This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh - Neonatologist - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalNewborn mechanical ventilation is a measure of respiratory support to ensure ventilation for babies with respiratory failure. The goals of mechanically ventilated infants are to optimize oxygen and CO2 exchange, alveolar ventilation, improve blood oxygenation, reduce work of breathing, and good coordination between ventilators and pediatric patients.
1. Overview of mechanical ventilation in neonates
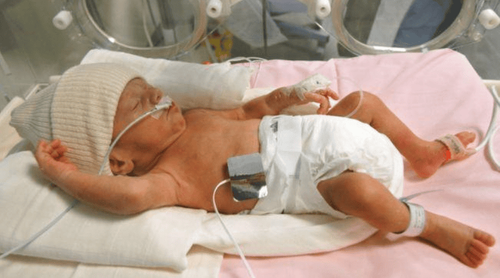
Ventilated neonates are those patients who need complete or partial respiratory support thanks to two common methods of ventilation as follows:Invasive ventilation: Artificial ventilation through the endotracheal tube or open airway management; Non-invasive ventilation: Artificial ventilation through a mask of the nose or nose and mouth. Steps to take for a mechanically ventilated infant include:
Evaluation of the patient; Select ventilator and breathing method; Set initial parameter and alarm level; Adjust ventilator parameters accordingly; Monitoring pediatric patients after mechanical ventilation; Take off the ventilator. Newborns on ventilators are usually reserved for severe illnesses, especially advanced respiratory failure, if the ventilator is left out, there is a risk of rapid death. In addition, pediatric patients also need many infusion machines, electric syringes, nasogastric tubes, etc. to support them, so taking care of a ventilated newborn is very difficult and requires someone with expertise. perform. The main care techniques for mechanically ventilated neonates are:
Intubation or tracheostomy care; Taking care of ventilator masks; Ventilator care; Monitor and detect complications promptly.
2. Indications for mechanical ventilation in infants
The doctor will appoint an infant on invasive mechanical ventilation (intubation, tracheostomy) or non-invasively (ventilation mask) in the following cases:Apnea attacks, ineffective breathing or depressurization Arterial blood CO2 > 50 mmHg; Severe hypoxia, arterial oxygen pressure < 60 mmHg with oxygen, continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP); Shock; Postoperative thoracic or abdominal surgery in the first hours; Hyperventilation reduces cerebral edema in pediatric patients with increased intracranial pressure. Usually, when emergency intubation is needed, it should be placed through the mouth because it is faster and the technique is relatively easy compared to the nasal passage. For children under 6 years of age, there is no need for an endotracheal tube with a balloon. The size and depth of the endotracheal tube length were estimated according to the age and body of each child.
If there is a rare complication of stenosis after one month of endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy is required. However, indications for tracheostomy in neonates with long-term mechanical ventilation are still controversial. Timing of tracheostomy is usually only set after 7-10 days of mechanical ventilation. The advantage of this method is that it is easy to care for, easy to aspirate sputum, and reduce dead space. The disadvantage is that you have to use a plastic endotracheal tube with a balloon to avoid air escape. In addition, advances in care techniques now also make it easier to aspirate sputum through the endotracheal tube.

3. Caring for a ventilated newborn
3.1. Endotracheal or tracheostomy care The goal of care for an invasively ventilated neonate is an endotracheal or tracheostomy that is clear, secures the tubing in the correct position, and prevents infection. Techniques include:Ventilation of airways by flapping technique, suction of sputum; Perform endotracheal tube dressing change, tracheostomy in the correct procedure, in the right position and ensure cleanliness, to avoid infection; Check the cuff pressure of the endotracheal tube, open the trachea. 3.2. Care of respirator mask The size of the mask must fit the patient's face; Do not fix the mask too tightly to avoid causing ulcers on the bridge of the nose or too loose, causing air to leak out, leading to a decrease in airway pressure; Fix the top mask around the head over the ears, the bottom around the back of the neck; The device can be turned off when the patient coughs; Remove the non-invasive ventilator while nursing to avoid causing aspiration and water into the lungs. Newborns on ventilators may be uncomfortable due to unwanted effects such as abdominal distension, suffocation...
3.3. Nutrition Newborns who start mechanical ventilation are usually fed intravenously, the nutritional composition requires lipids and should not be provided with all the energy by Glucose to limit the increase of CO2.
When the baby is stable about 24 hours after mechanical ventilation, it is possible to:
Feed partially intravenously or through a nasogastric tube; Nutrition milk with powder 10% yeast treatment or Enalac 25% depending on age; Divide meals into small, slow drips over 1-2 hours. 3.4. Infection prevention Techniques to prevent infection by mechanical ventilation in neonates include:
Position the baby with the head elevated 30°; Observance of the basic rules for the prevention of hospital-acquired infections; Disinfect ventilators and change ventilator wires according to the correct procedure; Ensure sterility when aspirating sputum and performing procedures; Dental hygiene for children; Respiratory and exercise physiotherapy; Turn every 2 hours; Timely weaning off the ventilator, soon switching to non-invasive breathing.

Hospitals that can perform the kangaroo method combined with mechanical ventilation must meet the following criteria:
Properly assess the child's health status; Care skills to coordinate neonatal resuscitation and kangaroo care of medical staff; Complete and modern medical equipment. Neonatal mechanical ventilation is an emergency for infants with postpartum respiratory failure, requiring prompt implementation and proper care. In order to limit the case of mechanically ventilated infants, the mother needs to monitor and manage the pregnancy well to detect and promptly treat if there is a risk of premature birth. At the same time, medical staff in the delivery room and operating room must also be trained to improve neonatal resuscitation skills, reduce the risk of death, enhance health and comprehensive development for children.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. Besides domestic specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. upon reaching adulthood. Advanced techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - craniofacial surgery, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.