This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesiology, Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalAppendicitis is a very common disease. This is usually a sign of an acute appendicitis and has a very serious course. If not recognized early, the consequences can be very unpredictable.
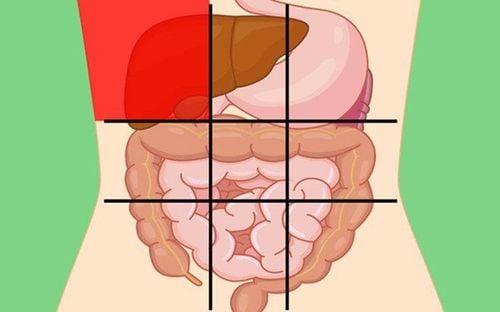
I. Where is the appendix located?
The appendix (Appendix) is a part of the digestive tract, located at the base of the cecum, near the junction connecting the small intestine (Ileum) and large intestine (Cecum). It is a thin tube about 2-4 inches (about 5-10 cm) long. Usually, the appendix is located in the lower right abdomen, but in many cases it is located in other locations nearby, even in the middle and left side of the abdomen. The role of the appendix: The actual function of the appendix is still controversial. It is hypothesized that the appendix acts as a storehouse of beneficial bacteria, to help restore the digestive system after episodes of diarrhea caused by digestive infections. Another theory is that the appendix is just a remnant of the digestive tract during human evolution.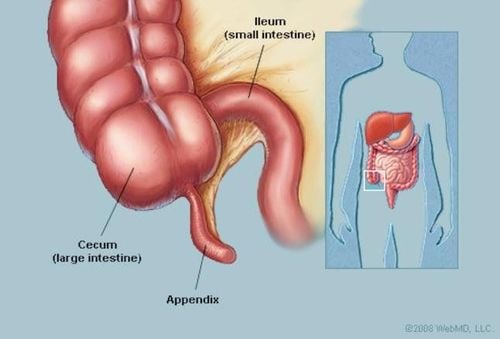
II. Appendiceal pain
There are 2 main causes of appendicitis
Appendicitis: The main cause of appendicitis pain. Appendiceal tumor : Less common. Appendicitis pain is usually resolved mainly by surgical intervention, rarely medical treatment is indicated.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.III. Appendicitis
1. Outline
Acute VRT is a common surgical emergency. Accounts for 60-70% of abdominal emergencies. Rate of VRT: 1/10,000 per year The average age of disease is 22, 10 - 30 (accounting for 70%) Rate of VRT with perforation complications: 19.2%. VRT in the elderly: 50% have complications. Western countries have a higher frequency of VRT than Asian and African countries Appendicitis is also the reason leading to abdominal surgery, accounting for the highest rate in emergency surgery in Vietnam.
2. Causes of acute appendicitis
Enlargement of lymph nodes (60%): Enlarged submucosal lymphatic cysts due to: Local response (intestinal infections due to salmonella, shigella...); response to systemic infections, to infections that cause lymphatic proliferative reactions such as acute respiratory infections, etc. Stagnation of fecal stones in the lumen of the appendix (35%). Foreign matter (4%): Small fruit seeds such as lemons, peppers or intestinal parasites such as roundworms, . . . Tumor of appendiceal wall, cecal wall pressing (1%).
3. Progression of appendicitis
Appendiceal clumps: RT is enveloped by surrounding structures, with little or no pus.
Examination of the right iliac fossa shows a hard, palpable, cardboard-like patch, with an indistinct boundary. It is sometimes difficult to distinguish between an appendix abscess and an appendiceal mass.
Progression can form an abscess, or the inflammatory response subsides and the patient has less pain.
Appendiceal abscess The time to form an abscess is usually 4-5 days.
VRTC ruptured pus and was isolated from neighboring organs such as the great omentum, small intestine, and surrounding, isolated to form an appendix abscess.
Clinical examination palpable a mass in the right iliac fossa with poor mobility, very painful to press.
Peritonitis May be localized to HCP or lower half of abdomen or generalized peritonitis.
Appendicitis is often due to late patient arrival or late diagnosis.
Clinical symptoms are usually patients with severe right iliac fossa pain, high fever ≥ 39oC.
On clinical examination, the patient showed signs of resistant pain of peritonitis in the right iliac fossa or throughout the abdomen.
4. Symptoms of appendicitis
4.1 Appendiceal pain
Is the first and always present symptom. The nature of pain is very diverse. However, appendicitis pain is typically characterized by the following: The pain begins around the navel or above the navel. After about 2-12 hours, the pain gradually increases and moves down to the right iliac fossa, continuous dull pain, increases when coughing or when changing positions, ... . This is the most reliable symptom to identify a case of acute appendicitis. In addition, as noted above, the location of the appendix is varied. Therefore, depending on the location of the appendix, patients will have very different feelings about the location of appendicitis: flank pain (postcecal appendix), hypogastric pain (small appendix), abdominal pain. In addition, the nature of appendicitis pain also depends on many other factors: the drug being used, the patient's tolerance, the patient's resistance , the patient's medical condition, ...
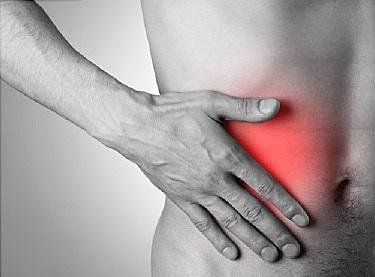
4.2. Fever
Usually mild fever ~38 degrees Celsius due to inflammation of the appendix. If there is a complication of peritonitis, the infection is severe, causing high fever.4.3. Digestive disorders
Patients may have other symptoms such as: Anorexia/loss of appetite, vomiting/nausea, diarrhea, rarely constipation. It is worth noting that the symptom of anorexia/loss of appetite, although not constant, is nearly always present in acute appendicitis, so much so that many experts consider the absence of this symptom to require reconsideration of the diagnosis. appendicitis . The order of appearance of symptoms is usually: Anorexia → Appendiceal pain → Vomiting. If vomiting precedes pain, careful consideration should be given.
5. Diagnosis of appendicitis
Due to the varied nature of appendicitis, appendicitis can be very easy or very difficult to diagnose. In fact, there is currently no single symptom, clinical sign or laboratory test that accurately diagnoses appendicitis in all cases. The diagnosis is often combined based on the clinical picture, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Despite the great advances in imaging techniques and laparoscopy now, the misdiagnosis rate of appendicitis has not decreased much, at 15.3%, equivalent to the rate of appendicitis perforation. . The rate of misdiagnosis is higher in women than in men (22.2% vs 9.3%).
6. Treatment of appendicitis
The principle of treatment of acute appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix. Surgery should be performed as soon as possible, as soon as the diagnosis is made. This is the natural and undisputed treatment for cases of necrotizing appendicitis or perforation causing peritonitis. Even many opinions suggest that even though the diagnosis of appendicitis is undetermined, if the patient has appendicitis-like pain and is progressing severely, surgery is still recommended to avoid ominous complications of appendicitis. . Antibiotic therapy can be applied to uncomplicated acute appendicitis in remote areas, who are at high risk for surgery or who refuse to operate. It should be noted that antibiotic treatment has a failure rate that requires conversion to surgery, requires closer and longer follow-up, and its effectiveness decreases over time.
7. Appendicitis in pregnant women
Diagnosing appendicitis in pregnant women is challenging because the symptoms of appendicitis are relatively similar to those commonly encountered in normal pregnancies. On the other hand, because the appendix is pushed up and out during pregnancy, the location of the appendix pain will also change. In terms of diagnosis, the use of CT-Scan is also a dilemma. Patients will have to be exposed to radiation (usually 400 times more than a chest X-ray film) and often use contrast material, so it is not suitable for pregnant women, leading to difficulties in diagnosis. However, in many cases, low-dose imaging without contrast is still acceptable. Pregnant women with suspected appendicitis are advised to have early surgery despite the relatively high risk of "mistaken" resection of the normal appendix, because appendicitis if progressed to necrotizing appendicitis causing peritonitis will increase the risk of appendicitis. pregnancy loss rate increased 4 times.
BECAUSE. Appendiceal tumor
It is a very rare disease. May be benign or malignant. Manifestations: Tumors on the appendix secrete chemicals that make the appendix inflamed, causing appendicitis pain and diarrhea. Tumor-associated appendicitis is usually milder and has a slow progression, not as acute as in appendicitis. This is a disease that usually does not require emergency intervention. The major diagnosis is similar to that of appendicitis. However, tumors are easily detected through imaging tools such as ultrasound, CT-Scan or MRI. The treatment is based on many factors, but is still mainly based on surgery. Appendicitis is a symptom of an abnormal condition of the appendix. Appendicitis pain has a very diverse nature, so it is difficult to recognize and diagnose accurately. However, due to the acuteness of the diseases that cause appendicitis, it is necessary to immediately bring the patient to the medical center for examination and diagnosis when it is suspected that the patient is showing signs of appendicitis. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.