This is an automatically translated article.
Mediastinitis is often secondary to another disease primarily related to surgery, esophageal perforation, and infection from surrounding areas, with incidence varying from case to case. In which, post-operative mediastinitis is the most common.
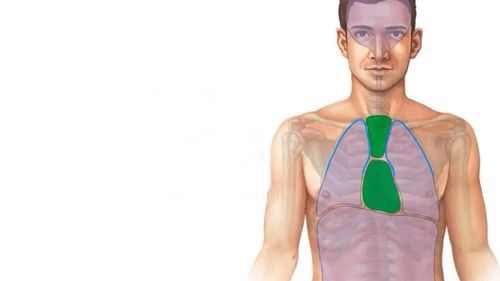
1. What is called mediastinitis?
Mediastinitis is a term used to describe all inflammation that occurs in tissues within the mediastinum. Because the infection here progresses quickly, so mediastinitis often has a very serious condition, and can even be fatal if not treated promptly. Most cases of mediastinitis require hospitalization and treatment in the intensive care unit.
Mediastinitis is divided into two types:
Acute mediastinitis Chronic mediastinitis. Acute mediastinitis is the most common form of mediastinitis. More rare chronic mediastinitis, in which granulomatous mediastinal lymphadenopathy or mediastinal fibrosis can occur as a result of infection or irritation over a long period of time.
Acute mediastinitis: most often caused by esophageal perforation or rupture of the esophagus (possibly due to esophagogastroduodenoscopy) or complications of cardiac surgery or penetrating chest trauma. In addition to the cause of esophageal rupture, acute mediastinitis can also be caused by infection at other sites (now uncommon), anthrax mediastinitis, and post-cardiac surgery mediastinitis.
Clinical manifestations of acute mediastinitis include:
Chest pain Fever Cough Shortness of breath, rapid breathing Tachycardia Pain when swallowing Pneumothorax at base of neck Severe systemic toxicity. Physical examination reveals tenderness and swelling of the sternum and sternoclavicular joints, in addition to other symptoms of acute mediastinal compression, typical of Boerhaave's syndrome (vomiting esophageal rupture). Chronic mediastinitis: usually due to granulomatous inflammation of the mediastinal nodes in sarcoidosis (granulomatous mediastinitis) or mediastinal fibrosis. Symptoms of granulomatous mediastinitis are usually poor.
Sclerosing mediastinitis often has signs of mediastinal compression such as:
Superior vena cava syndrome. Symptoms of tracheal compression. Symptoms include compression of blood vessels and nerves, paralysis of the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the phrenic nerve.

Mỗi tình trạng viêm trung thất lại có biểu hiện lâm sàng của bệnh khác nhau
2. Causes of mediastinitis
There are many possible causes of mediastinitis, which are divided into the following groups:
Causes originating from structures within the mediastinum
Esophageal perforation: this is the most common cause of mediastinitis. mediastinitis. The reason leading to esophageal perforation can be complications of endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, cardiac surgery. Trauma to the chest and abdomen: is also a cause of mediastinitis. Lung infection, osteomyelitis at the sternum joint can spread to the mediastinum causing inflammation here. Granulomatous diseases such as tuberculosis cause inflammation of the lymph nodes in the mediastinum. Causes of mediastinitis spreading from other areas include:
Pharyngitis Tonsillitis, peritonsillar and subpharyngeal abscesses Middle ear infections Sinusitis Dental abscesses Salivary gland infections Post-surgery infections of the head and neck Causes of mediastinitis caused by microorganisms:
Infection can be caused by a variety of bacteria such as Staphylococcus spp, Fusobacterium spp, Bacteroides spp, Streptococcus spp, Peptostreptococcus spp and Pseudomonas aeruginosa that can cause the condition this inflammation. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) may be involved in this condition when it occurs after heart surgery. Mediastinitis can sometimes be caused by tuberculosis or a fungal infection.
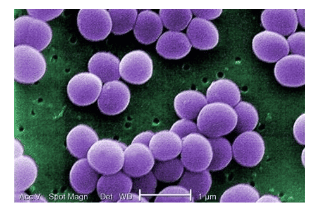
Một số vi sinh vật gây bệnh có thể là nguyên nhân gây ra viêm trung thất
3. What medical techniques help diagnose mediastinitis?
Your doctor will usually diagnose mediastinitis based on symptoms if you are at risk or are prone to mediastinitis, such as recent surgery involving the chest or esophagus or have a medical condition. TB develops from infection with the TB bacteria.
