Malaria patients need to be carefully cared for, especially in their diet. In addition to rest and good care, nutrition also plays a very important role in protecting and improving their health, helping patients recover more quickly
1. How dangerous is malaria?
Malaria is one of the most common infectious diseases and a very serious problem for public health. The disease is caused by the Plasmodium parasite, which is transmitted from person to person when these people are bitten by mosquitoes.
Everyone can be infected with malaria. Immunity to malaria is incomplete and short-lived, so people can be reinfected immediately. There is no cross-immunity, so a person can be infected with two or three other types of malaria parasites at the same time.
With proper treatment and care, people with malaria can usually recover completely. However, severe malaria can progress extremely rapidly and cause death within hours or days. For most severe cases, special care and treatment are required to avoid dangerous complications.
Malaria in children causes blood loss and direct brain damage and is at risk of neurological and cognitive impairment, behavioral disorders, and epilepsy.
2. Caring for malaria patients
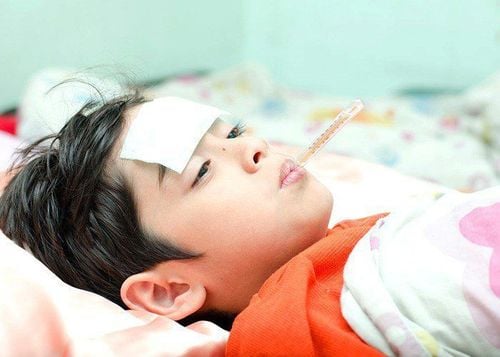
People with malaria often have typical symptoms such as high fever, chills, sweating, and diarrhea. Therefore, patient care must be based on these symptoms.
- Avoid letting mosquitoes continue to bite the patient: The most basic thing in caring for malaria patients is to avoid mosquitoes from biting the patient to limit the spread of the disease to the community.
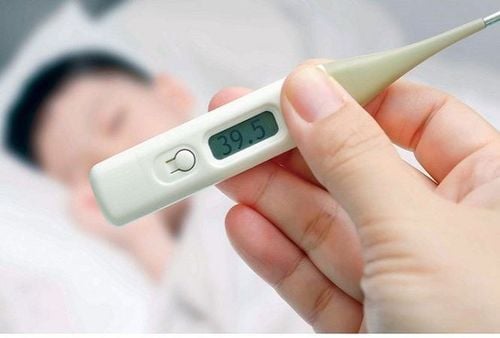
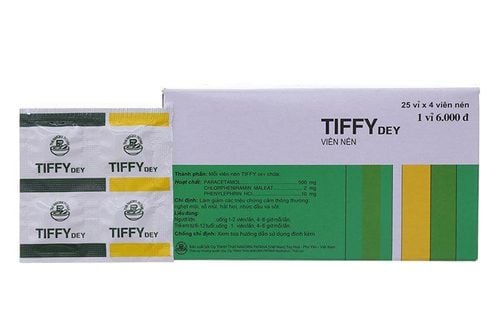
- Reduce fever: When the temperature is above 39 degrees Celsius, the patient is easily agitated, restless, delirious, vomiting, etc. Children have convulsions. Therefore, fever should be reduced by measures such as loosening clothes, lying in a cool place, wiping the body with a warm towel... When the fever is too high, above 40 degrees Celsius, paracetamol can be used to reduce the fever.
- Preventing anemia: When the fever is persistent, especially in pregnant women and children. Anemia in malaria patients (usually due to a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin) due to red blood cell rupture, iron metabolism disorders, and malnutrition.
- Therefore, when having malaria, it is necessary to supplement iron, increase vitamins, especially vitamin A, and drugs containing Zn (zinc, which helps metabolize iron) and folic acid. When the patient is severely anemic, a blood transfusion is needed.
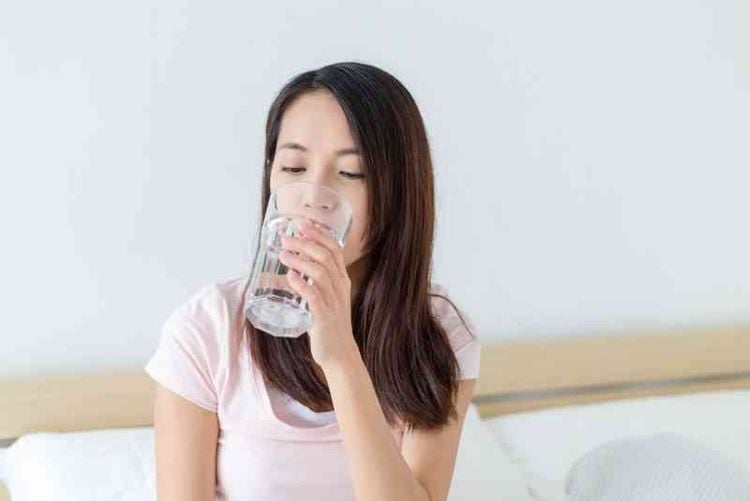

- Avoid dehydration: People with malaria often have high fever, excess sweat, and especially diarrhea, so it is necessary to replenish enough water during treatment and care for the patient. Water also helps to eliminate toxins in the body more easily and quickly. You can replace filtered water with boiled water mixed with Hydrite or Oresol to replenish electrolytes.
