Article by Dr. Le Tuyet Nga - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital
Chickenpox is an acute infectious disease that can break out into an epidemic. This disease occurs in both adults and children, but children are the main ones and it is highly contagious. In hospitals, the number of chickenpox cases shows signs of increasing with many cases of dangerous complications.
In clinical practice, children with chickenpox and children with hand, foot and mouth disease have many symptoms that are easily confused, so here are some signs that parents can help distinguish the disease.
1. Distinguishing between chickenpox and hand, foot and mouth disease
1.1 Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a group of infectious skin diseases caused by the Varicella Zoster virus. It is recorded that more than 90% of people who have not been vaccinated are at risk of infection. The disease usually appears in the spring in children under 10 years old. However, the disease can also occur in adults, especially pregnant women.
This disease is transmitted quickly, transmitted directly from one person to another. The route of transmission is usually through the air, healthy people will get sick if they come into contact with saliva from chickenpox patients when they sneeze, cough, etc. If not prevented in time, it will become an epidemic.
In addition, chickenpox can be transmitted from burns when they break out or from damaged, ulcerated skin from chickenpox patients. In particular, pregnant women with chickenpox have a very high risk of transmitting the disease to the fetus through the placenta.

Symptoms of chickenpox
The signs of chickenpox are divided into 3 stages:
Incubation period: From 14-17 days (usually no clinical symptoms).
Onset period:
Onset stage: similar to other viral infections, patients have symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, ... In particular, chickenpox in children often has no warning signs of the disease.
About 1 day, there may be no fever or a mild fever, young children often do not want to play, cry. There are cases of high fever of 39-40 degrees Celsius, restlessness, delirium, convulsions, accompanied by sore throat, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, swollen lymph nodes behind the ear, the signs at this stage are easily confused with the common cold, so you should see a doctor as soon as possible, especially during the epidemic season
Full-blown period (rash period):
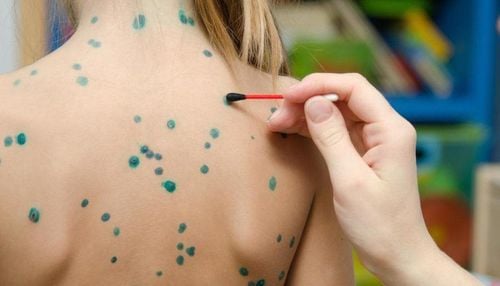
At first, there are red patches, a few hours later they become clear blisters, very shallow as if placed on the skin surface, after 24 to 48 hours they turn yellow, have a spherical shape 2mm above the skin surface. The rash appears scattered all over the body including the hairline and in the mouth.
There are almost no rashes on the soles of the feet or palms of the hands.
The rash appears every 3-4 days, so rashes can be seen on the same area of skin at different ages.
After 4-6 days of the disease, if there are no complications or infections, the blisters will burst, dry, flake off and gradually recover, the chickenpox spots will dry up, form dark brown scabs and fall off after a week.
Chickenpox does not leave permanent scars, unless there are ulcers and secondary infections. After recovering from the disease, the child's body will be immune to the virus strain that causes the disease. Children with chickenpox only get the disease once
Medicine has provided an effective vaccine to prevent chickenpox
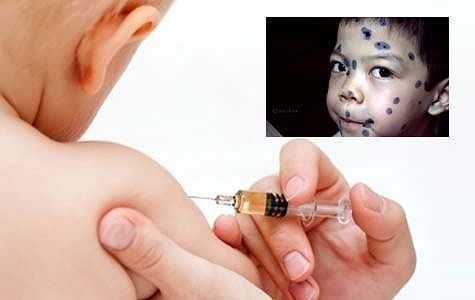
1.2 Hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease is mainly caused by the Enterovirus group of intestinal viruses, most commonly Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus type 71. In which, Coxsackie A16 virus rarely causes neurological complications and can heal on its own within a few days. In contrast, Enterovirus type 71 (EV71) causes many dangerous complications such as encephalitis, meningitis, pneumonia, myocarditis and can lead to death.
In addition to Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus type 71, some other strains of group A viruses such as Coxsackie A4-A7, A9, A10 or Coxsackie group B viruses (B1-B3, and B5) can also cause the disease.
Symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease:
The disease is often characterized by fever, sore throat and rash with blisters.
Incubation period 3 - 6 days.
The onset period begins with easily recognizable symptoms including:
- Children have fever, fatigue, mild fever (37.5-38 degrees Celsius) or high fever (38-39 degrees Celsius).
- Sore throat.
- Lesions, pain in the teeth and mouth.
- Excessive drooling.
- Loss of appetite.
- Diarrhea several times a day.

During the full-blown period (usually starting 1-2 days after the onset of the disease), children begin to show typical symptoms of the disease such as:
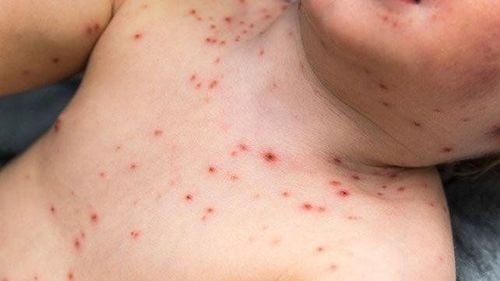
Children have a rash in the form of blisters on the palms, soles, knees, and buttocks. The blisters are 2-10mm in diameter, gray, oval. They can protrude or be hidden under the skin, feel rough to the touch, are not painful, and do not itch.
Mouth ulcers: blisters with a diameter of 2-3mm appear on the mucous membranes of the cheeks, gums, and tongue of children, which are easily broken. When broken, they form ulcers that cause pain when eating and make children cry.
