Mai Vien Phuong
Master, Medical Doctor,
Written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
When people think of the most dangerous diseases in the world, they immediately think of incurable, quick-acting diseases. But in fact, many of these diseases are not in the top 10 causes of death worldwide. An estimated 56.4 million people died worldwide in 2015, and 68% of them were due to slow-progressing diseases.
Perhaps even more surprising is that some of the most dangerous diseases are partly preventable. Unpreventable factors include where a person lives, access to preventive care, and the quality of health care. All of these factors contribute to risk. But there are still steps people can take to reduce their risk. Read on to see the top 10 diseases that cause the most deaths worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
1. Ischemic heart disease, or coronary artery disease
The world's deadliest disease is coronary artery disease (CAD). Also known as ischemic heart disease, CAD occurs when the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart become narrowed. Untreated CAD can lead to chest pain, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
The impact of CAD is worldwide. Although it is the leading cause of death, mortality rates have decreased in many European countries and in the United States. This may be due to public health education, access to health care, and better forms of prevention. However, in many developing countries, mortality rates from CAD are increasing. Increased life expectancy, socioeconomic changes, and lifestyle risk factors play a role in this increase.
Risk factors for CAD include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Family history of CAD
- Diabetes
- Being overweight
Talk to your doctor if you have one or more of these risk factors. You can prevent CAD with medication and by maintaining good heart health. Some steps you can take to reduce your risk include:
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a balanced diet low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables
- Avoid smoking
- Drink only in moderation
2. Stroke
A stroke occurs when an artery in the brain becomes blocked or leaks. This causes brain cells that are deprived of oxygen to begin dying within minutes. During a stroke, you may experience sudden numbness and confusion or difficulty walking and seeing. If left untreated, a stroke can cause long-term disability. Risk factors for stroke include:
- High blood pressure
- A family history of stroke
- Smoking, especially when combined with birth control pills
- Being African American
Being female
Some stroke risk factors can be reduced with preventive care, medications, and lifestyle changes. In general, healthy habits can reduce your risk.

3. Lower respiratory tract infection
A lower respiratory tract infection is an infection in the airways and lungs. It can be caused by:
- Influenza, or the flu
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Tuberculosis
Viruses commonly cause lower respiratory tract infections. They can also be caused by bacteria. Coughing is the main symptom of a lower respiratory tract infection. You may experience difficulty breathing, wheezing, and a tight feeling in your chest. Untreated lower respiratory tract infections can lead to respiratory failure and death.
Risk factors for lower respiratory tract infections include:
- Influenza
- Poor air quality or frequent exposure to lung irritants
- Smoking
- A weakened immune system
- Crowded child care facilities, which primarily affect infants
- Asthma
- HIV
One of the best preventive measures you can take against lower respiratory tract infections is to get a flu shot every year. Wash your hands often with soap and water to avoid spreading germs, especially before touching your face and before eating. Stay home and rest until you feel better if you have a respiratory infection, as rest helps promote healing.
4. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a long-term, progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are types of COPD. In 2004, about 64 million people worldwide were living with COPD. Risk factors for COPD include:
- Smoking or secondhand smoke
- Lung irritants such as chemical fumes
- Family history, with the AATD gene linked to COPD
- History of respiratory infections as a child
There is no cure for COPD, but the progression of the disease can be slowed with medication. The best way to prevent COPD is to stop smoking and avoid secondhand smoke and other lung irritants. If you experience any symptoms of COPD, getting treatment as soon as possible will improve your outlook.
5. Trachea, Bronchial, and Lung Cancer
Respiratory cancers include cancers of the trachea, larynx, bronchi, and lungs. The main causes are smoking, inhalation of secondhand smoke, and environmental toxins. But household pollution such as fuels and mold also contributes.
A 2015 study reported that respiratory cancers account for about 4 million deaths each year. In developing countries, researchers predict that the rate of respiratory cancers will increase by 81 to 100 percent due to pollution and smoking. Many Asian countries, especially India, still use coal for cooking. Emissions from solid fuels account for 17 percent of lung cancer deaths in men and 22 percent in women.
Trachea, bronchial, and lung cancers can affect anyone, but they are more likely to affect people with a history of smoking or tobacco use. Other risk factors for these cancers include family history and exposure to environmental factors, such as diesel fumes.
Other than avoiding smoke and tobacco products, it is not known what else can be done to prevent lung cancer. However, early detection can improve outcomes and reduce symptoms of respiratory cancers.
6. Diabetes
Diabetes is a group of diseases that affect the production and use of insulin. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas cannot produce insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the insulin cannot be used effectively. Type 2 diabetes can be caused by a number of factors, including poor diet, lack of exercise, and being overweight.
People in low- to middle-income countries are more likely to die from complications of diabetes. Risk factors for diabetes include:
- Excess body weight
- High blood pressure
- Older age
- Not exercising regularly
- Unhealthy diet
Although diabetes is not always preventable, you can control the severity of your symptoms by exercising regularly and maintaining a good diet. Adding more fiber to your diet can help control your blood sugar levels.
