This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital. Doctor has nearly 20 years of experience in the field of gastroenterology - Hepatobiliary tract.Esophageal spasm is a rare disorder of esophageal motility. Patients often have symptoms such as chest pain that is not related to the heart, difficulty swallowing, feeling of food stuck in the throat,... Early examination and treatment have an important role, and treatment methods are very important. Treatment reduces pressure on the esophageal sphincter, helping to improve symptoms and conditions.
1. What is esophageal spasm?
The esophagus is at the beginning of the digestive tract, a hollow tube that runs from the wide neck to the stomach. The esophagus is composed of a very complex longitudinal muscle system - esophageal sphincter, which is influenced by many factors such as the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system, hormone levels,... The most common esophageal disorders are esophageal spasm , achalasia and reflux esophagitis .Esophageal spasm is a motility disorder of the esophagus that causes difficulty swallowing and other problems. This is a rare disease that occurs when nerve cells in the esophagus degenerate, leading to dysfunction of the esophageal muscles and inability to close the lower esophageal sphincter.
Esophageal spasm can occur in both men and women, concentrated in middle age, the rate of women is higher than men. It is estimated that the incidence is about 1 in 100,000 people per year. Esophageal spasm is easily misdiagnosed as other esophageal motility disorders such as esophageal reflux. Early detection of the disease is important because esophageal spasms can increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer .
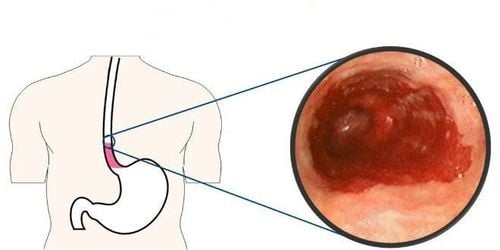
2. Symptoms of esophageal spasm
Symptoms of esophageal spasms include:Non-cardiac chest tightness Difficulty swallowing Choking Gastroesophageal reflux or heartburn Reflux of stomach contents Feeling like food is stuck in the chest and like lumps in the throat Weight loss, malnutrition Esophageal spasms have two forms, namely diffuse esophageal spasm and local esophageal spasm. In diffuse esophageal spasm, the patient experiences continuous contractions in the esophageal muscle, often vomiting food and liquids. For localized esophageal spasm, the patient has local contractions that cause strong pain in the esophagus. Local spasms are less likely to induce vomiting.
3. Esophageal spasm, what to do?
3.1 Diagnostic methods If there are signs of the disease, the patient needs to go to medical facilities for other visits. To diagnose the disease, the doctor will rely on the clinical symptoms and results of tests and imaging tools such as:X-ray of the esophagus: the patient will drink barium, barium-containing liquids will be taken. temporarily covers the lining of the esophagus so that it can be seen on X-ray images. Esophageal manometry: a thin tube is passed through the nose or mouth into the esophagus to evaluate the effectiveness of the esophageal muscles during swallowing. Esophageal pressure is measured inch by inch, the recorded results accurately reflect the working status of the esophageal muscles in each area. Esophageal endoscopy: an endoscope is passed through the mouth and down the throat into the esophagus to look at the inside of the esophagus. Esophageal endoscopy is used to rule out a number of diseases such as invasive esophageal tumors, esophageal fibrosis, esophagitis, etc.
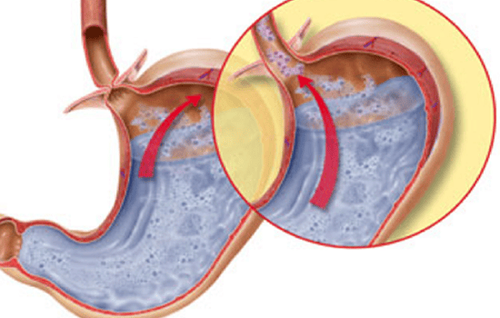
3.2 Methods of treatment
Currently, there is no treatment that can restore esophageal muscle function. Treatments are aimed at reducing pressure on the esophageal sphincter. Musculoskeletal surgery or esophageal dilation are considered the most effective methods. Drug treatments or botox injections may be an option if the patient is unable to undergo surgery or chooses not to have surgery.Myotomy is an invasive procedure in which the muscle fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter are separated. Myotomy is often performed along with fundusectomy to prevent progression of reflux esophagitis. Pneumatic esophageal dilation: air pressure is used to break down the fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter. The complication of the method is the risk of perforation of the esophagus after the procedure, so it is necessary to take barium esophagography after the procedure to ensure that the esophagus is not perforated. The method of esophageal muscle dilation, if done correctly, will be highly effective in treatment, the results will last for many years. Botox injections: injections into the esophagus are done endoscopically. The advantages of the method are few side effects, low risk of complications, and quick patient recovery. However, symptoms often recur and patients have to have multiple injections. Drug treatment: although drug treatment is not effective. But for those who can't have surgery and botox treatment is not effective, can use some drugs that relax the smooth muscle, including the esophageal sphincter, such as calcium channel blockers, nitrate drugs, etc. .. Some other drugs such as tranquilizers, antidepressants,... can be used depending on each case. Surgery to remove the esophagus, or part of the esophagus, is a last resort in severe cases, when other treatments have failed. To improve swallowing, patients should avoid straining during meals. Should eat liquid, soft food, divided into small pieces to make swallowing process easier. Because esophageal spasms increase the risk of developing cancer, patients need to see their doctor regularly to monitor the disease, even if treatment is effective.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.