On the buttocks of infants and young children, blisters appear.
Systemic signs: perceptual disorders, delirium, convulsions,
In addition to the typical symptoms above, depending on each individual, hand, foot and mouth disease also appears with additional symptoms such as: Very few blisters alternating with erythema or only erythema. In some cases, the child only has mouth ulcers.
If the disease is mild, after 7-10 days of home care, the child will fully recover. In case the child has a high fever (over 39 degrees Celsius) lasting more than 48 hours with symptoms such as vomiting, trembling hands and feet, convulsions, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, and striped skin, the family needs to take the child to the hospital immediately.
After recovering from the disease, the child's body will be immune to the virus strain that causes the disease. However, according to the results of many studies, children can get hand, foot and mouth disease many times and the next time they get sick is caused by a different virus strain than the previous time.
There is currently no specific vaccine to prevent the disease in Vietnam.
2. What dangerous complications does chickenpox cause?
Chickenpox is considered benign but can still cause serious complications if not treated promptly. Some common complications include:
Blister infection, internal bleeding: this condition is common in chickenpox in children because it is difficult for children to control, causing blisters to burst or peel, leading to infection, pus and ulcers.
- Encephalitis and meningitis: complications that are common in both adults and children. This complication often occurs 7 days after the blisters appear. However, adults are at higher risk of this complication than children. If not treated promptly, it will lead to death.
- Varicella pneumonia: easy to get in adults with symptoms such as coughing a lot, even coughing up blood, chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Perinatal chickenpox: complications in pregnant women. If the mother has chickenpox 2-5 days before or after giving birth, it is very harmful to the fetus. Children can be infected with the disease from their mothers or suffer from disabilities and death.
- Shingles: Although the disease has been cured, the varicella virus still clings to the nerve roots. If the nervous system is weakened, the virus will reactivate and cause shingles
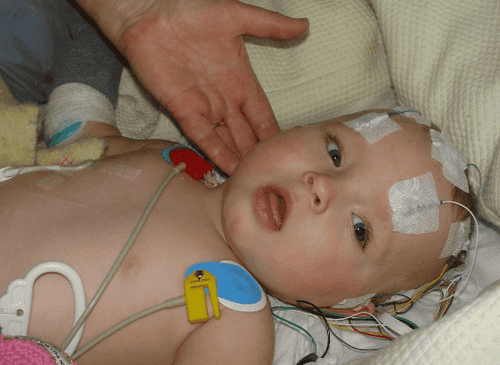
3. How to prevent chickenpox
The following suggestions will help parents take care of their children properly and minimize the risk of complications of the disease as well as help the child recover quickly:
- Children with chickenpox need to be in a negative pressure isolation room to prevent infection to healthy people. After being discharged from the hospital, they still need to be isolated until they are completely cured.
- Caregivers must wear N95 masks (for those who have not had chickenpox) and surgical masks (for those with a history of the disease or who have been vaccinated against chickenpox). When taking your child to a specialist or performing tests, you should also wear a mask for your child. In addition, you need to clean before and after taking care of your child.
- Use methylene blue or castellani solution to apply on blisters or broken burns.
- Absolutely do not let your child scratch, causing blisters and pus to spread to the surrounding skin. You should have your child wear cloth gloves to avoid affecting the blisters.
- Combine antibiotics or antipyretics for chickenpox patients according to the doctor's instructions.
- Clean the nose and throat every day with 0.9% saline.
- Dress your child in soft, sweat-absorbent clothes and especially keep your child's skin clean to prevent unwanted complications. Bathe your child in warm water and change clothes right in the bathroom.
- Feed your child soft, liquid foods that are easy to swallow and digest. In particular, give your child plenty of water or fruit juice.
- Use separate personal items such as towels, cups, spoons, chopsticks, etc.
- Avoid contact with crowded areas to prevent infection.
- Limit exposure to wind because the body is susceptible to colds and makes the disease worse.
Currently, medicine has provided an effective vaccine to prevent chickenpox. In particular, young children need to be vaccinated against chickenpox. Parents with young children need to monitor and vaccinate their children on schedule
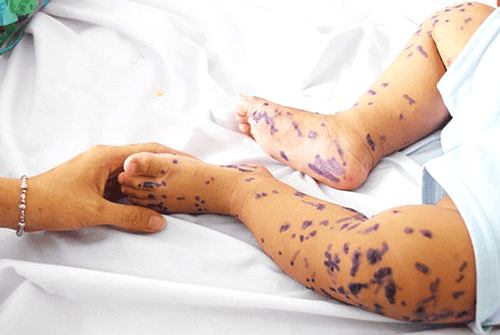
In cases where chickenpox has not been vaccinated but has come into contact with a chickenpox patient, they must be vaccinated within 3 days. Note that they must not share personal items or touch the blisters of a person with chickenpox.
Chickenpox patients must be isolated from family members and the community. The room of a chickenpox patient must be cleaned with a cleaning solution.
Chickenpox in children can be cured if detected early and treated properly. Parents should take good care of their children and themselves to avoid the risk of infection.
Chickenpox vaccination helps prevent the disease effectively. Customers can register for chickenpox vaccination at Vinmec International General Hospital.
Vinmec International General Hospital uses high-quality vaccines with clear origins, suitable for the age of vaccination, ensuring safety from the stage of import, storage to use. Before vaccination, all customers are screened before vaccination by specialists to ensure good health when vaccinated. 100% of vaccinated customers are monitored and re-evaluated for health before leaving. In particular, the Post-Vaccination Monitoring Room is fully equipped with emergency equipment; the team of doctors and nurses are trained in anaphylaxis emergency treatment to ensure timely and correct handling when an incident occurs.
To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.