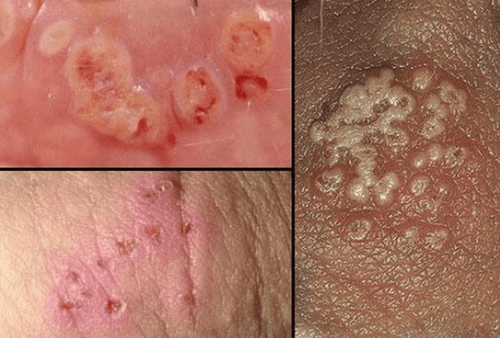
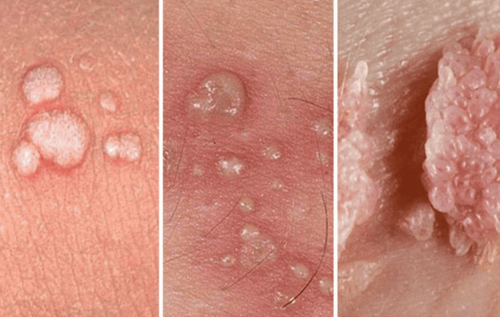
Genital warts are a significant social disease that can spread rapidly if not properly prevented. If left undetected and untreated, this condition can lead to various unpredictable complications. Therefore, understanding the clinical symptoms of genital warts is essential for early detection.
1. What are genital warts?
Genital warts are also known as condyloma acuminatum. This is a social disease, transmitted mainly through unsafe sex that is quite common in today's society. The virus that causes genital warts is Human Papillomavirus (HPV). This virus has about 120 strains, of which 40 strains are agents that cause disease through sexual contact. HPV-16 and HPV-18 are the causes of genital warts in 90% of cases.
Genital warts appear in both men and women, but statistics show that women have a higher incidence of the disease. The reason for this is that women are often exposed to male semen during sexual intercourse, and the vaginal environment can create good conditions for the virus to develop. In addition to transmission through unprotected sex, the disease can also be transmitted by reasons such as mother-to-child transmission or sharing personal items with an infected person.
Genital warts can cause significant discomfort for patients and lead to various unpredictable complications. They often make individuals feel self-conscious and anxious about social interactions, negatively impact their sex lives, and may cause burning sensations during movement, etc. For pregnant women, genital warts pose additional risks, including the possibility of miscarriage, preterm delivery, and stillbirth. Furthermore, there is a risk that the fetus may become ill after birth or contract the infection through breastfeeding. Complications can extend to serious health issues, such as cervical cancer, penile cancer, etc, which can result in infertility, sterility, or even death.
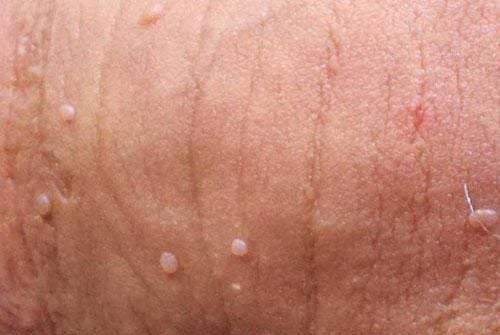
2. Clinical Manifestations of Genital Warts
When the virus enters the body, it remains hidden in the epithelial layer of the skin and does not initially cause symptoms. The incubation period lasts from 2 to 9 months, and the symptoms can vary between men and women. Typically, men experience symptoms of genital warts sooner than women do. In women, the symptoms are often less pronounced and may only be detected once the condition has progressed to a more severe stage. Specifically:
2.1 Symptoms in Men
- First Stage: The genitals and the skin around the foreskin area, as well as the inguinal folds, etc, may appear covered with soft, pale pink, slightly raised single warts. These warts are generally painless and do not cause itching, making them difficult to recognize;
- Later Stage: The warts can grow and cluster together to form patches that may reach several centimeters in diameter. These patches resemble a chicken's comb or cauliflower in appearance and feel soft and slightly moist to the touch. If pressed firmly, the fluid inside the patches may ooze out. In some instances, warts can grow to the size of a fist, may contain blood, and have unpleasant-smelling fluid.
2.2 Symptoms in Women
Due to the complex structure of women's genital organs, genital warts can develop quietly without obvious symptoms. By the time, symptoms become noticeable and a woman decides to see a doctor, the condition has progressed to a later stage.

Typically, about three weeks after having sexual contact with someone who has HPV, a woman may notice light pink warts in her genital area. These warts can have fluid inside and may bleed easily. They can appear on the labia majora, labia minora, vagina, and uterus, often without causing any noticeable symptoms. However, if there is sexual activity or friction, the warts may break, leading to bleeding and possibly an infection.
Genital warts can appear on the genitalia of both males and females, as well as in the mouth, on the tongue, and around the anus. Besides, patients may experience other symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, and pain during sexual activity, etc.
If you experience symptoms of genital warts, it is important to visit a reputable medical facility for an examination, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help prevent serious complications associated with the disease. Additionally, getting the HPV vaccine is a wise decision to lower the risk of contracting genital warts and various other illnesses caused by the HPV virus.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers A basic gynecological examination and screening package designed to help customers detect and treat gynecological diseases early. This package allows for the early identification of inflammatory diseases, making treatment more accessible and affordable. It also includes screening for early detection of gynecological cancers, such as cervical cancer, even in the absence of symptoms.
A basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers is available without age restrictions. It may be recommended for individuals experiencing the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Issues with menstruation, such as unusually long or irregular periods
- Unusual vaginal discharge, characterized by a foul odor or an abnormal color
- Pain or itching in the genital area
Female customers may be at risk due to factors like poor personal hygiene, unsafe sexual practices, a history of abortion, etc.
Additionally, other symptoms, include abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the genital area, and irregular vaginal bleeding.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.