This is an automatically translated article.
Erythrocyte sedimentation is the most commonly used blood product in daily clinical practice. This is the fastest method to raise the hemoglobin concentration in the blood, ensure stable circulating volume, respiratory function for organs, especially in cases of acute blood loss.1. What is erythrocyte sedimentation?
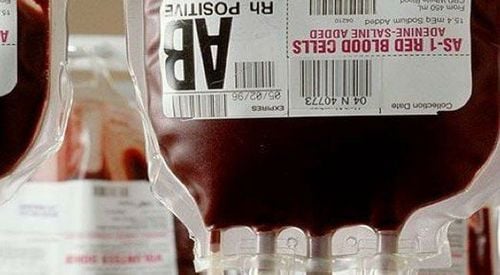
Sedimented red blood cells, also known as red blood cell concentrate, is the remains of whole blood after plasma has been extracted after centrifugation or sedimentation without any further processing. any other.
At this point, because the plasma has been separated, the "settled red blood cell" blood product actually includes all blood cells, including white blood cells and platelets. However, the actual volume of a RBC mass unit is only about 60% (15% error) of the original whole blood volume of the same unit.
In which, the minimum amount of hemoglobin is 10g from each 100ml of prepared whole blood and the hematocrit ratio is from 65 to 75%.
Hồng cầu lắng gồm các tế bào máu, bạch cầu và tiểu cầu
2. What are the indications for using erythrocytes?
Indications for erythrocyte sedimentation are the most widely used in blood products. Accordingly, erythrocyte sedimentation is used when:
Replace red blood cells for patients with severe anemia with Hb below 6 to 8 g/dL; can be used with colloidal solution in case of acute blood loss. Cases of acute blood loss requiring red blood cell transfusion may be trauma after a traffic accident, gastrointestinal bleeding or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. The patient is undergoing surgical intervention with a state of surgery with a lot of blood loss until the Hb is less than 7 g/dL. Patients with acute leukemia should maintain Hb above 8 g/dL for patients in remission, in stable patients, or in patients who have received treatment if there are no clinical abnormalities. Hb should be maintained above 9 g/dL in patients requiring chemotherapy, chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression, or concomitant cardiopulmonary disease. Thalassemia patients need to maintain Hb above 9.5 g/dL in the first years of life to ensure the development of the body. Patients with chronic anemia require erythrocyte sedimentation rate transfusion if Hb is less than 7 g/dL or when the patient has symptoms of anemia and comorbid cardiopulmonary disease.
3. How to store and use erythrocytes?
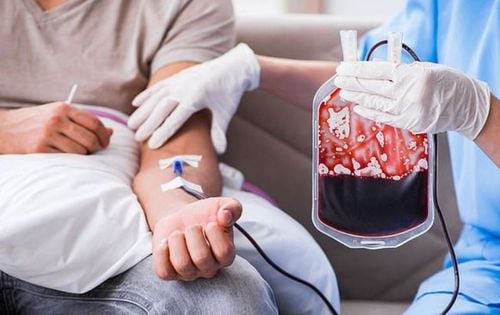
Truyền hồng cầu lắng phải hoàn tất trong thời gian là 40 phút
After preparation from whole blood, erythrocytes should be stored in a suitable medium. The required condition is a temperature between 2°C and 6°C. Only when this is the case, the shelf life of erythrocytes deposited is not more than 21 days with Citrate-Phosphat-Dextrose anticoagulant and no more than 35 days with Citrate-Phosphate-Dextrose-Adenin solution.
Prior to infusion of erythrocytes or blood products in general, appropriate testing for the ABO and Rhesus systems should be performed. Red blood cells removed from the refrigerator should be thawed and transfused within 30 minutes, and should be completed within 4 hours.
In adults, each unit of blood on average raises Hb by 1 g/dL or Hct by 3%. However, since ideal blood counts vary with age, the average erythrocyte sedimentation volume required to transfuse is about 10 to 20 ml/kg body weight. If the patient has a pre-existing chronic anemia, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate should be less than 5 ml/kg body weight concurrently with the infusion lasting more than 4 hours.
If a rapid infusion of erythrocytes is possible due to the critical condition, an additional 0.9% sodium chloride infusion line running parallel to the transfusion line is required. The volume of 0.9% NaCl required is equivalent to the volume of blood.
Closely monitor the patient's state of consciousness and vital signs as prescribed during the entire time of blood transfusion. If there are signs of suspicion of a blood transfusion accident, the erythrocyte sedimentation unit that is being transfused should be stopped immediately and destroyed, absolutely not re-transfused to the patient. At the same time, treat blood transfusion complications in accordance with each level.
If the patient has had a blood transfusion accident, it is necessary to keep the information in the medical record to warn for the next blood transfusion (if necessary) as well as to select a more appropriate red blood cell preparation such as red blood cells. poor white blood cells or washed red blood cells. At this time, the risk of accidents will be significantly reduced.
In summary, erythrocytes are familiar and commonly used blood products. This is the first indication when the patient has acute blood loss, in order to raise the hemoglobin level quickly and save the patient's life. However, it is always important to understand the above things to remember to use erythrocytes safely and effectively for patients.
Customers who need medical examination and treatment at Vinmec can go directly to the facilities of Vinmec Health System or contact to make an appointment HERE.
MORE:
Blood transfusion: When should it be done? Basic principles of blood transfusion The role of blood group determination before blood transfusion