This is an automatically translated article.
Collagen is a structural protein found in connective tissues throughout the body such as skin, bones, tendons and ligaments. As we age, our bodies make less collagen, and some people try to make up for it by taking collagen supplements.
1. Health benefits
Despite claims that collagen supplements can firm skin, fight age-related damage, promote bone health, and provide other benefits, there are only a few Rigorous independent research has tested the effects of these supplements.
Many of the studies investigating the benefits of collagen supplements have been on a small scale or limited to certain areas. In addition, much of the research is funded by large corporations that supply collagen so could serve to benefit from positive results.
Here are some findings from current studies.
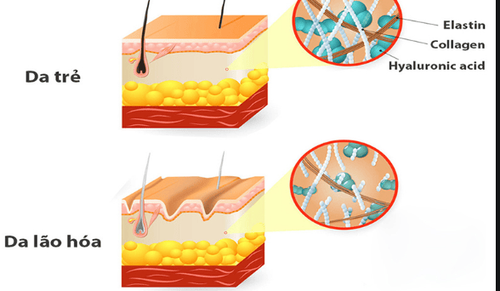
Skin Collagen makes up 75% of the dry weight of the skin. As you age, the inner layer of your skin loses collagen and becomes less supple and more susceptible to damage.
In a 2015 study, scientists evaluated whether supplementation could improve collagen density of skin tissue in a laboratory setting.
Da đã lão hóa
Their results show that the supplements can improve both skin hydration and the collagen network in the skin with the potential to improve signs of skin aging.
In a 2014 study in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, for example, women ages 35 to 55 used a collagen c supplement or a placebo once daily for eight weeks. At the end of the study, those taking collagen had improved skin elasticity compared to those taking a placebo.
Finally, a 2019 review of studies investigating oral collagen supplements evaluated collagen's effects on wound healing and skin aging.
The study authors concluded that collagen supplements are generally safe and can increase skin elasticity, hydration, and density. However, the authors also say that more studies are needed to determine the appropriate dosage and investigate medical applications.
Bone Health Currently, it is not clear whether collagen supplements can improve bone health.
In a 2010 study published in the journal Maturitas, researchers found that collagen supplements failed to improve bone health in postmenopausal women. In this study, 71 women with osteoporosis were assigned to take a hydrolyzed collagen supplement or a placebo every day for 24 weeks. The results showed that the collagen supplements did not produce any effect on bone metabolism.
But a 2018 study published in Nutrients concluded that taking collagen peptides increased bone mineral density in postmenopausal women.

collagen peptide làm tăng mật độ khoáng xương ở phụ nữ sau mãn kinh
Body Composition Some people may take collagen to preserve muscle mass or reduce fat mass. Current studies are still limited and have provided mixed results.
A 2019 study published in Nutrients investigated whether collagen supplementation combined with resistance training could affect body composition in men who regularly exercise. 57 men took part in a 12-week program that combined resistance training with collagen supplements or a placebo pill.
The researchers found that both groups increased muscle size and increased muscle size to the same extent. However, those taking collagen supplements showed a slight increase in fat-free mass, which is believed to be related to improvements in connective tissue.
Another small trial comparing hydrolyzed collagen protein supplements with whey protein supplements in older women. A 2009 study published in the Journal of the American Dietetic Association found that taking hydrolyzed collagen supplements can help maintain lean body mass.
Joint pain Collagen helps stimulate the production of cartilage that covers and protects bones. Cartilage helps joints move smoothly. As we age, collagen and cartilage production decreases. There is some evidence that collagen supplements can reduce joint pain and other symptoms of osteoarthritis.
In 2019, researchers evaluated investigations investigating the impact of collagen supplements on osteoarthritis symptoms. A meta-analysis published in International Orthopedics concluded that collagen was effective in reducing stiffness associated with osteoarthritis, but was less effective in reducing pain and limited joint function.
2. Possible side effects
Bổ sung collagen có thể bị rối loạn tiêu hóa nhẹ
There are some reports that collagen supplements may cause mild gastrointestinal symptoms or affect taste perception in the mouth. Additionally, people with fish, shellfish, or egg allergies should avoid collagen supplements because many collagen products are made with these ingredients.
There is also some concern that stimulating collagen synthesis may also increase oxidative stress and generate reactive oxygen species.
Several collagen products have been recalled by the FDA for false product advertising. According to the FDA, products that stimulate collagen production or remove wrinkles are considered drugs, not supplements. These products must provide evidence of safety and effectiveness. If no evidence (or insufficient evidence) is provided, these products will not be marketed.
Collagen supplements have not been tested for safety and note that the safety of supplements in pregnant women, nursing mothers, children and people with medical conditions or taking medication has not been established. evaluate.
Therefore, to know exactly at what age to take collagen, you need to have a medical examination first and be advised by a doctor whether to use it or not, if so, at what time and in what dosage.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: medicalnewstoday.com, verywellhealth.com












