There is currently no specific treatment or vaccine for HFMD. Therefore, to prevent the disease, it is necessary to closely monitor children, practice proper personal hygiene, and supplement essential nutrients to increase resistance.
1. Overview of HFMD
HFMD is a syndrome caused by an intestinal virus, commonly found in infants and children. If children with HFMD are properly cared for, the disease will quickly recover and will not leave dangerous complications.
Symptoms of HFMD in children include:
- The first typical signs of HFMD in children are mild fever, sore throat, loss of appetite, fatigue, and a rash with blisters. One to two days after the high fever appears, the child begins to have mouth pain.
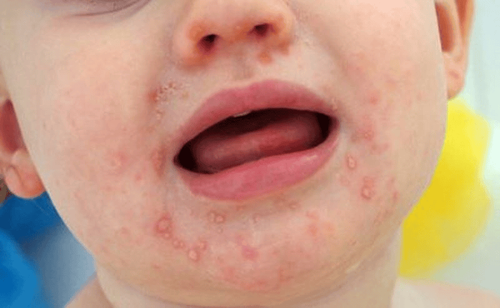
- Examining the child's throat may reveal small red spots that later turn into blisters and often progress to ulcers. These lesions can be seen on the tongue, gums, and inside the cheeks.
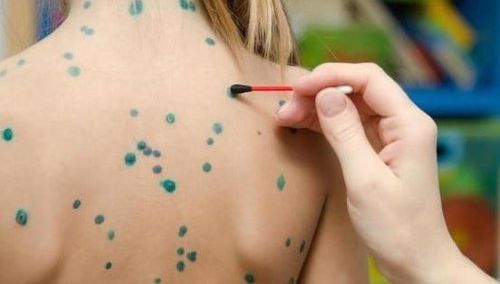
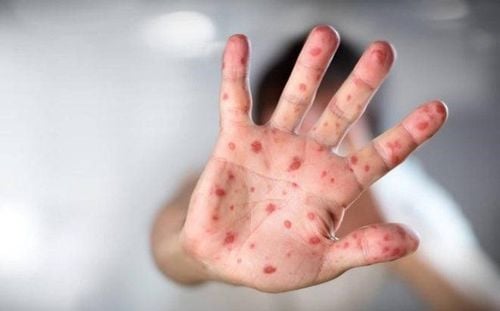
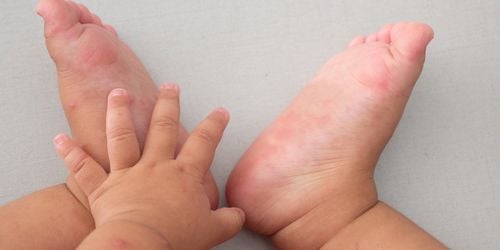
- The rash appears in 1-2 days with flat or raised lesions, red blood, and some blisters. This rash is not itchy and is usually localized on the palms or soles of the feet; the rash often appears on the hands, feet, and mouth, so the disease is called HFMD.
Most cases of HFMD will recover, but some patients, if the cause is type EV71, may have more complicated disease progression because the HFMD virus will damage the central nervous system, showing typical meningitis. Symptoms are high fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, and vomiting.
People of all ages can be infected with the HFMD virus, but not all get sick; the disease only occurs in bodies that do not have immunity against the HFMD virus.

2. Instructions for cleaning and disinfecting clothes for children with HFMD
- When children have HFMD, parents should bathe them in a room with antibacterial soap, not with shower gel because shower gel is not capable of killing bacteria.
- Clean the child's teeth and tongue daily with salt water to avoid secondary infections.
- Do not wrap the child in a blanket; avoid wind and sunlight, which is what parents should do because it will make the disease worse. Some parents are impatient and pop the blisters, which should not be done because they will gradually deflate and disappear.
- Clothes, diapers, towels, etc. of infected children after washing with soap need to be disinfected with boiling water or water mixed with the chemical Cloramin B. Do not wash with clothes of children who are not infected.
- Clean children's toys by soaking them in a disinfectant solution. After soaking in the disinfectant solution for 30 minutes, take them out and rinse them with clean water, then dry them before letting the child play.
- The nutritional regimen for children with HFMD also needs to be noted. Children should be fed soft, liquid foods. Do not feed children solid, spicy, hot foods; supplement children with fresh fruit juice. If the child is breastfeeding, increase the number of times and duration of breastfeeding. If the child has a high fever, give the child more ORS solution and cool the child.
When a child with HFMD has some unusual signs, the child should be quickly taken to a medical facility, preferably a pediatric department, pediatric hospital, or infectious disease examination and treatment facility.

3. What to do to prevent HFMD?
There is currently no specific treatment or vaccine for HFMD. Therefore, to prevent the disease, it is necessary to closely monitor children, practice proper personal hygiene, and supplement essential nutrients to increase resistance.
The HFMD virus spreads very quickly through the digestive tract, secretions from the nose and mouth, and feces of sick children. Therefore, in the classroom, HFMD in children can easily spread to other children. If infected, children should be isolated at home and not go to school for the first 10–14 days.
HFMD virus exists in the child's body for 3-6 days before causing the first symptoms. After recovering from the disease, the virus still exists in the child's respiratory tract for 1-3 weeks and in the feces for several weeks to several months. Therefore, even after recovering from the disease, parents still need to keep their children clean and avoid letting them come into contact with healthy children, making the disease more serious.
Parents must clean their hands before preparing food, before feeding, holding children, after going to the toilet, changing diapers, and cleaning children. At the same time, eat cooked food, drink boiled water, and ensure that eating and drinking utensils are washed clean before use, preferably soaked in boiling water.
Parents should not chew food for children, do not let children eat with their hands, suck their fingers, suck on toys, or pacifiers; cut children's fingernails and toenails clean. Train children to wash their hands with soap under running water many times a day.
Daily bathing and hygiene should use soap because shower gel is not capable of killing bacteria. Parents do not let children share napkins, handkerchiefs, eating and drinking utensils, and toys that have not been disinfected.
Clean the house with disinfectant solutions. Disinfectants that can be used at home are chloramine B and javel water.
In summary, cleaning and disinfecting surfaces, floors, and children's toys is very important. This is one of the measures to help prevent HFMD in children.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.