Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is caused by the Enterovirus. Most cases occur in the summer and early autumn, primarily affecting children under five years old. However, adults can still contract the disease if they have never had HFMD before or if their immune system cannot fight off the virus.
1. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in Adults
The Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus 71 are the primary causes of HFMD, which mainly spreads through the gastrointestinal route.
HFMD is commonly found in young children, especially those under five. However, adults can also get the disease if their immune systems fail to combat the virus.
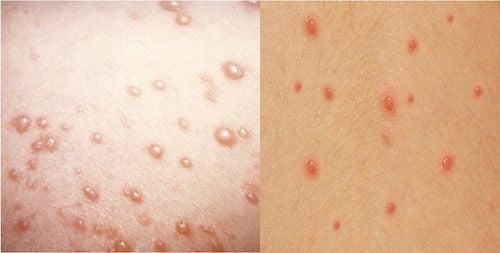
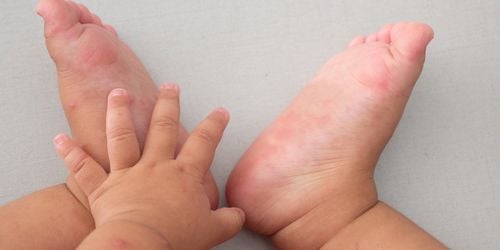
The disease is characterized by fever, clusters of blisters on the palms, soles of the feet, mouth ulcers, and a body-wide rash. In adults, HFMD can lead to more severe complications compared to children and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to HFMD. Contracting HFMD during pregnancy may result in severe complications for the fetus, such as an increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or infections during pregnancy.
2. Warning Signs of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in Adults
HFMD often begins with symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, sore throat, fatigue, or even lethargy.
After having a fever, sores may appear and develop in the mouth, causing the patient to feel pain. These sores are called herpangina, appearing as spots usually located deep in the oral cavity. They can also blister and become even more painful. Along with the sores or some time after they appear, a rash and itching on the palms or soles of the feet may occur. The rash can spread to the arms, legs, buttocks, genitals, abdomen, and back of the patient
Typical symptoms of HFMD in adults include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Fatigue, sometimes lethargy
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Sore throat
- Muscle pain
- Loss of appetite
- Painful blisters on the tongue, gums, and inside the cheeks
- Red rashes on the palms, soles, buttocks, abdomen, or back, though these do not itch
While children often display clear symptoms, adults may experience milder or no symptoms at all.
HFMD is highly contagious across all ages. Maintaining personal hygiene is key to a healthy life, reducing the risk of diseases in general and HFMD in particular.

3. How Does Hand, foot, and mouth disease Spread in Adults?
HFMD is caused by an infectious virus that spreads through nasal and throat secretions, including saliva, mucus, fluids from mouth sores, or feces.
Additionally, the virus can be transmitted through:
- Close personal contact with an infected person
- Inhaling virus-contaminated air from sneezing or coughing
- Touching contaminated objects like toys, tables, chairs, or door handles
- Contacting virus-contaminated water, such as sharing drinks or swimming in the same pool with an infected person
To treat and prevent the spread of HFMD, patients should visit healthcare facilities for appropriate treatment plans, especially children. Any unusual symptoms should be reported to doctors immediately. It is crucial to ensure patients stay hydrated and consume soft, easily digestible foods during illness.
HFMD typically resolves on its own after 7–10 days. There is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment available.
4. Complications of HFMD
Although rare, HFMD can lead to severe complications involving the nervous system, such as meningitis or spinal cord inflammation. Doctors and specialists advise immediate medical attention if HFMD symptoms are suspected.
In recent years, severe HFMD outbreaks worldwide have been linked to a less common strain of Coxsackievirus compared to EV71 or Coxsackievirus A16. This new strain, CV A6, affects both children and adults. First identified in Finland in 2008, CV A6 is associated with lesions around the mouth, palms, and rashes on the abdomen and back.
HFMD is highly contagious and has no specific treatment. The best prevention is maintaining good personal hygiene, particularly frequent handwashing with soap.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.