This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastroenterologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy.1. Esophageal spasm
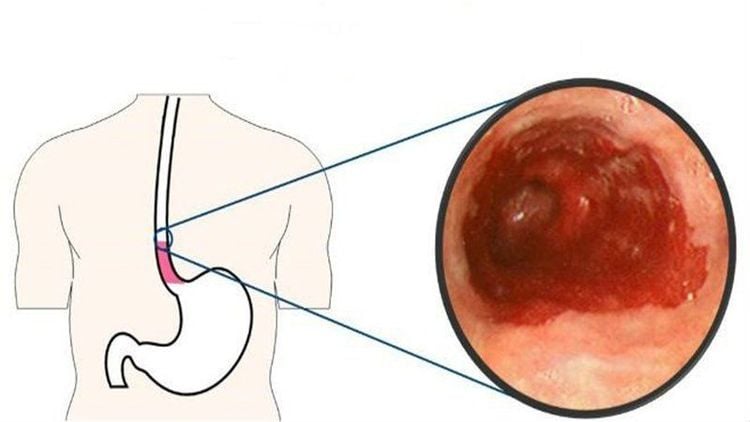
Esophageal spasm is a disease caused by the fact that the lower esophageal sphincter cannot open automatically when performing the swallowing reflex, resulting in the fact that food and saliva secretions cannot move from the esophagus. down to the stomach. In addition, esophageal spasm also causes the loss of esophageal smooth muscle peristalsis. Esophageal spasm is caused by degeneration of the esophageal muscle, especially by the effects of the nerves that supply the esophageal muscles.To explain this situation, some studies have shown that when patients have esophageal spasm leading to esophageal stricture, the body will lose neurons that inhibit Nitric Oxide and neurons that contain Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptides in the esophageal plexus.
2. What are the signs and symptoms of achalasia?
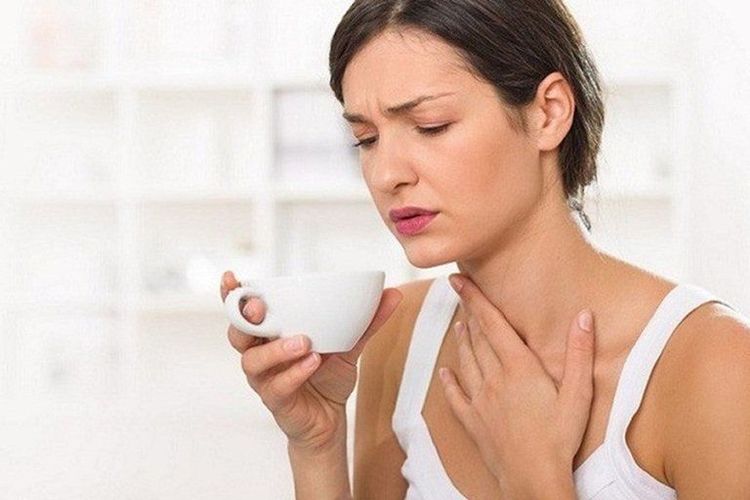
The clinical manifestations of esophageal stricture include:Difficulty swallowing: This is the most characteristic sign of esophageal spasm, present in almost all patients with esophageal stricture. Difficulty swallowing in the first stage often occurs with solid foods, then it will get worse, patients have difficulty swallowing even with liquid foods, patients have a feeling that food is stuck and stuck. The posterior region of the sternum Vomiting: Is a phenomenon that occurs in patients with esophageal stricture after eating, usually occurs in about 60% - 90% of patients, vomiting usually occurs when the patient in a supine position. Reflux: Also one of the common symptoms of patients with esophageal stricture, accounting for about 59% - 81%. Reflux usually does not appear early but occurs in the late stage, after eating, it can even cause the patient to cough, choke on food and have to use the method of gagging to vomit. Chest pain: The location of pain described by the patient is the back of the sternum, which is more painful when swallowing.

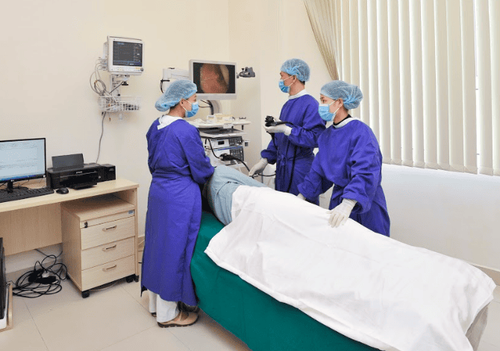
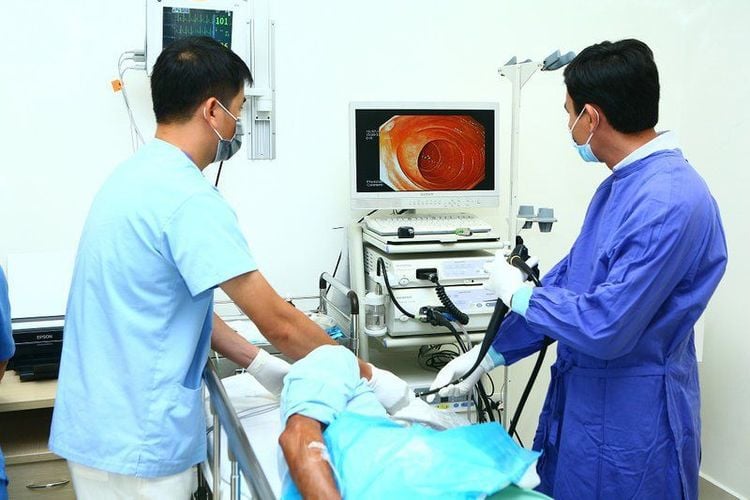
Contrast esophagoscopy by X-ray: This is one of the most basic techniques to screen for esophageal spasm, very effective. Some images can be found in patients with achalasia such as pallor of the limb, loss of esophageal motility, the transport of contrast agent through the esophagus is very slow due to the narrowing of the esophageal cardia... Esophageal X-ray using contrast agent: The purpose of this method is to investigate esophageal spasm, evaluate after treatment with Balloon dilation method. X-ray of the esophagus needs to go through 3 times: 1 minute, 2 minutes and 5 minutes after the patient is drinking Barium with the amount of 100 to 250ml. Esophageal manometry: Is a highly valuable technique in the diagnosis of esophageal spasm. Esophageal endoscopy: It is an effective subclinical in the differential diagnosis of esophageal stricture with pseudospasm of the heart or cardia cancer. In patients with achalasia, there will be esophageal dilatation as well as esophageal torsion.
3. Cardiac spasm treatment
Some methods are applied to treat cardiac spasms as follows:Maintain a suitable diet: Patients need to adhere to eating liquid food, containing enough calories needed for the day, divided into small portions. meals during the day. When eating, the patient should pay attention to perform some movements such as stretching the neck after swallowing as well as breathing heavily to make the food easier to move down to the stomach. In addition, the patient must drink warm water, do not eat a lot of food before going to sleep, do not use alcohol, do not smoke and eat a lot of spicy food... Medication: Some drugs are prescribed. For patients with esophageal spasm, it is a sedative, spasmolytic, a relaxant for the lower esophageal sphincter, protein infusion or blood transfusion in cases where the patient's body falls into a state of exhaustion. Botulinum toxin injection: Botulinum is a toxin found in virulent bacteria, used for injection and the lower esophageal sphincter by endoscopic method to relax this muscle, to treat dysphagia in patients with gastroesophageal stricture. manage.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.