This is an automatically translated article.
Most of the torsades de pointes are related to the ECG with prolonged QT interval in the previous time. Although occurring in a short time, torsades de pointes can lead to ventricular fibrillation, which is dangerous to the heart health of the patient.
1. What is vertex torsion?
Torsade de pointes syndrome is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia characterized by delayed repolarization of the myocardium and an abnormally prolonged QT interval.
Torsion is characterized by fast, irregular frequency QRS complex and axial rotation. The consequences of torsades de pointes syndrome can cause ventricular fibrillation, affecting the circulatory system and having a very high risk of death.
The QT interval in long torsades de pointes has many different causes, which can be congenital or as a result of drug use. When the QT interval is prolonged, arrhythmias occur, causing premature depolarization afterload and unevenly distributed refraction between different regions of the myocardium.
2. Diagnosis of torsades de pointes syndrome
To diagnose torsade de pointes syndrome, it is necessary to rely on clinical and subclinical:
Clinical: Patient may faint, heart rate 200-250 beats/min, palpitations, palpitations, Subclinical: Electrocardiogram showed that the QRS complex rotates around the fixed axis, the torsades de pointes, the QT interval lasts about 0.44s. In addition, electrocardiography should also be performed in family members with risk factors for torsades de pointes due to congenital long QT to screen for this pathology.
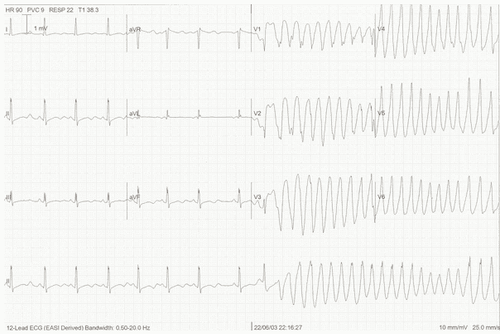
Hình ảnh điện tâm đồ bệnh lý xoắn đỉnh
3. Treatment of torsades de pointes syndrome
For treatment of critical torsades de pointes or abstinence therapy, a strong thoracic punch may be applied. Or in the case of prolonged torsades de pointes leading to hemodynamic disorders of the patient, asynchronous electric shock is the first choice. In electric shock, the initial energy applied to the patient is usually 50-100J, then increases to about 360J depending on the case.
Treat electrolyte disturbances by intravenous administration of Magnesium Sulfate 1-2g, repeated thereafter but a maximum of 2-4g over 15 minutes. Some patients may need to replace potassium and calcium on a case-by-case basis. If the patient is taking drugs that cause torsades de pointes, i.e. drug-induced torsades de pointes syndrome or are at risk of electrolyte disturbances, these drugs should be discontinued immediately. Some patients may experience bradyarrhythmias that need to be treated with intravenous isoproterenol, temporary pacemaker placement, and injection of Lidocaine to shorten the QT interval.
For patients with torsades de pointes syndrome due to congenital long QT interval, it is necessary to have a long-term treatment plan, including beta-blockers, stenting, permanent pacemakers, ablation pacemakers. automatic vibration ICD...
Torsade de pointes is a condition caused by abnormally prolonged QT interval with congenital causes or certain drugs. Treatment of torsade de pointes syndrome requires a combination of methods, especially with congenital diseases that require long-term treatment to bring the best effect to the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.