This is an automatically translated article.
Pancreatic cancer begins in the tissues of the body's pancreas. Pancreatic cancer is difficult to detect in the early stages, while if detected early at this stage, it can be cured. This article will provide information on the diagnosis and early detection signs of pancreatic cancer.
1. Pancreatic cancer
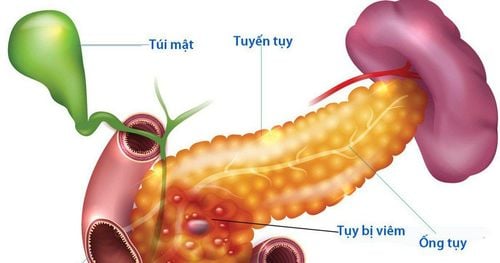
1.1. Pancreatic cancer concept Pancreatic cancer occurs when cancer cells start in the tissues of the pancreas - an organ located deep in the back of the stomach. The pancreas is responsible for releasing enzymes that aid in digestion and producing the hormone insulin that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
When pancreatic cells proliferate, they form tumors. These tumors can be benign or malignant (also known as cancerous) if they tend to spread to other tissues and organs of the body through the bloodstream.
Pancreatic cancer is difficult to detect in the early stages because they often leave no symptoms or symptoms are often unclear, making the patient mistaken for some other health problem. The methods applied to treat pancreatic cancer such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or combined chemotherapy and radiation... depend on the extent and stage of the cancer.
1.2. Symptoms of pancreatic cancer

When cancer cells grow and metastasize to other organs, they can cause a number of symptoms such as:
Abdominal pain, pain may spread to the back Loss of appetite, loss of appetite, loss of appetite weight for no specific reason. Jaundice, yellow eyes Light colored stools Dark urine Itching, skin allergies Patients diagnosed with diabetes are also at risk of pancreatic cancer because the tumor causes the pancreas not to produce enough insulin hormone to regulate blood sugar. Constantly feeling tired, restless, anxious Occurrence of abnormal blood clots. 1.3. Causes of Pancreatic Cancer Currently, experts and scientists are still not able to find the main cause of pancreatic cancer, but several factors can increase the risk of this type of cancer including smoking. leaves and certain genetic mutations.
Before understanding the factors that increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, it is necessary to understand the structure and function of the pancreas. The pancreas is about 15cm long and is shaped like a pear lying on its side. They secrete several hormones including insulin that help the body balance blood sugar levels as well as digest food and absorb nutrients.
Factors that can increase the risk of pancreatic cancer include:
Smoking Diabetes Chronic pancreatitis can lead to mutations in pancreatic cells Family history of certain syndromes Genetic conditions that increase the risk of cancer such as BRCA2 gene mutations, Lynch syndrome, and atypical melanoma syndrome. Family history of pancreatic cancer Obese people Elderly people have also been shown to have a higher risk of pancreatic cancer A highly reliable study has shown that a combination of 3 factors Medications, diabetes, and an unhealthy diet spike the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn biết gì về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy?
Ung thư tuyến tụy phổ biến thứ 10 trong những bệnh ung thư mới và là nguyên nhân thứ 4 gây tử vong do ung thư ở nam, nữ. Bài trắc nghiệm này sẽ kiểm tra kiến thức của bạn về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và cách điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy.
Bài viết tham khảo nguồn: medicalnewstoday 2019
2. Diagnosis and early detection of pancreatic cancer
2.1. Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer Pancreatic cancer often goes undetected until it has progressed and spread to other organs. The longer the duration of pancreatic cancer, the more obvious the symptoms of the disease and the easier it is to diagnose.
The diagnosis of pancreatic cancer usually occurs when patients come to the doctor with one of the symptoms such as abdominal pain, weight loss, itching or jaundice. Patients will be asked to provide information about the time of onset of symptoms, history of smoking, diabetes or family history of pancreatic cancer. On physical examination, the doctor may detect a small tumor in the abdomen and swollen lymph nodes around that area.
Based on the initial diagnosis, the doctor will order a number of imaging tests including:
Computed tomography : A method that uses a scanner to project X-rays from different angles to the body. to obtain detailed images of the inside of the abdomen. A CT scan can make it easier for doctors to diagnose pancreatic cancer. Magnetic resonance imaging: Using ultrasound waves and a scanner to create detailed images of the abdomen, especially the area around the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. Ultrasound: This technique uses a transducer that emits high-frequency sound waves and captures the reflected waves to display images of the abdominal organs to diagnose pancreatic cancer. However, today, when imaging techniques show that a tumor appears in the pancreas, it is still not possible to diagnose whether it is pancreatic cancer or not. Final conclusions can only be made after conducting a biopsy, taking tissue from the tumor itself for testing. Biopsies can be performed in several ways:
Percutaneous needle biopsy: With the help of an X-ray, the technician inserts a thin, sterile needle into the tumor site to drain fluid and other organs. cells from there. Retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A flexible endoscope with a camera on the tip is passed through the mouth near the pancreas to collect images from it or perform a biopsy of the tumor. Laparoscopy: Instead of being passed through the mouth, the laparoscope is passed through a small incision in the patient's abdomen to collect tissue from the tumor for biopsies and to determine if cancer cells have been removed. metastasized to other organs around it yet. However, laparoscopy is rarely indicated because of the higher risk associated with other biopsy methods.
>> See more: Molecular biology test in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer – Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
2.2. Early detection of pancreatic cancer Like many other cancers, pancreatic cancer is often difficult to treat successfully if not detected early. Methods for early detection of pancreatic cancer that are still being studied for effectiveness include:
Blood tests: Certain substances such as carcinoembryonic antigens and CA 19-9 are increased in people with pancreatic cancer. . However, blood tests are also difficult to detect cancer early because when the concentration of these substances increases, it also means that the cancer has entered the metastatic stage. Endoscopic ultrasound: The American Cancer Society recently concluded that up to 10% of pancreatic cancer cases are due to changes in DNA structure of genetic origin. Researchers are considering the application of endoscopic ultrasound to screen and detect pancreatic cancer early for even healthy members of families with a history of pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic cancer is a disease that is becoming more and more common, especially in men over 45 years old. Pancreatic cancer tends to progress silently, leaving few symptoms in the early stages, so it is classified as one of the most dangerous types of cancer. Currently, there are many studies being conducted to find out methods to help diagnose pancreatic cancer early to increase the possibility of treatment such as blood tests or endoscopic ultrasound, but the effectiveness of these methods is generally not. achieve expectations.
If you have a family history of pancreatic cancer, talk to your doctor for advice on the necessary screening tests. Periodic general health examination, combined with medical history declaration, not only helps to screen the risk of pancreatic cancer, but also detects other diseases early for timely treatment.
Early cancer screening is considered a perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce the cost of treatment and especially reduce the mortality rate in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers a HIGH-TECH CANCER CHECKLIST PACKAGE to help with gene testing, imaging, and biomarkers for early tumor detection. Vinmec International General Hospital has many packages of early cancer screening.
With facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience. At Vinmec, the examination process becomes fast with accurate results, saving costs and time for patients.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Source: webmd.com & mayoclinic.org