- Rest during treatment: During the recovery process, the patient needs to rest more than ever, and not be active, because the drugs used to treat malaria cause various side effects.
- Hygiene: The patient needs to clean their teeth, body, bed, and pillow regularly; and wear cool clothes.
- Accommodation: The patient's accommodation needs to be clean; the room is airy, ensuring full air circulation.
3. Nutrition for malaria patients
3.1. What should malaria patients eat?
Nutrition also plays a very important role in protecting and improving the health of malaria patients, helping them recover more quickly so as not to harm other organs such as the kidneys, liver, or digestive system. So what should be eaten when people have malaria? Accordingly, patients should eat according to the following regimen:
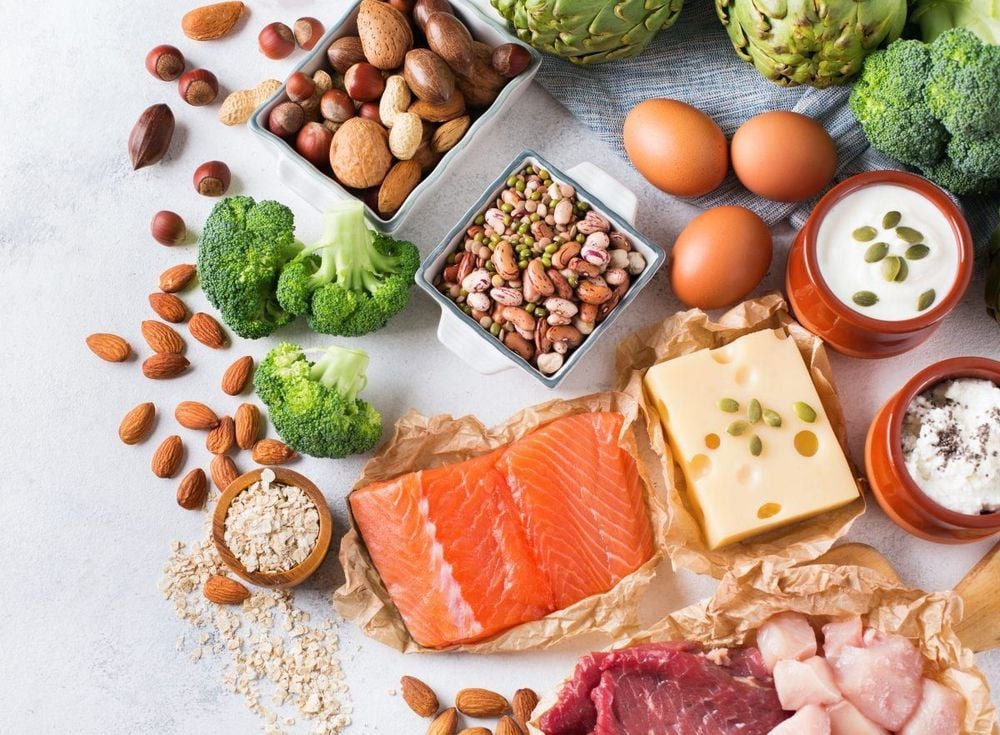
- Nutritious foods: When having malaria, the immune system will be weakened, so a nutritious diet will help patients have good resistance against bacteria. Foods to eat include: green vegetables (tomatoes, Malabar spinach, water spinach, mustard greens, amaranth, etc., boiled or cooked in soup); seaweed (regulates the intestines and promotes red blood cell production); taro, sweet potatoes, etc. (contains a large amount of vitamin C, helps absorb minerals, and promotes red blood cell production); and seafood (rich in iron and vitamins B12, A, C, helps keep blood and liver healthy).
- Increase protein: foods rich in protein include milk and dairy products, apples, avocados, nuts (cashews, almonds, walnuts, etc.), and meat (poultry, beef).
- Supplement vitamin C: When having malaria, patients should eat fruits such as oranges, tangerines, grapefruits, etc. because they contain huge amounts of vitamin C, help increase resistance, and replenish water for the body.
Eat liquid and soft foods: Soup, pho, liquid, and soft foods that are easy to swallow should be cooked with chicken, pork, or beef to help patients supplement nutrition for the body and limit discomfort.

3.2. What should not be eaten when having malaria?
When having malaria, patients should limit:
- Eating too much fat: Using too much fat will increase the risk of nausea, indigestion, and loose stools.
- Chicken eggs: Eggs increase body temperature, so people with malaria should not eat them.
- Alcoholic beverages, tea, caffeine, and cold water: These products are harmful to the liver, leading to a weakened immune system.
- Drinking cold water causes sore throats.
- Spicy, hot foods: Spices and spicy foods increase body heat, so people with fever should limit spicy foods.
To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.