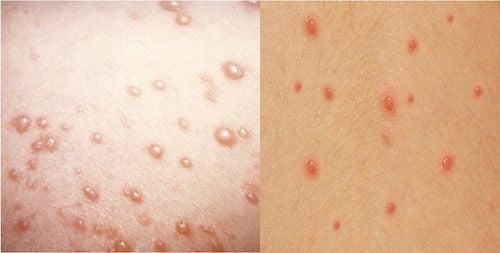
- Smallpox lesions are smaller and contain less fluid compared to the water-filled, easily ruptured vesicles of chickenpox, which can become infected if hygiene is not maintained.
- Smallpox poses a greater threat to life. Variola virus exists in two strains: Variola major, which causes severe smallpox with a mortality rate of 20–50%, and Variola minor, which causes milder smallpox with a mortality rate below 1%. On average, smallpox has a mortality rate of 15–20%. However, according to the WHO, smallpox has been eradicated since 1978 and is no longer a threat.
- The incubation period for chickenpox ranges from 10–21 days, while smallpox has a shorter incubation period of 7–14 days.
- Vaccines for smallpox and chickenpox are different, and the timing and methods of immunization vary.
- Diagnostic methods differ: chickenpox is diagnosed clinically based on symptoms and vesicle testing, while smallpox is confirmed through vesicle fluid analysis and tissue culture studies to detect increased cell counts.
2. Differentiating symptoms of smallpox and chickenpox
2.1 Similarities
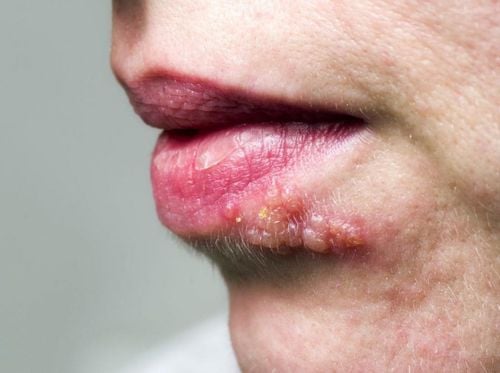
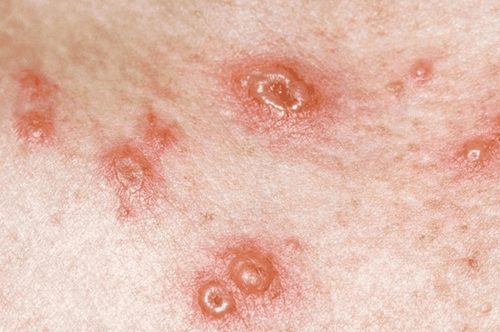
- Both diseases cause pustules or vesicles that result in skin damage lasting 2–4 days. These lesions eventually rupture, dry out, and scab over, potentially leaving dark scars.
- Patients with either disease may experience high fever, fatigue, and headache 1–2 days before other symptoms appear.
2.2 Differences
- Smallpox can cause additional symptoms such as body aches and difficulty moving.
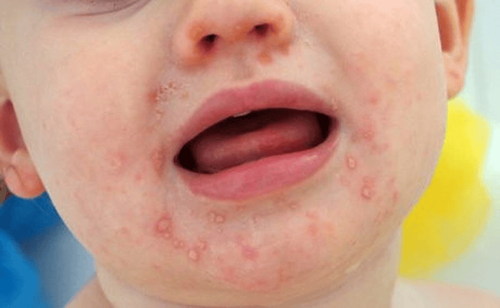
- Chickenpox rashes appear in clusters, predominantly on the face, abdomen, and back, and less frequently on the arms. The rash often begins on the face and chest, then spreads to other areas, including the eyelids, mouth, and genital region.
- Smallpox lesions concentrate more on the hands and feet. Early signs include small spots on the tongue and inside the mouth, which may release a large amount of virus into the throat.
- Chickenpox can reoccur in individuals who have previously contracted it, but immunity is usually complete after recovery. Smallpox, on the other hand, has been eradicated and only exists in national laboratory reserves for research purposes.
To conclude, both chickenpox and smallpox, whether in adults or children, can lead to severe complications. It is crucial to seek medical care at reputable hospitals upon detection of either disease. Self-treatment at home is strongly discouraged, as it can result in infections and worsen the condition, especially in children
For more health, nutrition, and beauty tips, visit Vinmec International General Hospital to safeguard the health of yourself and your loved ones.
To schedule an appointment at the hospital, please contact the HOTLINE or book directly HERE. Download the MyVinmec App to manage, track, and schedule appointments conveniently anytime, anywhere.