This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Currently, the applications of artificial intelligence have a lot of potential in the medical field. In addition to artificial intelligence-based applications, such as disease data processing, imaging, and pathological image recognition, robotic surgery has revolutionized surgical procedures.
1. Difficulties of pancreatic cancer treatment
Pancreatic cancer is a complex cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, the prognosis is very poor, the 5-year survival rate is less than 1%. Although there are systematic treatment plans, the effectiveness of radiation therapy is poor because of the deep location of the pancreas and the tissue characteristics of the cancer. The special nature of pancreatic cancer also leads to drug resistance after chemotherapy, which makes surgical treatment difficult due to the large number of vital organs surrounding the pancreas and the complexity of its interpretation. surgery. However, the application of artificial intelligence has the ability to replace or assist humans in the clinical diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn biết gì về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy?
Ung thư tuyến tụy phổ biến thứ 10 trong những bệnh ung thư mới và là nguyên nhân thứ 4 gây tử vong do ung thư ở nam, nữ. Bài trắc nghiệm này sẽ kiểm tra kiến thức của bạn về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và cách điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy.
Bài viết tham khảo nguồn: medicalnewstoday 2019
2. The 5-year survival rate of pancreatic cancer treatment is still very low
Pancreatic cancer of high malignancy. Although curable with radical resection, the 5-year survival rate is still very low. One study used population models and machine learning algorithms to predict recurrence risk in pancreatic cancer patients 2 years after surgical resection. After collecting the features considered to have the most influence on iteration, the most representative feature variables were selected, which were then used to train the machine learning algorithm. On repeated training, logistic regression was found to be the best predictive algorithm after cross-validation.
This model has high accuracy in predicting recurrence probability for a patient 2 years after surgery, suggesting that machine learning algorithms can be useful for identifying high-risk patients and developing develop adjuvant treatment strategies. However, the sample size of that study was small and there was no uniform standard for treatment. Therefore, this machine learning algorithm can be improved in future research by using larger samples and uniform processing.
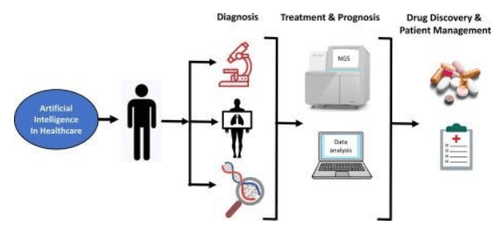
3. Application of artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer prognosis
3.1. Overview and advantages of pancreatic cancer and artificial intelligence Artificial intelligence applications in healthcare have made great progress in recent years. Artificial intelligence can avoid the influence of subjective thinking; deal with large volumes of data; aid in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Therefore, the application of medical artificial intelligence is a topic of considerable interest. Artificial intelligence is also widely used in the field of pancreatic cancer. Applications include diagnosing cancer by processing image data and using machine learning to accurately distinguish cancer subtypes. Robotic surgery is also widely applied to compensate for the shortcomings of traditional laparoscopic surgery.

3.3. “Machine learning” algorithms can also be used to develop prognostic classifiers Machine learning can also be used to develop prognostic classifiers to predict cancer patient survival pancreas, by integrating multiple DNA methylation states of the mucin gene involved in pancreatic cancer. As a non-parametric machine learning method, ANN is also used to assess survival rates of pancreatic cancer patients. Similar to the working mode of the brain, the patient's variables are collected as processing factors, these factors are related to each other arranged and connected layer by layer. Each connection has an associated weight, each weight value can be passed to the next node layer, each lower layer can aggregate the input values of the upper layer, and the final layer is the output value. Output values are generally binary and can be used to determine if a patient has survived 7 months.
3.4. The malignancy of pancreatic cancer is closely related to the invasiveness of its tumor cells. Mathematical model of tumor progression as a physiological and biomechanical model as personalization of the model according to the clinical measurements of the target patient. The volume of the entire tumor can be predicted, including its size, shape, and area involved.
4. New prospects
It has excellent application prospects for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. In terms of molecular diagnostics, imaging, and chemotherapy, machine learning can help researchers process data, perform analysis, and obtain experimental results. In radiation therapy, artificial intelligence is mainly used to automatically plan radiation targets and predict radiation doses. The development of robotic pancreatic surgery has increased the accuracy of pancreatic surgery and reduced complications, but automation cannot be fully achieved without constant training and verification. Therefore, for a long time in the future, most applications of artificial intelligence for pancreatic cancer will continue to be used as practical auxiliary tools.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been implementing cancer screening packages. At Vinmec, there are fully modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI..., blood marrow test, histopathology, immunohistochemistry test, gene test, lab test molecular biology, as well as a full range of targeted drugs, the most advanced immunotherapy drugs in cancer treatment. Multimodal cancer treatment from surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy in cancer treatment, new treatments such as autoimmunotherapy body, heat therapy...
Thanks to modern facilities, a team of qualified doctors and medical staff, perfect medical services have brought confidence, health and good quality of life to patients. medical examination and treatment at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:
1. Adamska A, Domenichini A, Falasca M. Pancreatic carcinoma: Current and developing therapies. Int J Mol Sci . Year 2017; 18 : 1338. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ]
2. Halbrook CJ, Lyssiotis CA. Using metabolism to improve diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer cell . Year 2017; 31 : 5-19. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ]
3.Ngiam KY, Khor IW. Big data and machine learning algorithms for healthcare delivery. Lancet Oncol . Year 2019; 20 : e262-e273. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ]
4. Bi WL, Hosny A, Schabath MB, Giger ML, Birkbak NJ, Mehrtash A, Allison T, Arnaout O, Abbosh C, Dunn IF, Mak RH, Tamimi RM, Tempany CM, Swanton C , Hoffmann U, Schwartz LH, Gillies RJ , Huang RY, Aerts HJWL. Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J Clin . Year 2019; 69 : 127-157. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ]