This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Truong Thanh Tam - Pediatrician at the Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.1. Histiocytosis in children with persistent impetigo
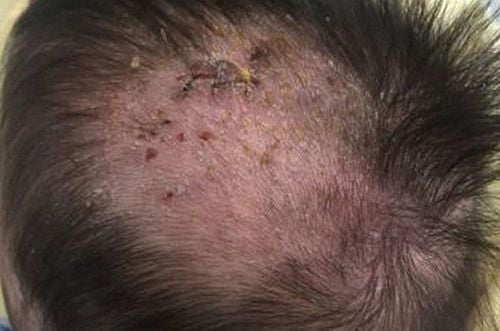
Early histiocytosis is very easy to confuse with the phenomenon of impetigo, which is common in young children. The condition will get worse even when the parents have taken the child to the doctor for dermatological treatment and the child begins to show symptoms such as vomiting, prolonged high fever, liver damage, diabetes insipidus. , appear lumpy on the skin, defect image on X-ray film. The above symptoms combined with the results of a skin biopsy will indicate that the child has a rare disease called Histiocytosis.Because children with histiocytosis will have the initial manifestation of impetigo, long-term dermatological treatment has not properly addressed the cause of the disease, local lesions increase and may spread to other agencies.
2. What is histiocytosis?
Histiocytosis is also known as Langerhans histiocytosis (LCH-Langerhans'cell histiocytosis). The disease is characterized by the abnormal proliferation and accumulation of Langerhans cells, a cell type of the macrophage monocyte system. Normally, this is a cell of the immune system, which plays a role in protecting the body, helping to fight against viruses, bacteria and disease-causing factors. However, in patients with histiocytosis, Langerhans cells multiply abnormally, instead of having a protective function, these cells overgrow, causing damage in many organs such as the nervous system. blood formation, liver, spleen, bone tissue, skin, lungs, lymph nodes... This is a rare disease, any age can be affected, but the disease is common in children. It is estimated that every year around the world, about 5.4 million children are infected with the disease, boys have a higher rate of disease than girls, children are usually diagnosed between 3-5 years old. Symptoms of histiocytosis are:Skin lesions: diffuse nodules resembling seborrheic eczema, accompanied by papule purpura, are often misdiagnosed as impetigo in children. Bone damage: The order of the affected bones from most to least is the cranial vault, the femur, the humerus, the mandible, the vertebrae, the clavicle, the ribs,... According to the studies, at the time. At the point of diagnosis, 70-80% of children have bone lesions on X-ray films. X-ray image shows bone loss, bone defect but no periosteal reaction. Injury to the hematopoietic system: children have anemia, splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, and in some cases, the presence of tissue cells in the bone marrow is detected. Liver damage: liver dysfunction, elevated liver enzymes, abdominal ultrasound shows enlarged liver. Lung damage: Children may have difficulty breathing, cough. When chest X-ray film shows diffuse pulmonary fibrosis or diffuse nodular infiltrates. Central nervous system damage: damage to the pituitary gland causing diabetes insipidus Eye protrusion, otitis media, lymphadenopathy, systemic symptoms of fever and weight loss. In order to diagnose the disease, in addition to clinical examination, performing subclinical tests and imaging studies, it is also necessary to biopsies the lesion site for anatomical examination.
3. How is histiocytosis treated?
Children diagnosed with histiocytosis will be treated with cytotoxic drugs (such as Vinblastine, Mercaptopurine,...), corticosteroids (prednisolone, ..). The child's treatment course will include a phase of aggressive treatment and maintenance therapy. Initial treatment usually lasts 6 weeks and maintenance treatment is 18 weeks. According to a study conducted at Ho Chi Minh City Oncology Hospital since 2004, 80% of pediatric patients have a good response to aggressive treatment, 81.2% responded to a good response after completing treatment. . The most common toxicity was agranulocytosis and erythrocytosis, but all were reversible with treatment. In some cases, treatment with radiation therapy or a stem cell transplant may be possible if other methods fail.If the child's head is persistent, dermatological treatment cannot be cured, parents should not be subjective, take the child to a medical facility with adequate facilities for a general examination to screen. early disease detection. Early detection and treatment of the disease when the lesions have not spread, children will have a higher response rate to treatment, giving children the opportunity to live healthy and symptom-free.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.