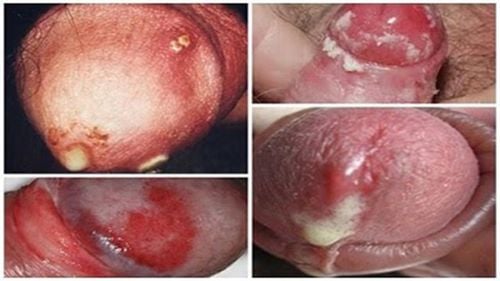
Under normal physiological conditions, there are anatomical differences in the urethra between men and women. The female urethra is shorter than the male urethra, making the symptoms of gonorrhea less pronounced in women. In terms of symptoms, gonorrhea differs between men and women. Due to the longer male urethra, the acute stage of gonorrhea in men is more pronounced, while in women, it is more subtle and easily overlooked.
1. What is gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This bacterium is often found in the vagina, cervix, eyes, mouth, anus, and especially in the urethra of men. Gonorrhea can occur in all individuals and age groups but is most common in men and women of reproductive age.
So, how is gonorrhea transmitted? The gonorrhea bacterium is transmitted from one person to another through unsafe sexual contact, from mother to child during childbirth, and through indirect transmission.
- Sexual transmission: This is the main cause of gonorrhea transmission, with about 90% of cases resulting from unsafe sexual contact. You are at high risk of contracting gonorrhea if you have sexual relations with multiple partners, especially with sex workers, homosexuals, and bisexuals.
- Mother-to-child transmission: A mother with gonorrhea can transmit the infection to her child during vaginal delivery. During labor, the baby passes through the birth canal and comes into contact with the bacteria in the mother's vagina, making it easy to contract the infection.
- Blood transmission: The gonorrhea bacterium exists in the blood of infected individuals. If you receive blood from an infected person or share needles with someone who has gonorrhea, the likelihood of contracting the infection is very high.
- Indirect transmission: The gonorrhea bacterium can be transmitted indirectly, such as through shared personal items or clothing. However, the gonorrhea bacterium is very weak and quickly dies outside the body, so indirect transmission is less common.
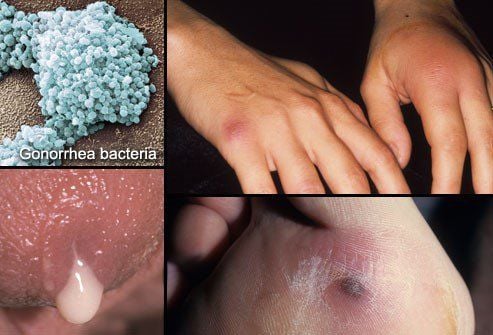
2. How is gonorrhea different in men and women?
In terms of symptoms, gonorrhea differs between men and women. Due to the longer male urethra, the acute stage of gonorrhea in men is more pronounced, while in women, it is more subtle and easily overlooked, making it a concerning source of infection.
2.1. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men
Symptoms of gonorrhea are evident in 90% of men during the early stages. Some symptoms of gonorrhea in men include:
- Pus discharge from the penis, with yellow pus: The more severe the infection, the more pus is discharged.
- Abnormal urination: Frequent urination throughout the day, with a burning and painful sensation during urination.
- Epididymitis: For men who do not initially show symptoms of gonorrhea, the bacteria can spread to surrounding areas such as the scrotum and testicles, causing epididymitis.
- Pain or swelling at the urethral opening due to inflammation; blood in the semen.
- Additionally, gonorrhea in men can cause frequent fatigue, exhaustion, mild fever, swollen groin lymph nodes, loss of appetite, leading to weight loss and imbalance in life.
2.2. Symptoms of gonorrhea in women
Gonorrhea in women differs from men. So how can gonorrhea in women be recognized? In the acute stage, symptoms of gonorrhea in women are subtle and unclear. According to statistics, about 97% of cases have no symptoms, and only 3% have mild, transient symptoms. Some symptoms, if present, are often mistaken for gynecological infections or bladder infections.
Only when the disease progresses to a severe stage do symptoms appear, such as:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge, typically white, with an unpleasant fishy odor.
- Red urethral opening.
- Frequent urination, with a burning and painful sensation during urination.
- Vaginal bleeding outside of the menstrual period.
- Abdominal pain, back pain, pelvic pain, especially pain during sexual intercourse.
- During examination, the cervix may be swollen, red, with pus discharge and bleeding.
- Gonorrhea in women can also cause fever.
3. Prevention of gonorrhea

Complications of gonorrhea in men can include inflammation of the reproductive organs such as the testicles, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles, leading to male infertility. Common complications of gonorrhea in women include anal inflammation, arthritis, meningitis, ectopic pregnancy, and female infertility. Therefore, preventing gonorrhea is crucial to avoid these dangerous complications.
To prevent gonorrhea, both men and women should:
- Use condoms, which are one of the most effective means of preventing gonorrhea, though not completely foolproof.
- Practice safe sex and be faithful to a single partner.
- If not in a long-term monogamous relationship, protect yourself by practicing safe sex as a routine.
- Do not share personal items with others, especially items in hotels, guesthouses, and public bathrooms.
- To prevent mother-to-child transmission of gonorrhea, women should have gynecological health check-ups before pregnancy and before giving birth.
- Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to support the body's health and resistance to bacteria.
- Have a general health check-up at least once a year. For those with a tendency to engage in unsafe sexual practices, regular check-ups every six months are recommended.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently offers a screening package for sexually transmitted diseases for both men and women of all ages, especially those at risk, such as those engaging in unsafe sexual practices, tattooing, or drug injection, patients requiring blood transfusions or blood products, and those in high-risk occupations such as healthcare workers, barbers, and tattoo artists. Individuals with suspected symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases should also seek medical consultation.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.