When inflammation occurs suddenly, symptoms are often so severe that a doctor can make an initial diagnosis even in people who are not at high risk involved.
To confirm the initial diagnosis, the doctor will order you to go for a number of paraclinical tests such as:
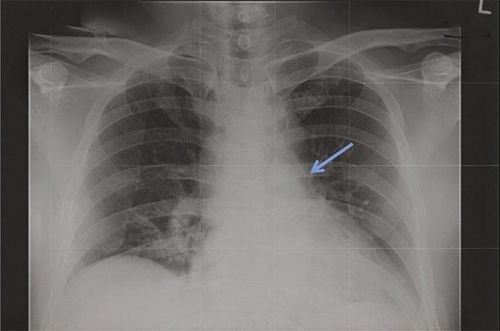
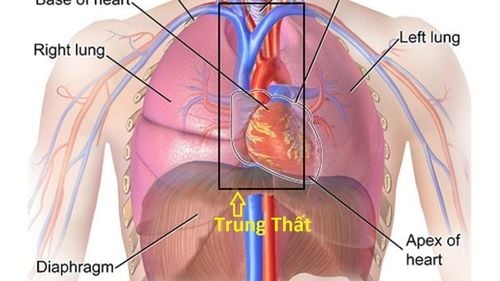
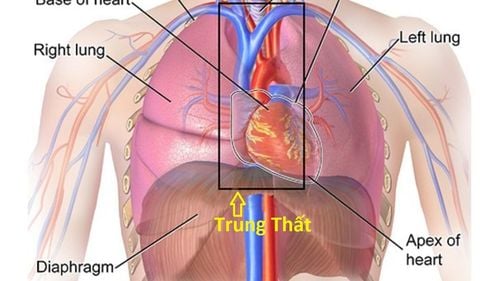
X-ray of the chest straight - inclined to evaluate mediastinal status: on the X-ray film, it is necessary to evaluate the limbs. Details: Images of mediastinal margins include: superior vena cava arch, aortic arch, right atrial arch, left ventricular arch. Azygos venous loop of the aortopulmonary window. Esophageal opacity. Left and right border of the spine. Spaces behind the sternum, behind the heart. Spine image. On the inclined plane (corresponding to the lateral thoracotomy), the mediastinum is divided into 3 regions:
Anterior mediastinum: from the posterior sternum to the anterior border of the trachea and the posterior border of the heart. Mediastinum: from the posterior limit of the anterior mediastinum to 1cm posterior to the anterior border of the spine. Posterior mediastinum: is the remainder to the rib trough of the spine. On the straight plane (equivalent to a straight chest film), the mediastinum is divided into 3 floors, including:
Upper mediastinum: from above the aortic arch. Mediastinum: from below the aortic arch to the lower border of the tracheal division. Lower level of mediastinum: is the continuation to the diaphragmatic arch. In the upright position, chest x-ray in the upright position allows to confirm the presence of a mediastinal syndrome.
Tilt film due to overlapping images of the bilateral lung fields into the mediastinum, so it is only intended to determine the location of pathological areas in the anterior mediastinum, mediastinum or posterior mediastinum.
Người bệnh được chỉ định chụp X-quang ngực để chẩn đoán tình trạng viêm trung thất
If the thoracic radiograph is in the supine position, the mediastinal shadow is often wider due to the raft of blood vessels ascending to the neck, such as the superior vena cava, brachiocephalic trunk, so it is easy to be confused with the balloon. pathologically enlarged mediastinum.
Chest CT scan: on CT film will give more accurate and detailed images than X-ray film. Supersonic. Biopsy: When mediastinitis occurs in a person who has had a sternotomy, the doctor may do a biopsy by inserting a needle through the sternum into the chest to collect a sample of fluid and have it examined. under the microscope. Esophageal endoscopy: In case of suspicion of mediastinitis due to esophageal perforation, esophagoscopy should be performed to detect the fistula or esophagogram with water-soluble contrast to detect the fistula. In some cases, it may be necessary for a doctor to combine several techniques to diagnose mediastinitis and find the cause of the condition, thereby recommending appropriate treatment.
Periodic health check-ups help to detect diseases early, so that there are treatment plans for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Standard 2020 General health check-up package VIP 2020 General health check-up package Special 2020 General health check-up package Children 2020 General health examination package Work permit - Issuance of work permits Examination results of people sick will be returned home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.