This is an automatically translated article.
Positive pressure ventilation helps to reduce nosocomial infections, especially pneumonia; The patient is comfortable, can communicate, eat by mouth, maintain personal activities or can breathe at home.
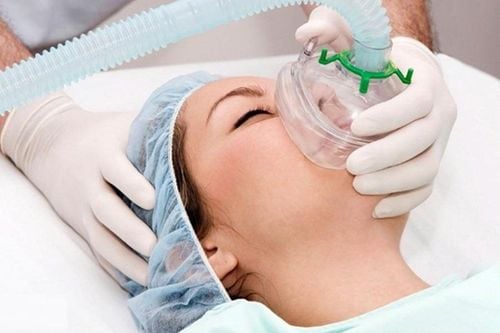
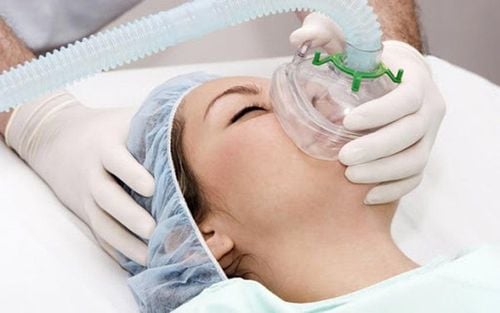
1. What is positive pressure ventilation?
Positive pressure ventilation is a method of artificial ventilation without the use of an endotracheal tube. This is a new step in respiratory resuscitation, especially in COPD exacerbations.
This method helps to reduce hospital-acquired infections, especially pneumonia; The patient is comfortable, can communicate, eat by mouth, maintain personal activities or can breathe at home.
Some types of positive pressure ventilators include:
BiPAP: Spontaneous breathing, non-invasive ventilation. CPAP ventilator: Is a form of non-invasive breathing machine, meaning that the user does not have to put a breathing tube - endotracheal intubation when using it, making the patient more comfortable than an invasive ventilator.
2. Indications and contraindications for positive pressure ventilation
Bệnh nhân bị phù phổi cấp được chỉ định thông khí áp lực dương
Indications for positive pressure ventilation in the following cases:
Risk of respiratory failure due to muscle fatigue that is reversible in 24 - 28 hours and mild to moderate respiratory failure. Acute hemodynamic pulmonary edema; acute quadriplegia. Hypoxia after extubation due to pulmonary edema or atelectasis. Mild glottis edema after extubation. In weaning from mechanical ventilation ; exacerbation of COPD. The patient is qualified for weaning, can be extubated early, and is on non-invasive mechanical ventilation for 1-2 days after extubation. Positive pressure ventilation is contraindicated in the following cases:
Apnea. The patient is uncooperative; does not protect the airway itself. Increased secretion of sputum, but cough is poor. Uncontrolled arrhythmia. Hemodynamic instability. Injuries, facial deformities. Upper airway obstruction.
3. Steps of positive pressure ventilation
Step 1: Prepare a BiPAP or CPAP non-invasive ventilator; Nose mask, Nose mouth mask.
Step 2: Record vital function, Sp02, blood gas before using ventilator for patient. Choose Mask that fits the patient, moisten, and tie the mask in place. Set IPAP 10cmH20, EPAP 5cmH20, adjust Fi02 to maintain Sa02 > 90%.
Step 3: Set the initial parameters based on the patient's size and condition and install the ventilator.
Step 4: Monitor and evaluate the patient's vital function.
4. Some complications after positive pressure ventilation
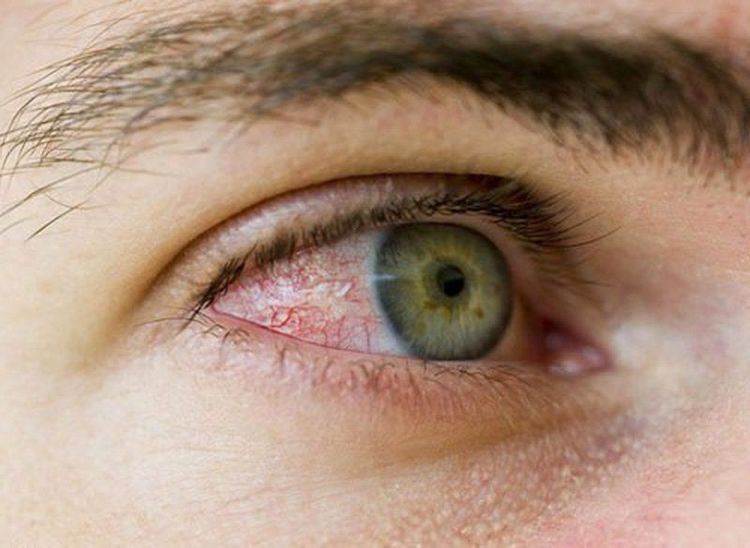
Bệnh nhân sau khi thông khí áp lực dương có thể bị viêm kết mạc
Gas entering the stomach causes bloating or choking into the lungs, ringing in the ears. Open masks cause conjunctivitis due to excessive air blowing into the eyes. Ulcers, necrosis of the bridge of the nose due to pressure. Dry phlegm due to not moistening. Pneumothorax and decreased cardiac output due to decreased return. Artificial ventilation techniques are performed at Vinmec International General Hospital with a highly configured ventilator system for ICUs for adults, children and infants.
In particular, the team of doctors performing the technique are all doctors from the Emergency Department with high professional experience.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.