This is an automatically translated article.
In modern medicine, many advanced equipments are developed to diagnose, care and treat patients, including mechanical ventilation, which is an activity to support the respiratory process for patients. patient. It is necessary to monitor the phenomenon of decreased oxygen in the blood during mechanical ventilation for timely treatment.
1. Indication for mechanical ventilation when?
Mechanical ventilation is indicated in many cases of respiratory disorders. Usually, the patient can be given oxygen to increase the oxygen concentration in the inspiratory stream, but in some cases, oxygen therapy cannot be met, so ventilation is required. artificial :
Severe arrhythmia, patient breathing too fast or breathing too slow. The lung resistance and elasticity of the patient are increased. Lung expansion is too low. The patient stops breathing. In addition, the following groups of diseases may have indications for mechanical ventilation:
1.1 Diseases that reduce alveolar ventilation Central nervous system damage: cerebral stroke, contusion, encephalitis... Nerve palsy... peripheral neuropathy, respiratory muscle paralysis: snake venom poisoning, Guillain Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis... Chronic lung/bronchial disease: PaO2 < 60 mmHg (normal 95 mmHg), PaCO2 > 40 mmHg (normal 40 mmHg ). The disease has increased muscle tone, prolonged systemic convulsions: systemic tetanus, cerebral malignant malaria, intermittent epilepsy, chemical poisoning, strychnine poisoning. 1.2 Severe hypoxemia Diffuse lung disease. Acute pulmonary edema with lung injury. Acute respiratory failure . Deep coma with increased secretion and stagnation of sputum. Heart and lung surgery causes a lot of blood loss. The patient is clinically dead or in the terminal stage.
2.The phenomenon of hypoxemia in ventilator patients
Bệnh nhân thở máy thường bị giảm oxy máu
Normal: PaO2 80-100mmHg (room air)
Mild hypoxia: PaO2 60-79 mmHg Moderate hypoxemia: PaO2 45-59 mmHg Severe hypoxemia: PaO2 < 45 mmHg Hypoxemia in mechanically ventilated patients This is a common complication and requires monitoring. Signs of hypoxemia are: cyanosis, sweating, lethargy, fatigue... Criteria for diagnosis of hypoxemia in mechanically ventilated patients are:
PaO2 < 60 mmHg SpO2 < 90% Oxygen saturation less than 90% is a clinical emergency).
3. Target for PaO2 adjustment in mechanically ventilated patients
Mild lung injury: goal PaO2 > 80 mmHg Moderate lung injury: goal PaO2 > 70 mmHg Severe lung injury: goal PaO2 > 60 mmHg Preterm birth: goal PaO2 60 - 80 mmHg Pulmonary hypertension : target >100mmHg to reduce pulmonary capillary pressure. When the patient has hypoxia in the blood, it is necessary to adjust the PaO2 based on the adjustment of the FiO2 parameter according to the principle: Oxygen will diffuse according to the pressure gradient, when increasing FiO2 leads to an increase of PAO2 thereby increasing PaO2.
4.Common complications of mechanical ventilation
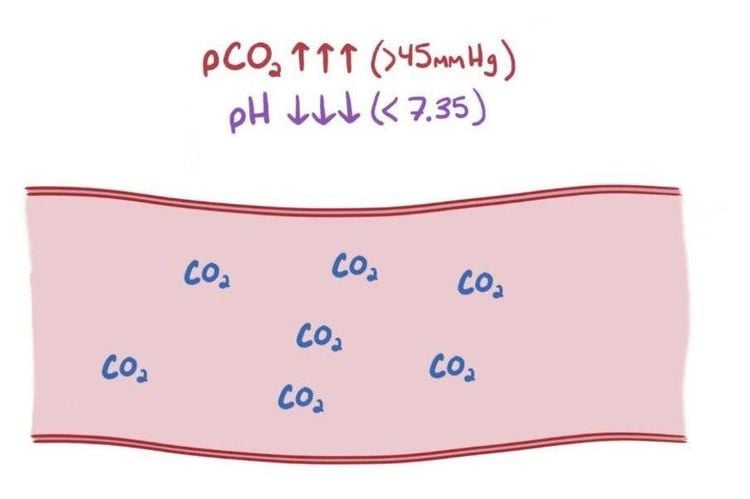
Nhiễm toan hô hấp là biến chứng có thể gặp với bệnh nhân thở máy
Artificial ventilation mechanical ventilation is an effective measure to help meet the patient's respiratory needs, but this technique also causes many complications.
Complications on lung parenchyma and alveoli: alveolar rupture causing pneumothorax due to high pressure pushing air into the lungs (80-100cm of water) to allow air to enter the alveoli can cause alveolar rupture, pulmonary bleeding and Pulmonary embolism due to gas, uneven distribution of air in the lungs due to chronic lung disease, sputum sputum. Cardiovascular complications: Decreased cardiac output, increased cardiopulmonary load, heart failure Decreased cerebral circulation due to hypoxemia, PaO2 decreased sharply during mechanical ventilation causing cerebral vasoconstriction. Minute ventilation decreases, PaCO2 increases and PaO2 decreases, causing cerebral vascular congestion, convulsions, arrhythmias, and ventricular fibrillation. Respiratory acidosis. Respiratory alkalosis. Digestive disorders: abdominal distension, intestinal paralysis, constipation Urinary disorders. Pressure Ulcers: Because when on ventilator, the patient is limited to changing positions every 2-3 hours. Ventilated patients are often seriously ill, perform many techniques such as: endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy, subclavian vein placement, urinary catheterization, gastrostomy, infusion techniques, etc., are susceptible to infections. must be in the hospital. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.