This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr., Doctor Tran Nhu Tu - Head of Diagnostic Imaging Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
X-rays are widely used in medicine and other fields such as aviation and space. How long-term exposure to X-rays affects health is a question that most patients care about when they are asked to take X-rays of their teeth or other parts of the body.
1. Overview of X-rays and X-rays
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation and are considered cancerous. However, the positive benefits of X-rays far outweigh any potential negative risks. In particular, X-ray is an important diagnostic imaging application that has been used by the medical industry globally for more than 100 years, thereby saving many patients' lives and playing a key role in a series of medical examinations. important discoveries in medicine.
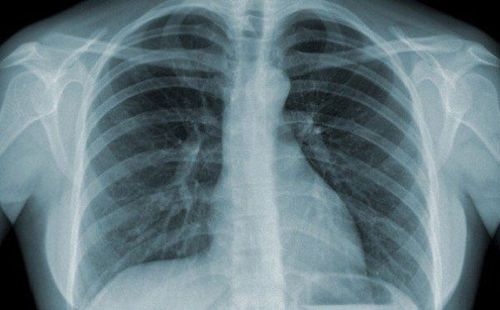
To create X-ray images, part or all of the patient's body is inserted into the machine and X-rays are emitted. The calcium present in bone with a high atomic number absorbed the X-rays and produced a white image on the resulting results. Abnormal problems in the body with a particular absorption rate of X-rays will be represented by varying degrees of black and white.
Chẩn đoán bệnh qua chụp X quang sẽ được thể hiện bằng màu đen
2. Types of X-ray tests
Types of X-ray diagnostic imaging exams include:
X-ray: This is a very familiar method and also uses the smallest amount of radiation. In which, the most common are dental X-rays, bone X-rays and chest X-rays to help detect many diseases. Computed tomography (CT) scan: The patient lies on the scanning table, moves into the scanner lap. The X-ray beam will scan around the body through the part of the patient to create an image. A CT scan uses a larger dose of X-rays than other X-ray techniques because a lot of images are taken in one scan. Digital subtraction angiography and intervention (DSA and intervention): In addition to playing an essential role in the non-invasive diagnosis process, radiographic examination is also used to treat a variety of diseases. Background erasable digital angiography opens up a field of interventional radiology that can intravascularly treat blockages (cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction...), vascular, arteriovenous malformations , bleeding in many organs, tumor diseases (uterine fibroids, prostate), cancers (treatment of liver cancer by embolization...). The placement of stents, metal spirals ... help treat many diseases. Thanks to X-rays, patients can be detected with other potential diseases without specific symptoms and signs, thereby having the opportunity to prevent and treat them early. The long existence of X-rays in medicine has proven that the importance and necessity of radiography far outweighs the risks of radiation.
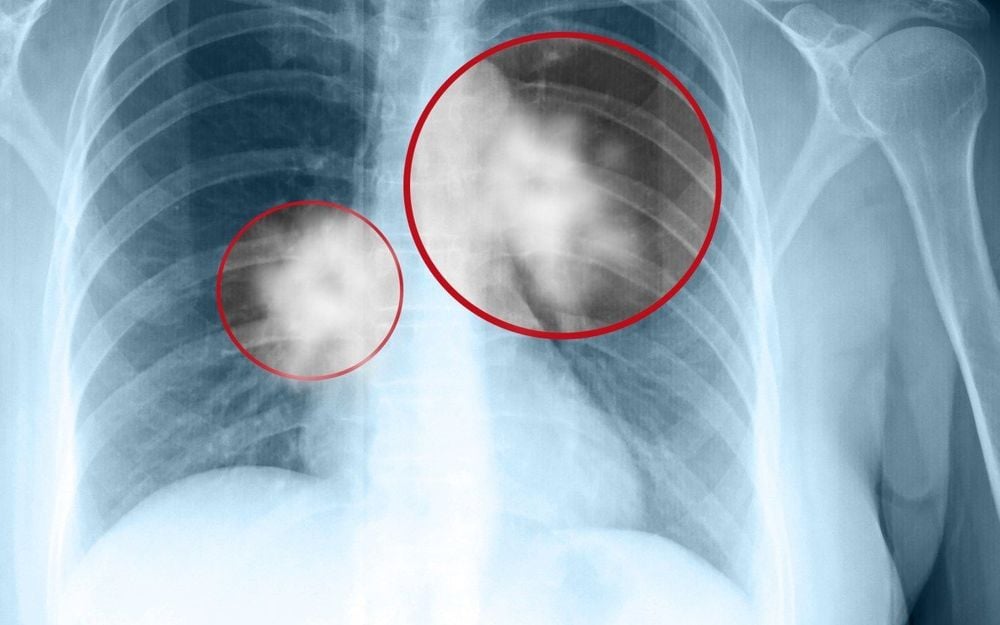
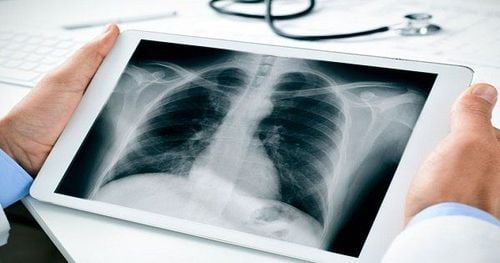
Chẩn đoán ung thư phổi nhờ vào chụp X quang.
