This is an automatically translated article.
The mediastinum is a part of the ribcage, containing organs that play an extremely important role, having vital meaning to the body.
1. What is the mediastinum and where is it located?
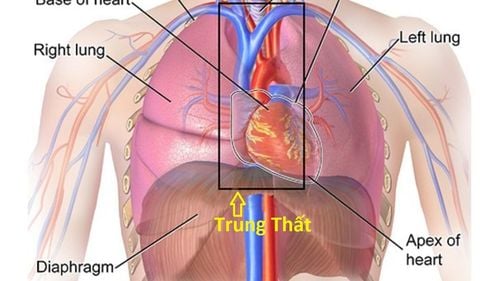
The mediastinum is an important part of the thoracic cavity, containing most of the parts of the ribcage except for the two lungs. The mediastinum is an anatomical trapezoidal cavity with 6 faces, defined by: above is the base of the neck, below is the diaphragm, in front are the thoracic vertebrae, on both sides are 2 parietal leaves.
For ease of description, the mediastinum is divided into several zones. There are different views of mediastinal division, of which three are common:
1.1. Classical division of mediastinum Suppose there is a vertical plane passing through the trachea and two bronchi as the boundary dividing the mediastinum into two parts, the anterior mediastinum and the posterior mediastinum.
1.2. Mediastinum division according to anatomical point of view The mediastinum is divided into four parts: anterior mediastinum, superior mediastinum, mediastinum and posterior mediastinum. In which:
The superior mediastinum lies in the plane passing directly above the pericardial space, at the level posteriorly with the vertebral fissure 4.5 and anteriorly with the mandibular cleft and the sternum body. The anterior mediastinum is anterior to the above-mentioned plane, a very narrow space located just before the pericardium and behind the sternum. The mediastinum occupies the central position, where the heart and pericardium are located. The posterior mediastinum lies below the above plane, a long, narrow tube that lies behind the heart and pericardium and anterior to the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae.
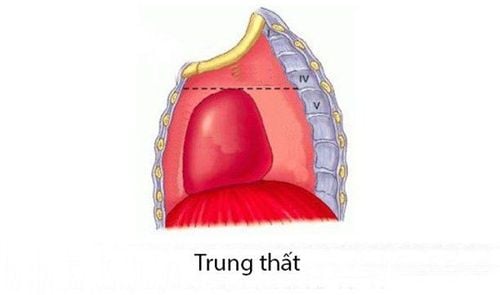
Cấu trúc chính của trung thất được chia làm 4 phần như hình ảnh
1.3. Mediastinal division from the point of view of surgery According to Thomas.W. Shields (USA) 1972, the mediastinum is divided into 3 compartments: anterior mediastinum, mediastinal mediastinum and posterior mediastinum:
Anterior mediastinum: anteriorly bounded by the sternum, posteriorly by great vessels and the outer membrane heart. The mediastinum, also known as the visceral cavity, is located between the anterior and posterior mediastinum. The mediastinum contains the major intrathoracic contents. The posterior mediastinum, also known as the paravertebral space, is a long and narrow tube containing many components connecting the 3 parts of the neck, thorax and abdomen such as the single vein system, the thoracic duct, and the X nerve.
2. Main components in mediastinal compartments
From an anatomical point of view, the main components in the mediastinal cavity include:
The superior mediastinum includes the trachea, thymus, cephalic veins, thymus, aortic arch, esophagus, chest tube. The mediastinum includes the heart, ascending aorta, pulmonary artery trunk, pulmonary veins, and phrenic nerves. The posterior mediastinum includes the esophagus and X nerves, the descending aorta, the thoracic duct, and the sympathetic nerves. The anterior mediastinum consists of small blood vessels, fatty tissue and connective tissue, in children the anterior mediastinum also has the thymus.
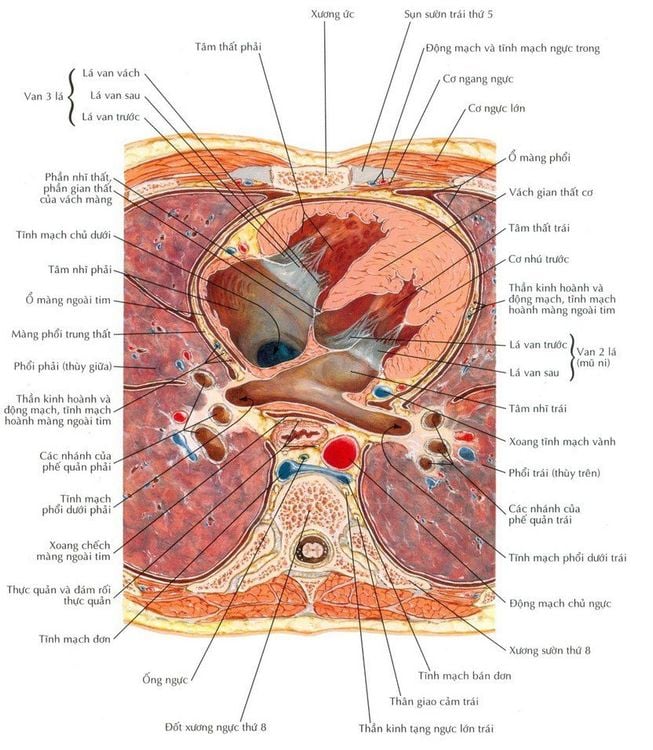
Hình ảnh thiết ngang cho thấy các thành phần tại khoang trung thất
Anterior mediastinum includes: internal thoracic bundle, thymus or thymus remnants, lymph nodes around the internal thoracic bundle, lateral lymph nodes in front of large blood vessels, fat and connective tissue. The mediastinum includes the heart, pericardium, great vessels, trachea, esophagus, right and left pulmonary veins, phrenic nerve, thoracic duct, single vein loop, and lymph nodes below the tracheobronchial trine. trachea and trachea, pericardial and pleural lymph nodes, fatty tissue and connective tissue. The posterior mediastinum, also known as the paraspinal space, consists of the sympathetic ganglia chain, the intercostal nerve bundle, the paraesophageal lymph nodes, and the lymph nodes of the intercostal vascular bundle.
MORE:
Learn about mediastinoscopy Is mediastinal tumor dangerous? How to treat mediastinal tumor?
Recommended video:
Vinmec - Flexible endoscopic laser lithotripsy removes stones up to 2.5 cm