This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Currently, the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning has been applied to non-invasively identify pancreatic cancer cell types, including revealing the subtypes and molecular characteristics of pancreatic cancer. .
1. Application of artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer radiotherapy
It takes a long time to precisely localize the target area of pancreatic cancer in radiation therapy. A recent study used machine learning to target unlabeled pancreatic cancer. A deep learning neural network consists of the following steps: Input of a complete X-ray image is acquired by a vehicle camera, then the image is processed by a computer, and finally changes are simulated between the model and the model. target and normal tissue.Trắc nghiệm: Bạn biết gì về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy?
Ung thư tuyến tụy phổ biến thứ 10 trong những bệnh ung thư mới và là nguyên nhân thứ 4 gây tử vong do ung thư ở nam, nữ. Bài trắc nghiệm này sẽ kiểm tra kiến thức của bạn về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và cách điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy.
Bài viết tham khảo nguồn: medicalnewstoday 2019
2. Model accuracy was re-evaluated through a retrospective study of pancreatic cancer
The output is the location of the verified plan target in the projected image. Goal planning can also be conducted by mimicking the human brain through artificial intelligence. This application of artificial intelligence is based on abdominal magnetic resonance (MR) -ART for automatic contour rendering in two steps. The first step is to compare the patient's MR image with the normal MR image. Due to the high MR resolution, it can roughly outline the object. In the second step, information is obtained directly from the pixel data through a supervised, adaptive, action-based support vector machine that learns and outlines from the pixel features. The information obtained through these two steps is then integrated by artificial intelligence, leading to the final result. This approach can obtain data science institute values greater than 0.86.
3. An artificial neural network model can be used to determine the appropriate dosage
Because the pancreas is located deep in the abdomen, radiation therapy requires not only accurate positioning, but also an appropriate dose. A medical application of artificial intelligence can be used to determine the appropriate dosage. The data is processed by the input, hidden layer and output, continuously weighted. After training, the errors are understood and the weight distribution of the hidden layer is adjusted. Inputs in artificial neural network data mining are geometrical planning parameters [including CT images, treatment plans, structures, and dose distributions calculated by the treatment planning system]. management (TPS)]. A single output was a dose prediction in TPS for the voxel.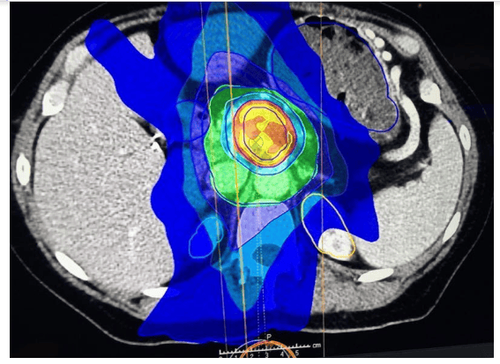
4. Artificial intelligence application in pancreatic cancer chemotherapy
Different subtypes of pancreatic cancer cells are sensitive to different chemotherapy regimens. The best way to identify cell subtypes is to diagnose through pathology. However, entering the pathology will inevitably cause some pain for the patient. Due to the heterogeneity and cystic structure of pancreatic cancerous tumors, the results of a puncture are often not ideal, and sometimes even give false-negative results.Thus, an application of artificial intelligence is machine learning has been applied to non-invasive pancreatic cancer cell type identification, including revealing the subtypes and molecular characteristics of the cancer pancreas. Using machine learning, pancreatic cancer-associated protein expression, mRNA transcription, DNA methylation, and miRNA were integrated. Pancreatic cancer is divided into two types. The identified subtypes have a clear response to the respective drug therapy and can therefore guide chemotherapy.
