This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Toan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. The doctor has a lot of experience in the treatment of Resuscitation - Emergency.1. What is mediastinal pneumothorax?
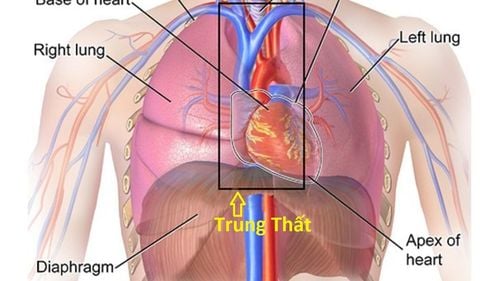
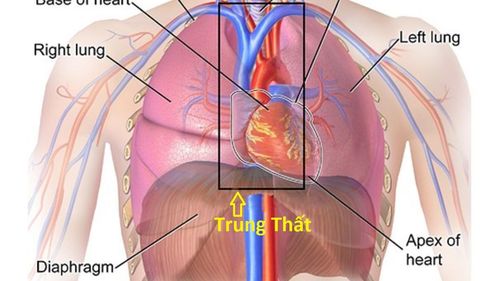
The presence of air or free gas in the mediastinum is called mediastinal pneumothorax. Pneumomediastinum is a benign and self-limiting condition that usually affects males.Pneumomediastinum can be caused by trauma, this condition is also known as spontaneous pneumomediastinum.
Air enters the mediastinum through disruption of the subcutaneous or muscular barrier (usually in the bronchial tree or esophagus); Gas-producing organisms present in the mediastinum or adjacent foci of infection; Pressure differentials between alveoli and pulmonary interstitium leading to alveolar rupture are three different mechanisms by which pneumomediastinum can occur. The pathophysiological basis of pneumomediastinum is the ultimate mechanism.
2. Causes of pneumomediastinum
Most often, pneumomediastinum occurs due to air leakage from any part of the lung or the airways into the mediastinum. Increased pressure in the lungs or airways can be caused by:
Severe cough Increased intra-abdominal pressure Sneezing. Vomit. The neck or chest area is infected. Sudden change in altitude. Insertion of a nasogastric tube causes esophageal laceration. Trachea tear. Breathe machine. May occur with pneumothorax or other diseases. The presence of free air in the mediastinum without an obvious cause is called spontaneous pneumomediastinum.

3. Signs of pneumomediastinum
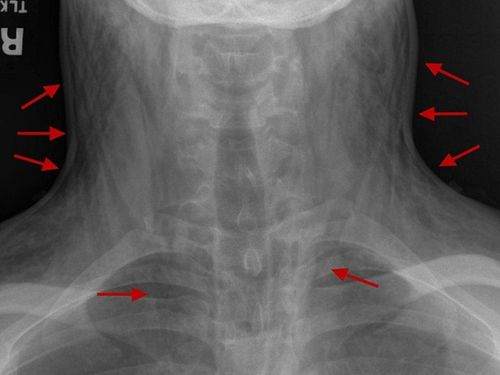
Spontaneous mediastinal pneumothorax is a rare, benign condition that mainly affects young people. The most common clinical manifestations are chest pain, dyspnoea, and subcutaneous emphysema.
Patients with pneumomediastinum may be asymptomatic. It usually causes chest pain behind the breastbone, which can spread to the neck and arms. Breathing and swallowing can increase pain.
The most common symptoms are chest pain , shortness of breath and a feeling of pain or discomfort in the neck. Chest pain is the most common symptom and is characterized by acute, retrosternal, pleural pain that may radiate to the neck, shoulders, or back. Less common symptoms include: Cough, difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, back or stomach pain.

4. Treatment of pneumomediastinum
Because the body will absorb gas gradually, patients with pneumomediastinum usually do not need treatment intervention. The purpose of the disease treatment method is mainly supportive treatment, including: Rest, pain relief, oxygen therapy, prophylactic antibiotics, bronchodilators, vitamins. Depending on the specific case, other methods can be applied, such as:
Clearer mediastinal nitrogen gas faster by breathing oxygen with high concentration. This method can be applied in the vast majority of cases of pneumomediastinum. However, when using high concentrations of oxygen, it is necessary to closely monitor the patient's blood gases. Depending on the specific case, can perform one-lung artificial ventilation, artificial ventilation with moderate airway pressure, low Vt, high respiratory rate (HFOV). Other supportive methods: When there is pneumothorax, put a pneumothorax. Surgical repair sutures perforation of the trachea, esophagus, and pleura. Use medication to treat pain symptoms, relieve cough. Emergency unit treatment is required if mediastinal compression is required. In addition to other treatments, a tube may be inserted into the air chamber to release the compression.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.