3. Radiation level when taking X-ray
In fact, normal and healthy people are still exposed to a certain amount of radiation in daily life, this is called background radiation. This radioactive source comes from the natural environment (radon) and cosmic radiation, including X-rays. These radiations are harmful but unavoidable, and the exposure concentration is also very low, so most people do not recognize their impact.
For X-rays, each type of test carries a different level of risk depending on the type and dose of X-rays used, as well as the part of the body to be examined. X-ray radiation levels can be compared with normal background radiation that all people encounter every day as follows:
Chest X-ray : Equivalent to 2.4 days of natural background radiation Skull X-ray : Equivalent to 12 days of natural background radiation Lumbar spine: Equivalent to 6 months of natural background radiation Intravenous urology: Equivalent to 1 year of natural background radiation Esophageal - stomach - small intestine: Equivalent to 2 years of natural background radiation Baryte colonoscopy: Equivalent to 2.7 years of natural background radiation Head CT scan: Equivalent to 243 days of natural background radiation CT belly : Equivalent to 2.7 years of natural background radiation. Radiation figures are estimated for adults. Children are more sensitive and susceptible to X-ray radiation. There is research that shows that CT scans in children can increase the risk of brain cancer and leukemia by up to three times, especially when injected into the abdomen and chest in high doses.
Chụp CT là phương pháp X quang sử dụng liều lượng phóng xạ cao nhất.
4. How is radiation from X-rays affected?
What are the risks of X-ray imaging tests? X-rays can cause DNA mutations and lead to cancer later in life. Therefore, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US government have classified X-rays as carcinogenic. However, each year in the US, only about 0.4% of cancer causes are due to CT scans, while this form is increasingly being applied by hospitals at the diagnostic stage. According to another study, the ability of X-rays to increase cancer risk is only about 0.6-1.8% for people under 75 years old. Thus, it can be seen that the benefits of X-ray methods far outweigh their potential negative consequences.
Aside from being associated with a slightly increased risk of cancer, the remaining short-term side effects of X-rays are very low and are unlikely to cause any other health problems. Pilots and astronauts who are highly exposed to cosmic rays at high altitudes are more likely to be affected than patients for examination and diagnosis alone. For nuclear plant workers, exposure to high levels of radiation can cause vomiting, bleeding, fainting, hair loss and peeling skin.
Overall, advances in imaging tests in the medical industry, including dental and chest X-rays, and CT scans, are crucial to helping doctors make an accurate diagnosis and choose the right course of treatment. This makes X-rays more beneficial than dangerous. It should be noted that radiography or radiological examinations should only be used in adults when absolutely necessary. For children, families should discuss with their doctor the possible risks and benefits to the child before agreeing to do so.
Reference source: health.harvard.edu; Cancer.org and Medicalnewstoday.com
SEE MORE
Are X-rays harmful to health? What is a X-ray: All you need to know The Link Between X-Rays and Pregnancy