7. Alzheimer's and Other Dementias
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive disease that destroys memory and disrupts normal mental functions. These include thinking, reasoning, and typical behavior.
Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia, with 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases actually being Alzheimer's. The disease begins by causing mild memory problems, difficulty recalling information, and memory loss. However, over time, the disease progresses and you may no longer remember large periods of time. A 2014 study found that the number of deaths in the United States from Alzheimer's disease may be higher than reported. Risk factors for Alzheimer's include:
- Over age 65
- Family history of the disease
- Inheriting a gene from a parent
- Present mild cognitive impairment
- Down syndrome
- Unhealthy lifestyle
- Previous head injury
- Long-term social isolation or poor interaction with others
There is currently no way to prevent Alzheimer's. One thing that may help reduce your risk is a heart-healthy diet. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, low in saturated fat from meat and dairy, and rich in good sources of fat such as nuts, olive oil, and lean fish can help reduce your risk of many diseases.
8. Dehydration from diarrhea
Diarrhea is when you have three or more loose stools in a day. If diarrhea lasts more than a few days, your body loses too much water and salt. This causes dehydration, which can lead to death. Diarrhea is often caused by intestinal viruses or bacteria that are transmitted through contaminated water or food. It is especially common in developing countries with poor sanitation.
Diarrhea is the second leading cause of death in children under 5 years old. About 760,000 children die from diarrheal diseases each year. Risk factors for diarrhea include:
- Living in an area with poor sanitation
- No access to clean water
- Malnutrition
- Weakened immune system
- According to UNICEF, the best prevention is good hygiene practices.
Good handwashing techniques can reduce the incidence of diarrhea by 40%. Improving water quality and sanitation as well as access to early medical intervention can also help prevent diarrhea.

9. Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a lung disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is an airborne bacteria that is treatable, although some strains are resistant to conventional treatments. TB is one of the leading causes of death in people with HIV. About 35% of HIV-related deaths are due to TB.
TB cases have decreased by 1.5% each year since 2000. The goal is to end TB by 2030. Risk factors and prevention
Risk factors for TB include:
- Diabetes
- HIV infection
- Lower body weight
- Close contact with others who have TB
- Regular use of certain medications such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants
The best way to prevent TB is to get vaccinated against bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG). If you think you have been exposed to TB bacteria, you may start taking a treatment called chemoprophylaxis to reduce your chances of developing the condition.
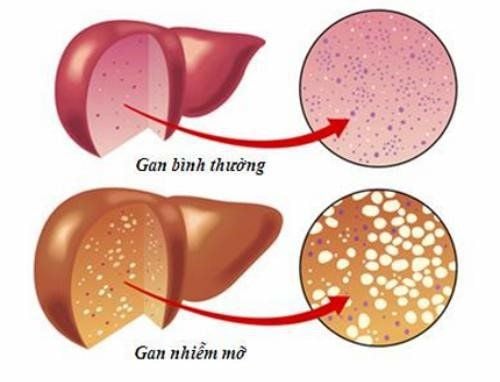
10. Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the result of chronic or long-term scarring and damage to the liver. The damage can be the result of kidney disease, or it can be caused by conditions such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. A healthy liver filters harmful substances from the blood and returns healthy blood to the body. When substances damage the liver, scar tissue forms. As more scar tissue forms, the liver has to work harder to function properly. Eventually, the liver may stop working. Risk factors for cirrhosis include:
Chronic alcohol use
Fat buildup around the liver (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
Chronic viral hepatitis
Avoid behaviors that can lead to liver damage to help prevent cirrhosis. Long-term alcohol use and abuse is one of the leading causes of cirrhosis, so avoiding alcohol can help prevent damage. Similarly, you can avoid non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by eating a healthy diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, and low in sugar and fat. Finally, you can reduce your chances of contracting viral hepatitis by using protection during sex and avoiding sharing anything that may have blood on it. This includes needles, razors, toothbrushes, etc.
One of the best ways to reduce your risk of any medical condition is to maintain a healthy lifestyle with good nutrition and exercise. Avoid smoking and alcohol abuse. In addition, you should also have regular health check-ups every year to detect any abnormalities early so that timely intervention can be made.
Vinmec International General Hospital is currently developing a general health check-up package for customers of all ages. With this examination package, you will be examined by a doctor for urine, liver, kidney, blood function, blood pressure, general X-ray, etc. Based on the examination results, the doctor will give the best advice on diet, sleep, and treatment appropriate to each person's physical condition.
The examination process at the hospital always meets high standards with the support of a team of specialized doctors and modern equipment.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
References
Statistics: Worldwide. (2016).
amfar.org/worldwide-aids-stats/
Stroke facts. (2015).
cdc.gov/stroke/facts.htm
Tardiff JC. (2010). Coronary artery disease in 2010. DOI:
doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/suq014
The top 10 causes of death [Fact sheet]. (2014).
who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/
Tuberculosis [Fact sheet]. (2016).
who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/
Tuberculosis: Global tuberculosis report 2016. (2016).
who.int/tb/publications/factsheet_global.pdf
What are the risk factors for lung cancer? (2016).
cdc.gov/cancer/lung/basic_info/risk_factors.htm