This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
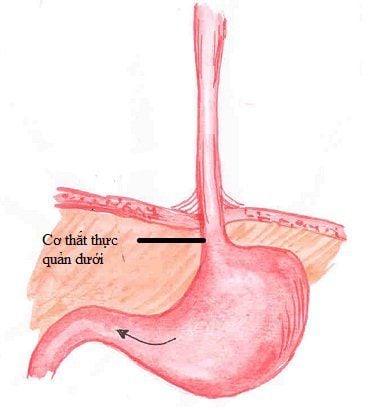
The esophagus is the first part of the digestive tube that carries food from the pharynx to the stomach, about 25cm long, relatively mobile, attached to surrounding organs by loose, flattened structures because the walls are close together. and has a tubular shape when swallowing food. This is an important organ of the digestive system.
Common diseases of the esophagus include:
1. Esophagitis
Esophagitis is inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, the digestive tract that connects the pharynx to the stomach. If left untreated, this condition can cause swallowing problems due to ulcers and scarring of the esophagus such as difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, and chest pain. In some cases, esophagitis can progress to Barrett's esophagus, a risk factor for esophageal cancer.
Esophagitis due to acid reflux from the stomach is the most common cause. There are also other causes of esophagitis, such as radiation therapy, medication, fungal inflammation, or allergies. Esophagitis changes the lining of the esophagus, which increases the risk of cancer. Not to mention long-term chronic esophagitis can lead to complications of ulceration or narrowing of the esophagus, making patients often choke or even unable to swallow dry food.
Common symptoms of esophagitis include: Difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, chest pain, burning chest, ...
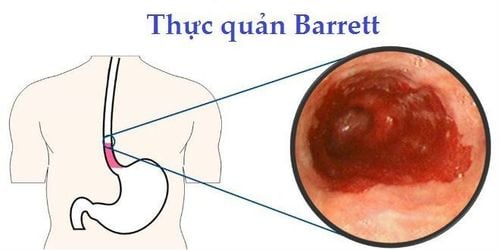
2. Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a lesion in the lower third of the esophagus, named after the doctor who first described it.
The mucosal (epidermal) cells of the esophagus are normally pinkish-white, consisting of squamous epithelial cells. The mucosal cells of Barrett's esophagus are tall, red (pillar cells). These columnar cells are similar to the mucosal cells of the stomach.
Most cases are caused by prolonged reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. This acid irritates the lining of the lower esophagus and causes esophagitis resulting in changes in the cells lining the esophagus as described above.
Barrett's esophagus itself causes no symptoms. However, you often have symptoms of prolonged acid reflux. These symptoms include: Heartburn, pain in the chest behind the breastbone and upper abdomen, nausea, sour mouth, bloating,...
3. Esophageal spasm
Esophageal spasm is a condition in which the smooth muscle of the esophagus relaxes ineffectively, preventing food from moving from the mouth to the stomach.
Classification of esophageal spasms according to location has 2 types: upper esophageal spasm and lower esophageal spasm. Another commonly used classification of esophagitis is diffuse esophageal spasm and local esophageal spasm.
The exact cause of esophageal spasm is currently unknown. Many theories have been put forward, in which damage to the nervous system that governs the functioning of the esophagus, infectious processes or genetic factors are considered to be the cause of the disease.
Symptoms of esophageal spasm are not specific and are quite similar to other diseases of the digestive tract, including: difficulty swallowing, nausea, vomiting, chest pain. Patients need to treat esophageal spasms early before the disease causes serious complications, the most dangerous of which is esophageal cancer.
4. Reflux Esophageal
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, also known as acid reflux, is a condition in which gastric juices flow back up into the esophagus from time to time. Gastroesophageal reflux disease can be physiological, functional (doesn't affect the body's daily life and physical development) or pathology can cause esophagitis, and some other respiratory complications, even dead.
Reflux is caused by the abnormal opening and closing of the lower esophageal sphincter (the muscle at the bottom of the esophagus) that causes stomach acid to back up into the esophagus. Other possible causes include: Gastric hernia or pressure on the stomach such as pregnancy or being overweight.
Common GERD symptoms include:
Always having trouble swallowing or having frequent hiccups Ợ Hot or burning sensation in front of the breastbone, sometimes spreading to the throat Tasting sour taste Sore throat, dry cough.
5. Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant tumors have arisen from the epithelial cells of the esophagus, causing the cells to divide according to the structure of the body, forming tumors.
This is one of the common cancers in the gastrointestinal tract. With different disease manifestations in each stage, esophageal cancer is often difficult to detect in the early stages, often when the disease has progressed, the patient can be detected and treated.
Cancers originating in the esophagus include two main types of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, depending on the type of cancer cell. Currently, science has not clearly determined what causes esophageal cancer, but can name the risk factors that lead to this disease as follows:
Abuse of stimulants such as alcohol, beer and smoking People who are obese, people with esophageal diseases People who have unscientific diets, abuse fats, lack vitamins A, B2, C; maintain the habit of eating a lot of foods containing nitrosamines... Some diseases are the basis for esophageal cancer to develop such as: nasopharyngeal cancer, small bowel disease, plantar keratosis .. Patient has a history of cancer in the head and neck area
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.