5. Radiographic analysis combined with machine learning models can produce highly sensitive and specific discrimination
In a retrospective observational cohort study with histopathological subtypes, after clinical and imaging data collection of patients, images were classified by double-blind method. After image processing, feature extraction, feature preprocessing, feature engineering and machine learning modeling, 70% of the queues were used for training and 30% of the queues were tested. This study shows that radiographic analysis combined with machine learning modeling can produce highly sensitive, highly specific discrimination between two molecular pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDAC) subtypes identified determined by the model.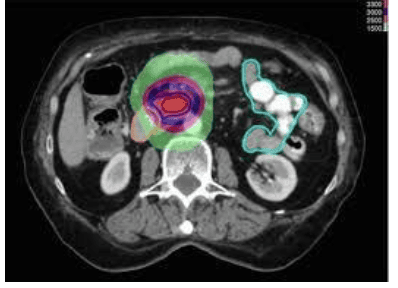
6. Radiometric characterization through machine learning can predict subtypes of PDAC
The analysis of radioactivity characteristics through machine learning can predict subtypes of PDAC. This has a lot to do with the response to chemotherapy and the patient's ability to survive. Artificial intelligence can also simulate the effects of tumor-targeting drugs on tumor-targeting genes. By combining machine learning, pharmacology, and metabolism, the effectiveness of targeted drugs does not depend solely on the status of individual genes. It is also related to the quantitative extent of the Wahlberg effect, which leads to the emergence of an in vivo therapeutic window.7. Application of artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer surgery
The first reports of laparoscopic pancreatectomy were published in the early 1990s and the first laparoscopic pancreatectomy was reported in 1994. Laparoscopic tail body surgery (LDP) is feasible and safe. Compared with open distal resection, laparoscopic tail-pancreatectomy has the advantages of less bleeding, shorter hospital stay, lower postoperative complication rate and short-term cancer efficacy. Laparoscopic tail-pancreatectomy is also increasingly being used for patients with high BMI, history of abdominal surgery, complications, and large tumors. Compared with open surgery for pancreatic cancer, laparoscopic surgery also has some limitations, such as two-dimensional surgical field of view, limited range of motion, fulcrum effect, and increased tremor of the agents. . However, robotic-assisted pancreatic cancer surgery (RDP) can make minimally invasive surgery more effective, while maintaining the advantages of laparoscopic surgery (less trauma, quick postoperative recovery and less bleeding).
8. Can robotic-assisted pancreatic cancer surgery optimize laparoscopic surgery without increasing side effects?
The question is whether robotic-assisted pancreatic cancer surgery can optimize laparoscopic surgery without increasing side effects. Several studies have found that robotic-assisted surgery is as safe and feasible as laparoscopic DP. Intraoperative blood loss, hospital stay, postoperative mortality and complication rates as well as postoperative pancreatic fistula rates in robot-assisted surgery were similar to laparoscopic tail-body surgery. Compared with open distal resection, the probability of pancreatic fistula in robot-assisted surgery was not increased and the probability of surgical complications, recurrence rate, mortality rate as well as hospital admission date were similar.Robotic-assisted distal total body resection and total body resection are comparable to traditional surgery in terms of safety as well as almost all outcome indicators. Robotic-assisted surgery is relatively safe, but compared with traditional surgery and laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery, it improves the rate of splenic vessel preservation and reduces the risk of switching to open surgery.
9. Advantages of robotic surgery
The Da Vinci robotic surgery system has unique characteristics that reflect the main advantages of laparoscopic surgery. There is a stable 3D view, wrist-like motion of the effects tool (seven degrees of freedom), no fulcrum, no shaking, and no scaling of the tool movement.10. Some limitations of robotic surgery
Although robot-assisted distal resection has potential benefits in preserving the spleen, the cost of robotic surgery is very high, which is one of the obstacles to its widespread use. it. Surgical robots also lack tactile sensory feedback and have a higher learning curve. Studies have shown that it takes up to 80 cases for a primary surgeon to become skilled, and laparoscopic surgery experience can shorten this process. In some complex cases, robotic surgery performs better than traditional laparoscopic surgery, such as spleen-conserving surgery with preservation of splenic vessels. For example, for patients with a high BMI, robotic surgery can reduce intraoperative blood loss and shorten hospital stays.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferencesAdamska A, Domenichini A, Falasca M. Pancreatic carcinoma: Current and developing therapies. Int J Mol Sci . Year 2017; 18 : 1338. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ] Halbrook CJ , Lyssiotis CA. Using metabolism to improve diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer cell . Year 2017; 31 : 5-19. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ]