This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thai Binh - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
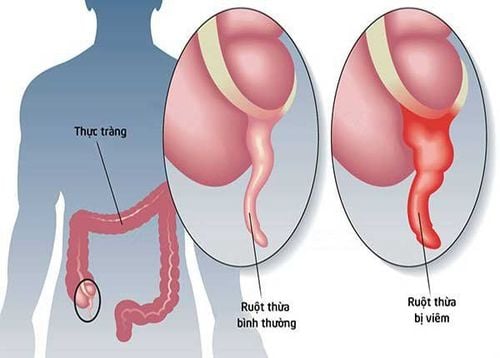
Clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis are very diverse, with typical conditions, the diagnosis is quite simple, however, there will also be many difficult situations that make the diagnosis often difficult and prognostic. detrimental to the patient.
1. General characteristics
Acute appendicitis is a very common abdominal emergency. The disease is mainly seen in children and adolescents (10-20 years old), but the fact that it can occur at any age and the variety of clinical manifestations of the disease makes the diagnosis often difficult, the prognosis is abnormal. benefit the patient.
Clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis are very diverse, with typical conditions, the diagnosis is quite simple, however, there will also be more difficult situations such as:
Due to the changing anatomical position of the appendix changes (postcaecal, subhepatic, intra-mesentery, left iliac fossa, pelvis...) Depending on the stage of progression and diagnosis (appendiceal mass, appendiceal abscess, peritonitis, inflammation) appendicitis pseudotumor...) Change in unusual pain symptoms: Either severe pain or only vague pain (appendicitis in nursing infants, in the elderly, in diabetics...)
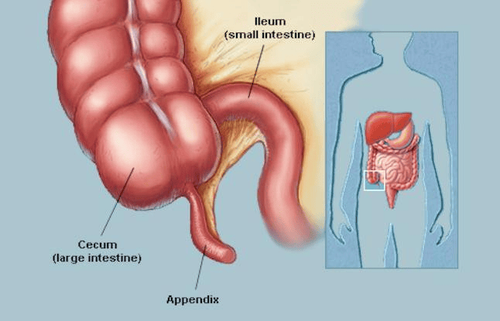
2. Typical clinical form of acute appendicitis
Easy diagnosis based on clinical examination. Typical functional symptoms:
Dull abdominal pain in the right iliac fossa. Typically, pain is around the navel or epigastrium, then spreads to the right iliac fossa. Digestive disorders : Nausea, loose stools or loose stools... Fever. Clinical examination:
Pain on examination: Painful pressure on Mac Burney's point in the right iliac fossa. Right iliac fossa wall reaction is a typical sign of acute appendicitis (but only seen in 53% of cases). Diagnostic tests:
Blood tests: WBC increased > 10,000/ml (multiple neutrophils > 75%) and blood CRP increased. Diagnostic imaging: Abdominal ultrasonography and computed tomography abdomen-subframe (CT abdomen-subframe): images of appendicitis and complications. Laparoscopy: It is both a diagnostic tool to confirm suspected cases and is also the best treatment method. However, the typical form accounts for only about 50% of cases of acute appendicitis, with the remainder being circumstances that make the definitive diagnosis of appendicitis much more difficult. Doctors and need help from imaging studies, especially CT abdomen - pelvis to help accurately and timely diagnose difficult-to-diagnose forms of appendicitis.
3. Atypical clinical forms of acute appendicitis
Post-cecal appendicitis: Atypical pain symptoms, examine the pain point on the right iliac crest, the patient will find relief when flexing the thigh. Abdominal ultrasonography and abdominal-pelvis CT add to the diagnosis. Appendiceal body in the mesentery: Also known as VRT "protrusion". This typically presents with a bowel obstruction (especially without a history of abdominal surgery) accompanied by fever. Pelvic appendicitis: Pain similar to salpingitis, broad ligament in women, sigmoid diverticulitis, urinary tract infection. Manifestations of symptoms are mainly in the bladder (painful urination, frequent urination) or rectum (tenderness, diarrhea ..). Subhepatic appendicitis: Pain in the right lower quadrant like hepatobiliary disease. Left-sided appendicitis: Found in visceral inversion or intestinal malrotation (may be known in advance, or confirmed by chest radiograph or unprepared abdominal radiograph).
4. Can appendicitis be confused with other conditions?
Breastfeeding children and under 3 years old: It is necessary to distinguish from the following diseases:
Common gastroenteritis, mesenteric lymphadenitis: Same symptoms around the umbilicus. However, mesenteric lymphadenitis is usually only mildly elevated in white blood cells. Small bowel intussusception also starts pain around the umbilicus, after spreading to the right iliac fossa, early stage without fever, rectal examination with blood helps to confirm the diagnosis... Children over 3 years old:
Urinary tract infection (common in children) girl). Meckel's diverticulum: Periumbilical abdominal pain with fever and signs similar to typical cases. Primary pneumococcal peritonitis: It is difficult to distinguish from the case of purulent appendicitis. Sudden onset, high fever very quickly, with primary infection (lungs, pleura), especially common in children with nephrotic syndrome (50%). In case of doubt, laparoscopy allows assessment of intact appendix, immediate endoscopic examination of peritoneal fluid if Gram-positive bacteria (pneumococcal or streptococci) Right bronchopneumonia: Shortness of breath, auscultation and auscultation Abdominal (with normal bowel sounds less suggestive of severe peritonitis). Adolescents:
In men the diagnosis is generally simple. Sometimes it is necessary to distinguish right ureteral stone pain, right kidney hydronephrosis, ileocecal inflammation, Crohn's disease (recurrent abdominal pain, diarrhea, abdominal CT to confirm the diagnosis). For younger women, it is more difficult to distinguish from gynecological pathology: Tubal inflammation (pain score will be lower, usually in the lower abdomen and bilateral pain, with recent vaginal discharge (note venereal disease) external genitalia), rupture of an ovarian follicle De Graff (occurs between two menstrual cycles) Elderly:
In men, it should be distinguished from perforated peptic ulcer disease (sudden stabbing pain) , later there may be localized pain in the right iliac fossa due to gastric juice flowing down the lateral-colic fissure, history of ulcerative stomach pain, recent perforation usually without fever, abdominal X-ray showing free air in the peritoneal cavity ...) In women, care should be taken to distinguish acute cholecystitis from appendicitis and vice versa, especially if the gallbladder is abnormally low, or the appendix descends below the liver.Acute cholecystitis often has a history. liver cramps, or digestive disorders, diarrhea with fatty foods, mild hyperbilirubinemia and alkaline phosphatase... In summary, with about 50% of patients presenting with atypical symptoms, the nine diagnosis Determining appendicitis is really not easy, making it easy for patients to miss or go to the doctor late and to have serious complications that affect their health and increase the patient's treatment costs. Therefore, when there are symptoms of abdominal pain and fever, we should not ignore, self-treat, self-monitor at home, but should go to reputable medical facilities for examination, diagnosis and intervention. timely treatment of this disease.
Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital owns a team of experienced, enthusiastic and dedicated emergency and gastroenterology doctors. Patients will be directly examined by gastroenterologists as well as used the most modern and advanced imaging tools for accurate diagnosis of appendicitis and timely interventional treatment. by endoscopic surgery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Treatment of appendicitis requires surgery or not? Handbook of things to know about acute appendicitis Children with fever with abdominal pain, vomiting: Beware of appendicitis